An ion exchanger is a synthetic material used in industrial water and wastewater technology to remove unwanted ions from liquids. Ion exchangers play a central role in water treatment, as they can specifically remove dissolved cations and anions and replace them with desired ions. This technology is used for softening, desalination, ultrapure water production and selective removal of certain ions .
Table of contents
Basics of ion exchanger technology
Ion exchangers are based on synthetic resins with a polymeric structure that are equipped with functional groups. These functional groups are able to bind ions from the solution and exchange them with other ions.
- Cation exchangers: Remove positively charged ions (cations) such as sodium (Na⁺), calcium (Ca²⁺) and magnesium (Mg²⁺).
- Anion exchangers: Remove negatively charged ions (anions) such as chloride (Cl-), nitrate (NO₃-) and sulphate (SO₄²-).
Types of ion exchangers
1. cation exchanger
Functionality
Cation exchangers contain acidic functional groups such as sulphonic acid groups (-SO₃H). These groups release hydrogen ions (H⁺), which are then exchanged with cations in the solution.
Types of cation exchangers
- Strongly acidic cation exchangers: Fully ionized over the entire pH range. They are suitable for applications such as softening and desalination.
- Weakly acidic cation exchangers: Effective in the neutral to slightly alkaline pH range. Ideal for removing carbonate hardness.
Areas of application
- Softening: Removal of calcium (Ca²⁺) and magnesium (Mg²⁺) to prevent limescale formation in pipes and boilers.
- Removal of heavy metals: Binding of toxic cations such as lead (Pb²⁺) or copper (Cu²⁺) from industrial wastewater.
2. anion exchanger
Functionality
Anion exchangers contain basic functional groups such as quaternary ammonium groups (-NR₄⁺). These groups exchange hydroxide ions (OH-) for anions in the solution.
Types of anion exchangers
- Strongly basic anion exchangers: Effective in the entire pH range, including the removal of weak acids such as silicic acid (H₄SiO₄).
- Weakly basic anion exchangers: Only bind strong acids (e.g. HCl, H₂SO₄) and are not suitable for weak anions.
Areas of application
- Nitrate removal: Removal of nitrate (NO₃-) from drinking water to comply with legal limits.
- Ultrapure water treatment: Removal of all anions, including weak acids such as silicic acid.

Photo: Our ALMA ION ion exchanger system with upstream ALMA FIL multi-layer filter
3. mixed bed resins
Functionality
Mixed bed resins combine cation and anion exchangers in a defined ratio to simultaneously remove cations and anions from the water. This method leads to almost complete desalination, as H⁺- and OH- ions are exchanged, which combine to form water (H₂O).
Areas of application
- Reinstwasserherstellung: In der Halbleiter- und Pharmaindustrie zur Erzeugung von Wasser mit einer Leitfähigkeit < 0,1 µS/cm.
- Polishing stage after reverse osmosis: Removal of residual ions after pre-treatment.
4. ultrapure water resins
Ultrapure water resins are specially developed mixed bed resins that are used for the production of ultrapure water. They are characterized by extremely high purity and exchange capacity. Applications include:
- Electronics production: Rinsing wafers in the semiconductor industry.
- Pharmaceutical production: Production of injection solutions (WFI - Water for Injection).
- Power plants: Production of water for steam boilers and turbines.
5. selective ion exchangers
Selective ion exchangers are specially developed resins that target specific ions, e.g. heavy metals or organic anions. Their selective capacity is achieved by chemically modifying the functional groups.
Areas of application
- Heavy metal removal: Removal of toxic metals such as arsenic (As), mercury (Hg) or chromium (Cr).
- Ammonium removal: In sewage treatment plants for the reduction of ammonium (NH₄⁺) from wastewater.
- Boron removal: Used in seawater desalination to remove boron (B³⁺).
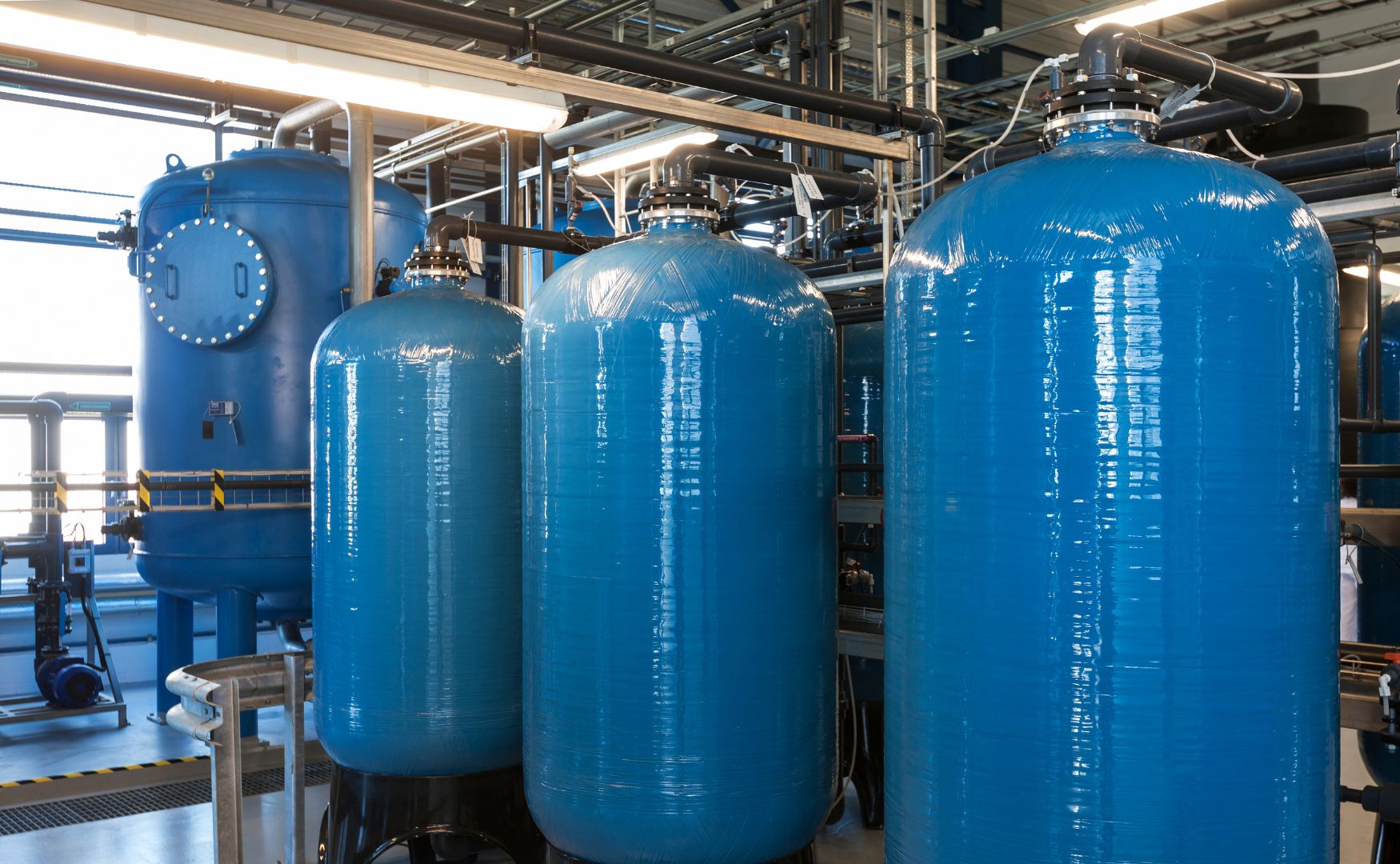

Photo: Ion exchanger in GRP tanks(ALMA ION)
Technical aspects and dimensioning
The selection and dimensioning of an ion exchange system depends on various factors:
- Ion concentration: The concentration of the ions to be removed determines the amount of resin required.
- Flow rate: Determines the contact time of the water with the resin and influences the efficiency.
- Operating temperature: Most resins are suitable for temperatures up to 60 °C, while special resins can withstand higher temperatures.
- Regeneration requirement: Regeneration is necessary to restore the exchange capacity.
Regeneration of ion exchangers
Ion exchangers must be regenerated regularly to regain their full capacity. The process differs between cation and anion exchangers:
Cation exchanger
- Chemicals: Regeneration with acids such as hydrochloric acid (HCl) or sulphuric acid (H₂SO₄).
- Reaction: The bound cations are replaced by H⁺ ions.
Anion exchanger
- Chemicals: Regeneration with alkaline solutions such as caustic soda (NaOH).
- Reaction: The bound anions are replaced by OH- ions.
Mixed bed resins
Mixed bed resins require separate regeneration of the cation and anion resins, which are then mixed again.
Advantages and challenges
Advantages
- High efficiency in the removal of specific ions.
- Adaptability to different applications through targeted selection of resins.
- Possibility of regeneration and reuse.
Challenges
- Costs for regeneration chemicals and disposal of rinsing water.
- Reduction of the exchange capacity in the event of contamination by organic substances or fouling.
- Strict monitoring and maintenance to prevent blockage or channeling.
Conclusion
Ion exchangers are indispensable tools in industrial water and wastewater technology. Their versatility, efficiency and adaptability make them the ideal solution for softening, desalination and ultrapure water production as well as for the selective removal of problematic ions. Sound planning, correct dimensioning and regular regeneration are essential to ensure long-term stable performance and to meet the high water quality requirements of modern industries.
For further information on our products, please feel free to contact us at any time!