A screen is a mechanical separating element that is used in industrial process water and wastewater technology for the removal of coarse solids from liquid flows. As the first cleaning stage in sewage treatment plants and water treatment plants, the screen protects downstream processes and systems from blockages, damage and wear. Its function is essential for the efficient and trouble-free operation of wastewater and process water treatment plants.
Table of contents
Definition and basic function
A screen is a grid or sieve element that is arranged at right angles to the direction of flow in the inlet of a clarification or water treatment system. It is used to mechanically separate coarse solids such as plastic, wood, textiles or other floating and suspended materials.
Tasks of the rake:
- Protection of the systems:
- Prevents damage to pumps, pipes and other mechanical components.
- Increased efficiency:
- Relieves downstream cleaning processes such as sand traps, flotation plants or biological tanks.
- Waste management:
- Collects coarse residues for disposal or further processing.
Types of rakes
The selection of a screen depends on the application, the type of medium to be treated and the operational requirements. The screens can be categorized according to the gap width, design and operating mode.
1. according to gap width
Coarse crushing:
- Gap width: >10 mm.
- Removes large solids such as branches, plastic containers or textiles.
- Application: Inlet of wastewater treatment plants or industrial wastewater.
Fine rake:
- Gap width: 1-10 mm.
- Suitable for smaller particles such as packaging film or biomaterials.
- Application: Drinking water treatment, industrial process water treatment.
Microrechen:
- Spaltweite: <1 mm.
- High-precision removal of small particles.
- Application: Highly contaminated waste water or special applications such as the food industry.
2. according to construction method
Bar rake:
- Parallel metal bars or profiles that effectively separate coarse materials.
- Robust and low-maintenance.
Drum rake:
- Cylindrical sieve element that rotates to continuously remove solids.
- Compact and suitable for higher loads.
Disk rake:
- Several rotating disks with openings that separate solids.
- Use where space is limited.
3. according to operating mode
- Manual rake:
- Solids are removed manually.
- Suitable for small systems or emergency applications.
- Mechanical rakes:
- Equipped with automated clearing device.
- Use in large installations or heavily loaded systems.
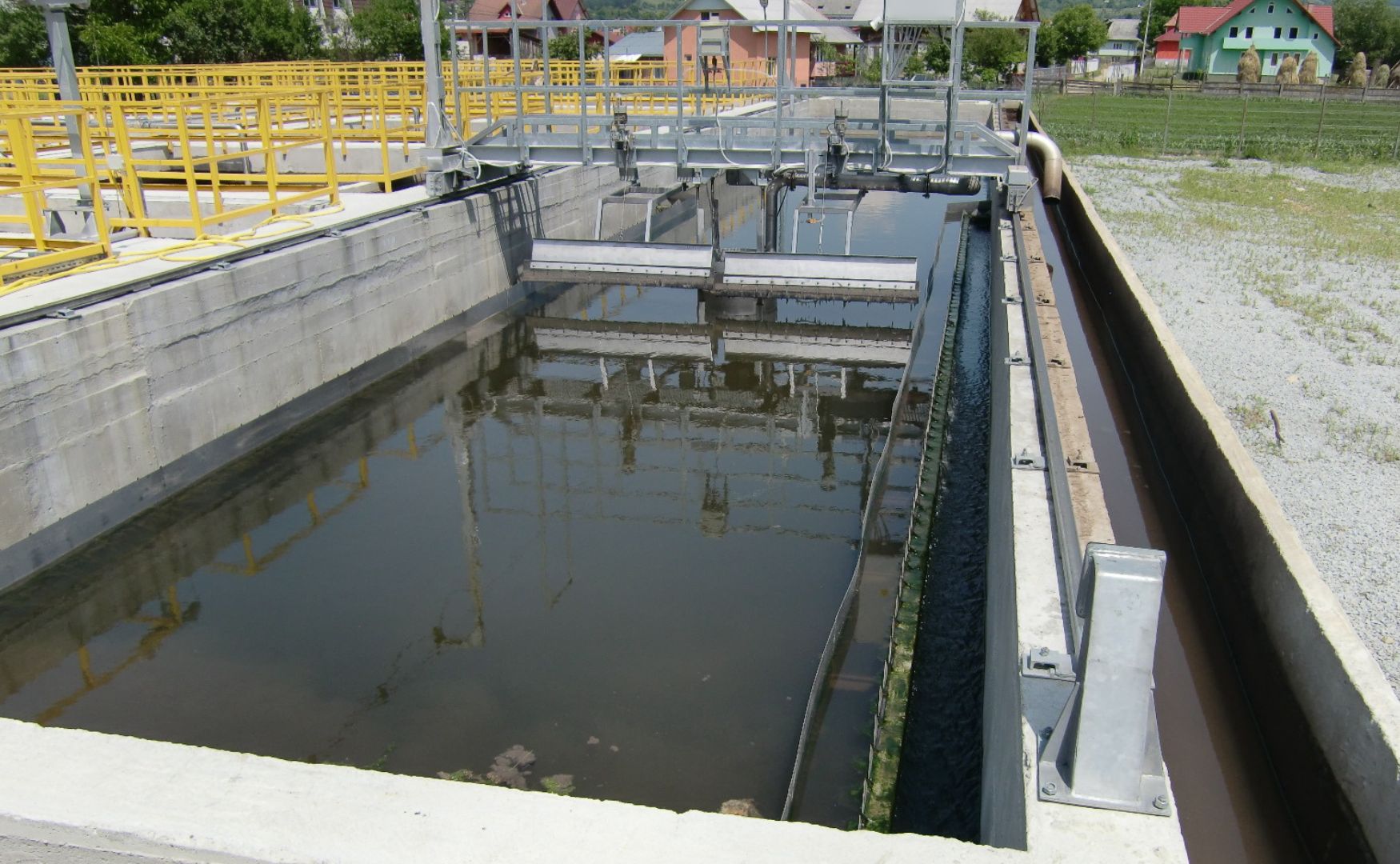

Photo: Automatic rake with broaching device
Technical structure of a mechanical rake
A mechanical screen consists of several components that are coordinated to ensure continuous and reliable removal of solids.
1st screen grid
- The heart of the rake, consisting of parallel bars, grids or perforated plates.
- Materials: Stainless steel (corrosion-resistant), plastic (lightweight and cost-effective).
- Gap width determines the separation performance.
2. clearing device
- Scrapers or rake arms move along the grate and remove solids.
- Drive via electric motors or hydraulics.
3. transport and disposal unit
- Conveys the collected solids into containers or conveyor belts.
- Optionally equipped with presses to reduce the volume of residues.
4. control system
- Automated control system regulates operation depending on flow rates and solids load.
- Sensors monitor blockages and trigger cleaning cycles.
Functionality of a computing system
Inflow of wastewater:
- The raw wastewater or process water flows through the bar rack.
Separation of the solids:
- Coarse or fine particles are retained on the bars or grids.
Removal of solids:
- Mechanical scrapers move the residues into the disposal unit.
Forwarding of the water:
- The pre-cleaned water flows to subsequent cleaning stages.
Challenges and solutions
Blockages:
- Regular maintenance and inspection are required to prevent deposits.
- Solution: Self-cleaning systems and optimized gap widths.
Corrosion:
- Constant exposure to aggressive wastewater.
- Solution: Use stainless steel or corrosion-protected materials.
Waste disposal:
- Large quantities of screenings are produced.
- Solution: Volume reduction through compacting presses.
Conclusion
A screen is an effective solution for wastewater containing coarse solids, such as packaging materials. Its robust design, wide range of adaptation options and high efficiency make it a key technology for the protection and optimization of plants. By using modern materials, automation and customized solutions, a screen system can be adapted to almost all operational requirements and thus contributes to sustainable and economical water treatment.
For further information on our products, please feel free to contact us at any time!