Trace substances are chemical compounds that occur in very low concentrations (in the range of micro- to nanograms per liter) in water and wastewater systems. They come from a variety of sources, such as drug residues, pesticides, industrial chemicals or cosmetics. Despite their low concentrations, they can have a considerable impact on the environment and health, as many trace substances are persistent, accumulate in organisms or have hormonal effects.
Origin and entry paths
- Pharmaceutical residues: These enter wastewater via excretions or the disposal of expired medicines.
- Pesticides and herbicides: They enter surface and groundwater through agricultural applications.
- Industrial chemicals: Compounds such as perfluorinated and polyfluorinated alkyl substances (PFAS) originate from industrial processes.
- Consumer products: Substances from cosmetics or household chemicals also contribute to trace substance pollution.
Technical challenges
Trace substances pose a particular challenge as they are difficult to detect in low concentrations and often cannot be adequately removed using conventional methods. They can disrupt ecosystems, for example by impairing the reproduction of aquatic organisms or promoting resistance in microorganisms.
Table of contents
Treatment process for the removal of trace substances
1. activated carbon adsorption
Activated carbon, especially in granular form (GAC) or as a powder (PAH), is often used to remove trace substances. The porous structure of activated carbon provides a large specific surface area on which the molecules of the trace substances can adsorb. This process is particularly effective for organic compounds and lipophilic substances.
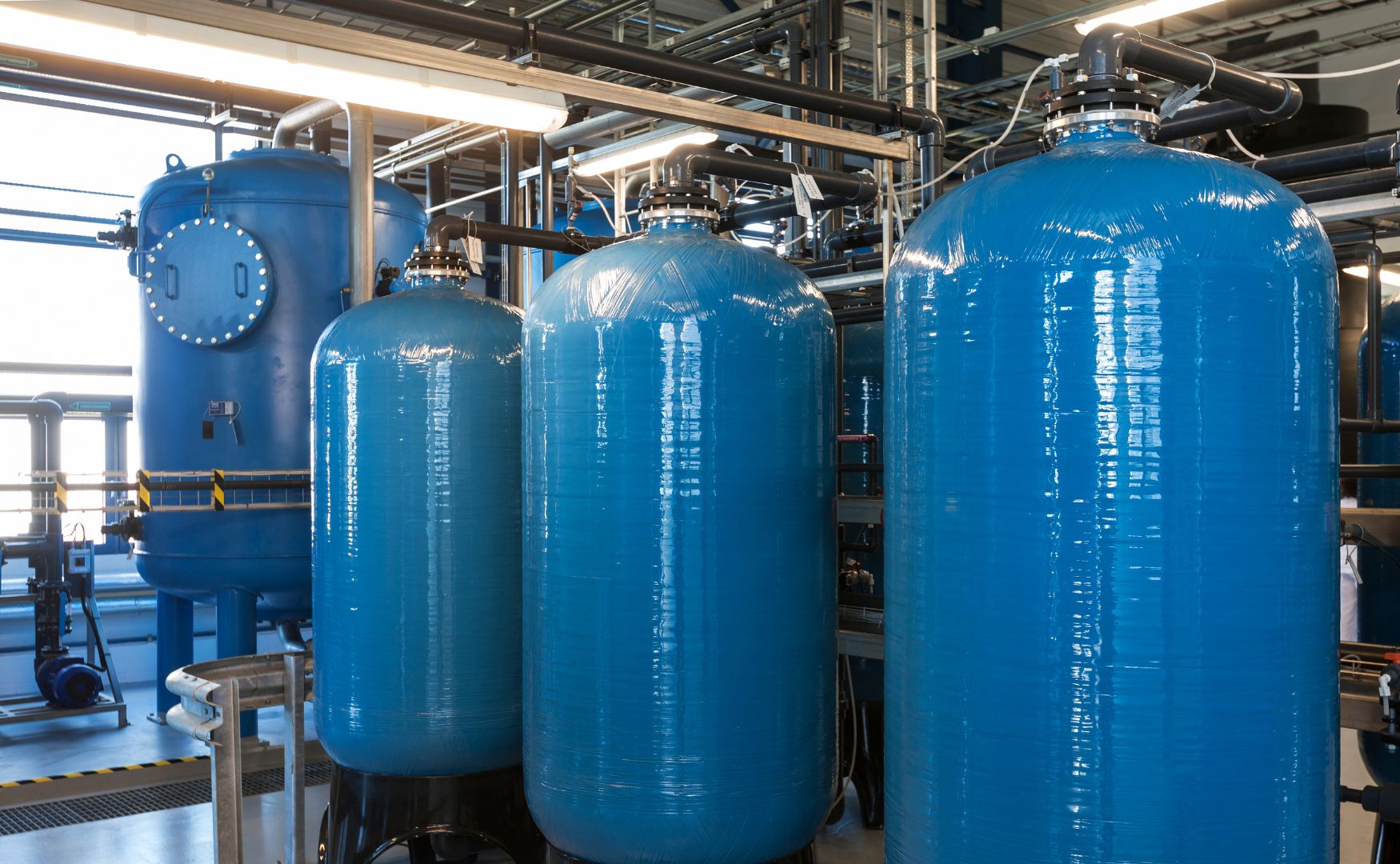

Photo: Our ALMA FIL AK activated carbon filters
2. ozonation
Ozone is a powerful oxidizing agent that can convert organic trace substances into less harmful compounds or mineralize them completely. Ozonation is particularly suitable for trace substances such as hormones, pharmaceuticals and pesticides.
3. Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOP)
AOPs combine oxidizing agents such as ozone or hydrogen peroxide with UV radiation to generate hydroxyl radicals. These highly reactive radicals efficiently oxidize a wide range of organic trace substances.
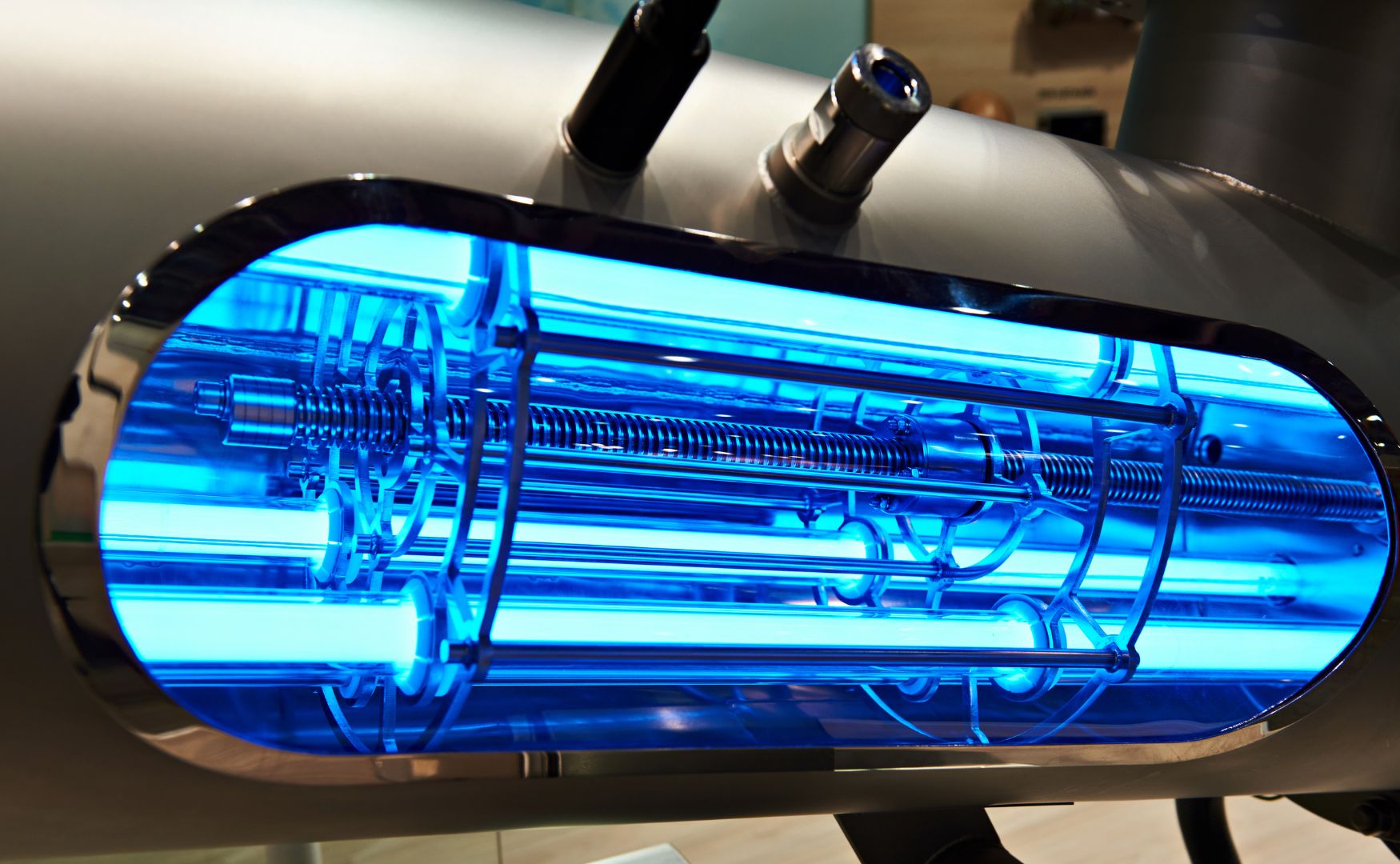
Photo: UV reactor in conjunction with the dosing of ozone or hydrogen peroxide in our ALMA OXI UV system
4. membrane process
- Nanofiltration (NF) and reverse osmosis (RO) provide a physical barrier against trace substances. They separate the dissolved molecules based on their size and charge.
- Micro- and ultrafiltration can be used in combination with adsorption processes or biological systems to increase efficiency.

Photo: Our ALMA OSMO Process reverse osmosis system for removing PFAS, installed in the ALMA MODUL technical room container
5. biological processes
- Activated sludge process and MBBR (Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor): Some microorganisms are able to break down certain trace substances.
- Biofiltration: In biofilter systems such as the ALMA BHU BioFil, biofilms can be used for the targeted elimination of specific trace substances.
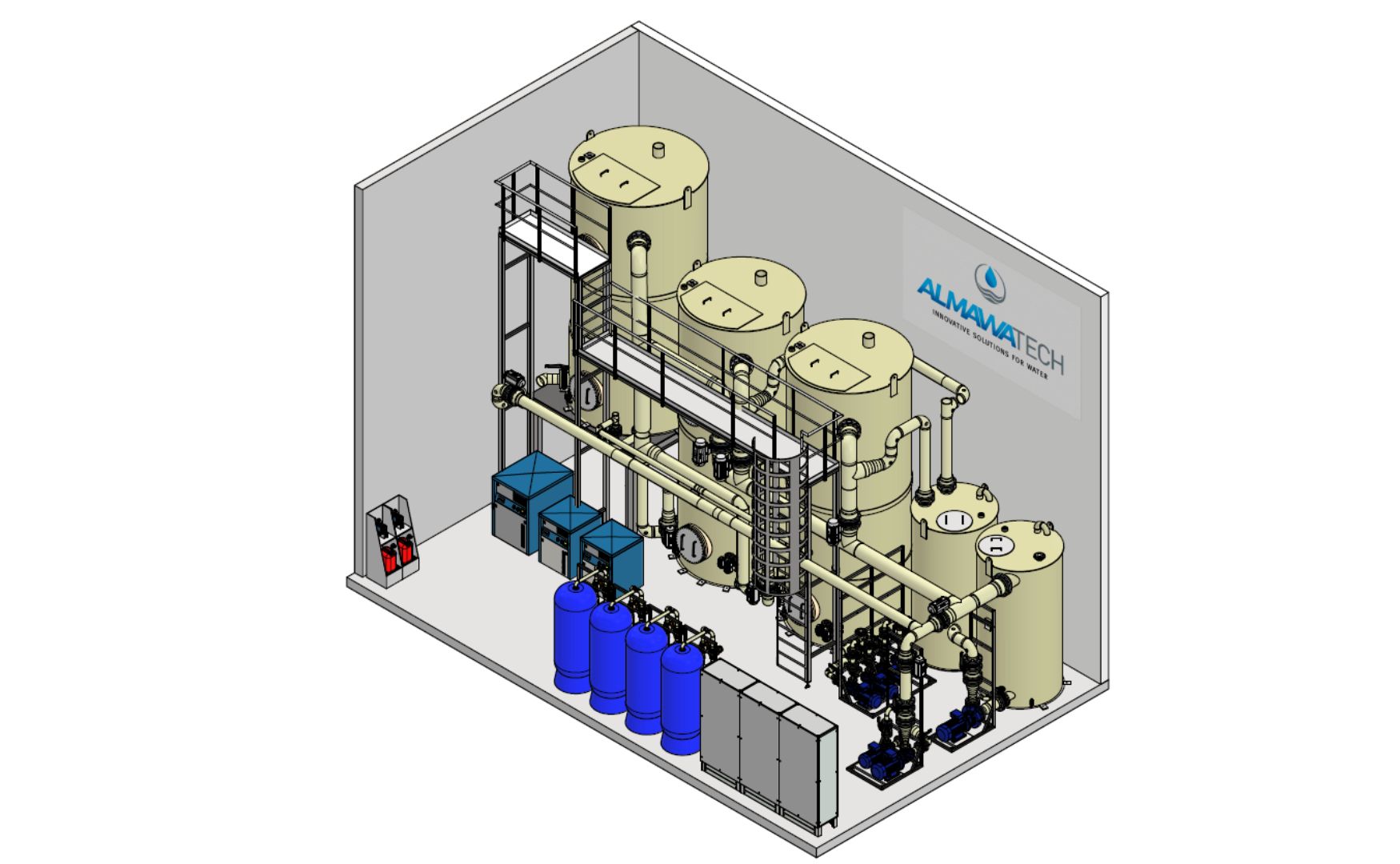
Photo: 3D design of our ALMA BioFil Compact biofiltration system
6. chemical-physical treatment
CP systems combine several physico-chemical processes to effectively remove trace substances from wastewater. Processes such as precipitation, flocculation, neutralization, filtration and oxidation are used. The efficiency of this method is particularly evident in the pre-treatment of industrial wastewater with high concentrations of pollutants.
Advantages:
- High flexibility in the removal of organic and inorganic trace substances.
- Effective pre-treatment for downstream processes such as membrane technology or biological systems.

Applications in various industries
Pharmaceutical industry
The wastewater is often contaminated with pharmaceutical residues, which are treated using membrane processes or AOP.Chemical industry
Various organic trace substances occur here, which can be efficiently removed by combinations of ozonation and activated carbon.Municipal wastewater treatment plants
A fourth treatment stage is increasingly being implemented to remove trace substances and sustainably improve water quality.Plastic production and recycling
Wastewater from plastic production often contains additives and microplastics. Trace substances such as plasticizers or flame retardants can be effectively removed using combined processes such as activated carbon adsorption and membrane technology.Disposal company
CP systems and AOPs play a key role in the treatment of hazardous liquid waste such as waste oils or solvents in order to break down hazardous trace substances.Electroplating industry
Electroplating produces wastewater with traces of heavy metals and organic complexing agents, which are removed using chemical-physical and membrane processes.- Surface treatment
Surface treatment includes processes such as painting, coating and metal finishing, which generate wastewater containing trace substances such as solvents, heavy metals and organic compounds. Chemicals such as cyanides or chromates are used in electroplating in particular. Chemical-physical processes such as CP systems and membrane processes are used here.
Conclusion
Trace substances represent a key challenge for modern water and wastewater technology. They require the use of advanced technologies and a targeted combination of processes to minimize their harmful effects on the environment. ALMAWATECH offers comprehensive solutions for the removal of trace substances, adapted to the specific requirements of various industries and applications.
For further information on our products, please feel free to contact us at any time!








