Filtrate refers to the liquid that has been separated from solids after a filtration process. It is the purified or clarified water that has passed through a filter medium while the insoluble particles have been retained in the filter. Filtrates play a crucial role in industrial water and wastewater treatment as they represent the quality of the treated water and are often reused or discharged into the environment.
Table of contents
Technical background to filtration
Filtration is a physical separation process based on the ability of a filter medium to retain solids while liquids flow through it. Filter media can consist of different materials, e.g. fabric, activated carbon, sand or membranes, which are tailored to the specific requirements of wastewater treatment.
1. mechanical filtration:
- Solids are retained due to their size and gravity. This takes place in systems such as sand filters, multi-layer filters or chamber filter presses.
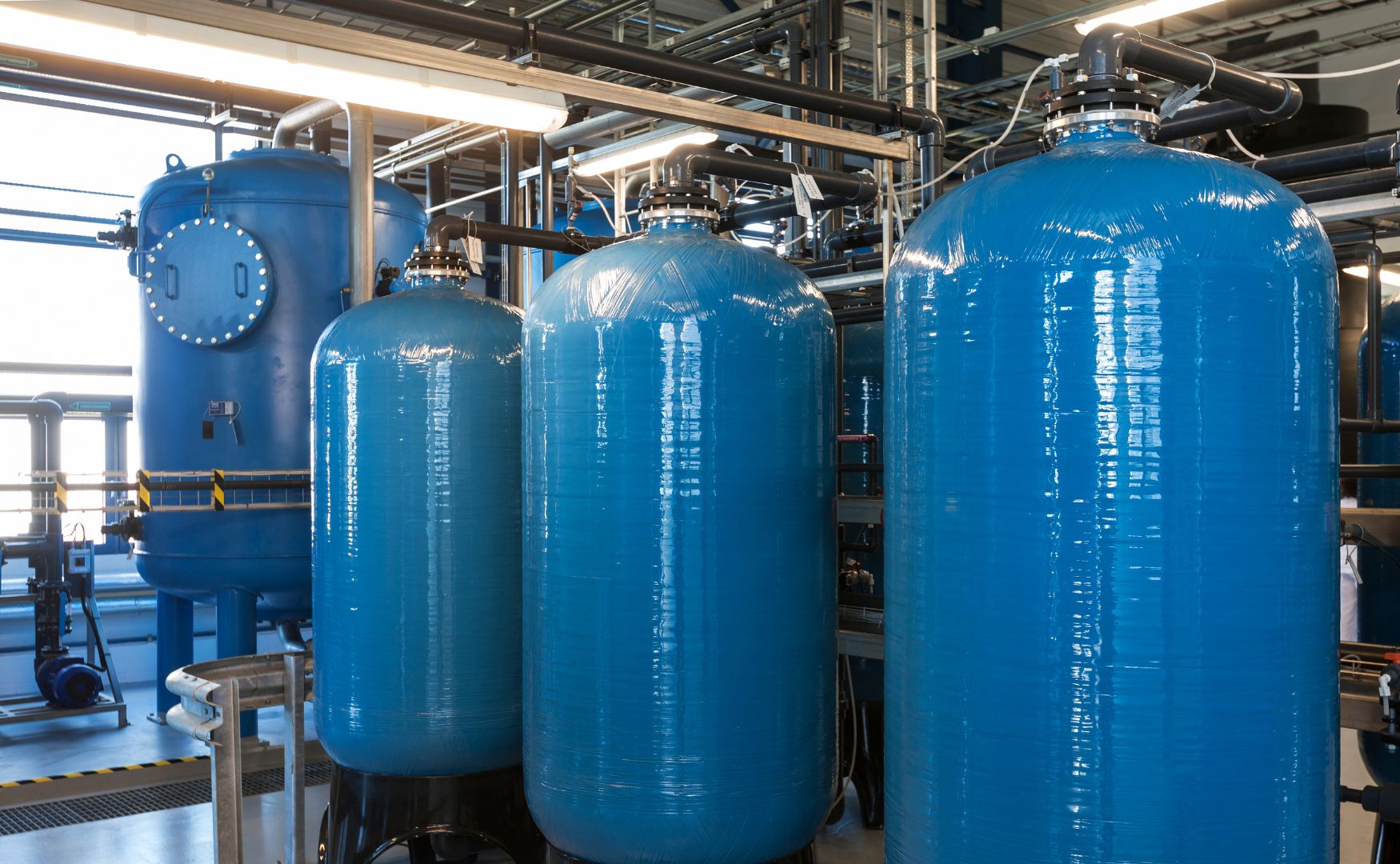

Photo: Our ALMA FIL multi-layer filters, which can also be operated with granulated activated carbon
2. membrane filtration:
- More advanced processes such as ultrafiltration or reverse osmosis use semi-permeable membranes to remove even dissolved substances and micropollutants.
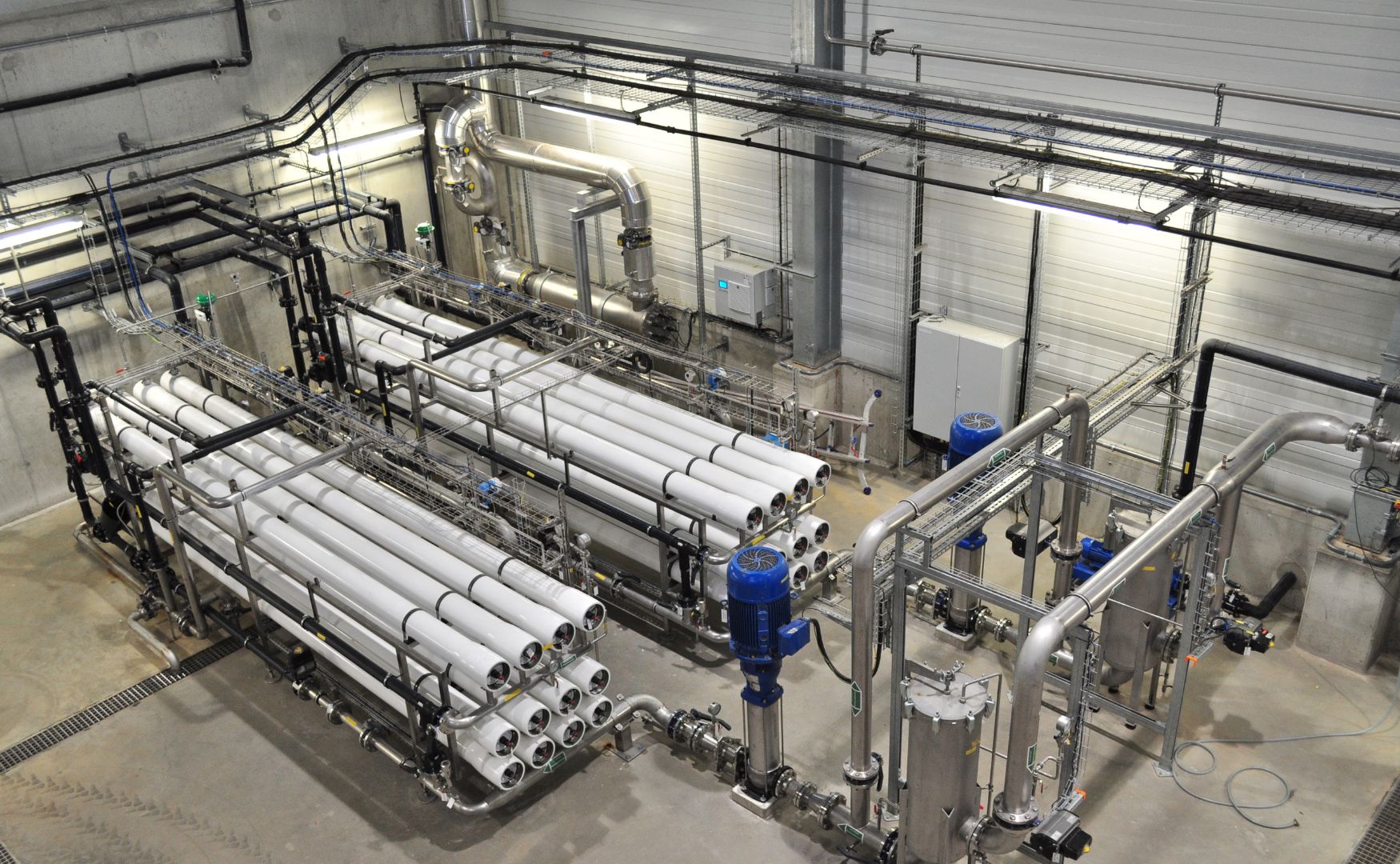

Photo: Our ALMA BHU BiosS-Treat reverse osmosis system for river water treatment
3. pressure filtration:
- This technology increases the flow rate by using pressure to force the liquid through the filter medium. Systems such as chamber filter presses or belt filter presses use this approach to separate solids.
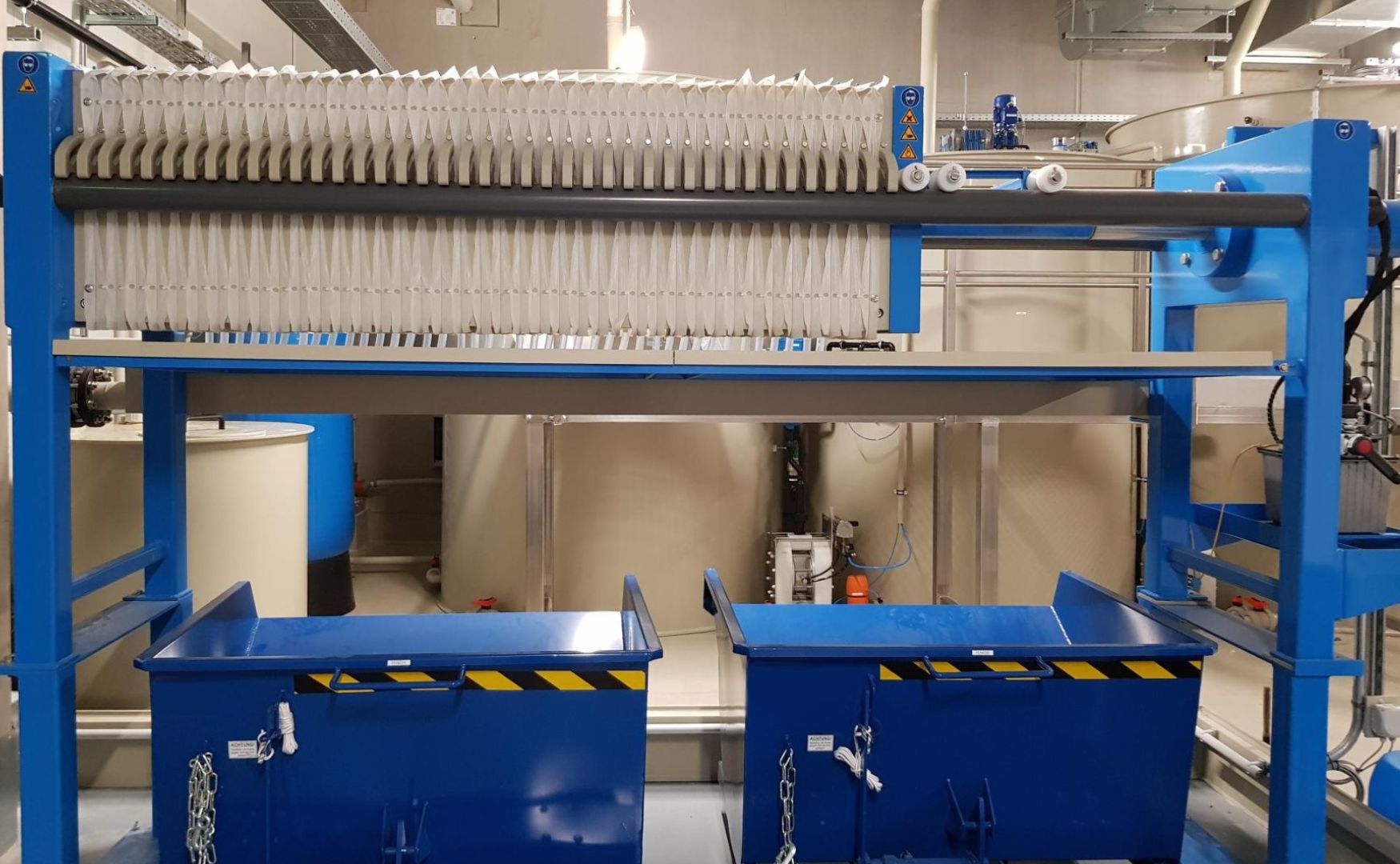

Photo: Our ALMA CFP chamber filter press for dewatering sludge from wastewater treatment
Quality characteristics of the filtrate
The quality of the filtrate depends on various parameters, including the size of the filter pores, the composition of the wastewater and the operating conditions of the filter system. Typical quality parameters are:
- Turbidity (turbidity): A measure of the solid particles remaining in the filtrate.
- Organic load: Measured by parameters such as chemical oxygen demand (COD) or biological oxygen demand (BOD).
- Inorganic constituents: Concentrations of metals or dissolved salts that remain in the filtrate.
Applications in practice
Filtrates are used in various industries for different purposes:
Return to the production process:
- In the food or chemical industry, the filtrate is often reused after cleaning, for example as cooling water or process water.
Direct discharge into water bodies:
- After successful filtration, filtrates that meet legal requirements can be discharged directly into rivers or lakes.
Further treatment:
- Filtrates from precipitation and flocculation plants or biofiltration systems can be further purified in subsequent treatment stages, for example by reverse osmosis or activated carbon filtration.

Photo: Our CP system ALMA CHEM MCW for the removal of heavy metals, AOX, cyanide and chromium compounds
Challenges and optimization
Filter clogging:
- Continuous operation can lead to clogging of the filter medium, which reduces the flow rate and efficiency of the system. Regular cleaning and the use of anti-fouling measures are necessary.
Chemical loads in the filtrate:
- In some cases, the filtrate may contain high concentrations of dissolved substances such as phosphates, nitrates or heavy metals despite filtration. Here, additional processes such as ion exchange or membrane processes are required.
Increased efficiency:
- The combination of different filtration techniques, such as the use of pre-precipitants or coagulantscan improve filterability and increase the efficiency of the systems.
ALMAWATECH solutions
ALMAWATECH offers customized filtration solutions to meet the specific requirements of various industries. With systems such as our chamber filter presses, reverse osmosis systems or multi-layer filters customers can effectively treat their wastewater streams and process water. For special requirements, such as the removal of very fine particles or dissolved substances, there are also membrane filtration systems are also available.
Our offer also includes the performance of pilot tests to determine the optimum filtration strategy for your application.
Conclusion
Filtrates are a central element in industrial water and wastewater treatment. They enable water to be returned to the production process or disposed of in an environmentally friendly manner. Careful selection and optimization of filtration processes is crucial in order to meet water quality requirements while minimizing operating costs.
For further information on our products, please feel free to contact us at any time!