Nitrogen reduction refers to the targeted removal of nitrogen-containing compounds from water or wastewater in order to avoid environmental damage such as eutrophication and to comply with legal requirements. The reduction of nitrogen compounds, in particular ammonium, nitrite, nitrate and organic nitrogen, is of central importance in industrial and municipal wastewater treatment.
Table of contents
Nitrogen compounds and their environmental impact
Ammonium (NH₄⁺):
Is oxidized by biological processes to nitrite and then to nitrate. Ammonium is toxic to aquatic organisms in high concentrations.Nitrite (NO₂-):
An intermediate product of nitrification that is highly toxic and can impair the oxygen uptake capacity of aquatic organisms.Nitrate (NO₃-):
Can lead to eutrophication in bodies of water and is a health risk, especially for drinking water supplies.Organic nitrogen:
Consists of proteins, amino acids and other organic compounds that are broken down by microorganisms.
Nitrogen reduction process
1. biological processes
Biological systems are particularly efficient at reducing nitrogen. Common methods include
Nitrification:
Ammonium is oxidized by nitrifying bacteria (e.g. Nitrosomonas and Nitrobacter) to nitrite and then to nitrate.Denitrification:
Under anoxic conditions, nitrate is reduced by denitrifying microorganisms to elemental nitrogen (N₂), which escapes into the atmosphere.Activated sludge process:
A proven process for nitrogen removal in municipal and industrial wastewater treatment plants.Biofiltration systems (e.g. ALMA BHU BAF):
These systems use biofilms on special carrier materials to break down nitrogen compounds.MBBR (Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor):
A combination of biofilms and activated sludge that enables efficient nitrification and denitrification.
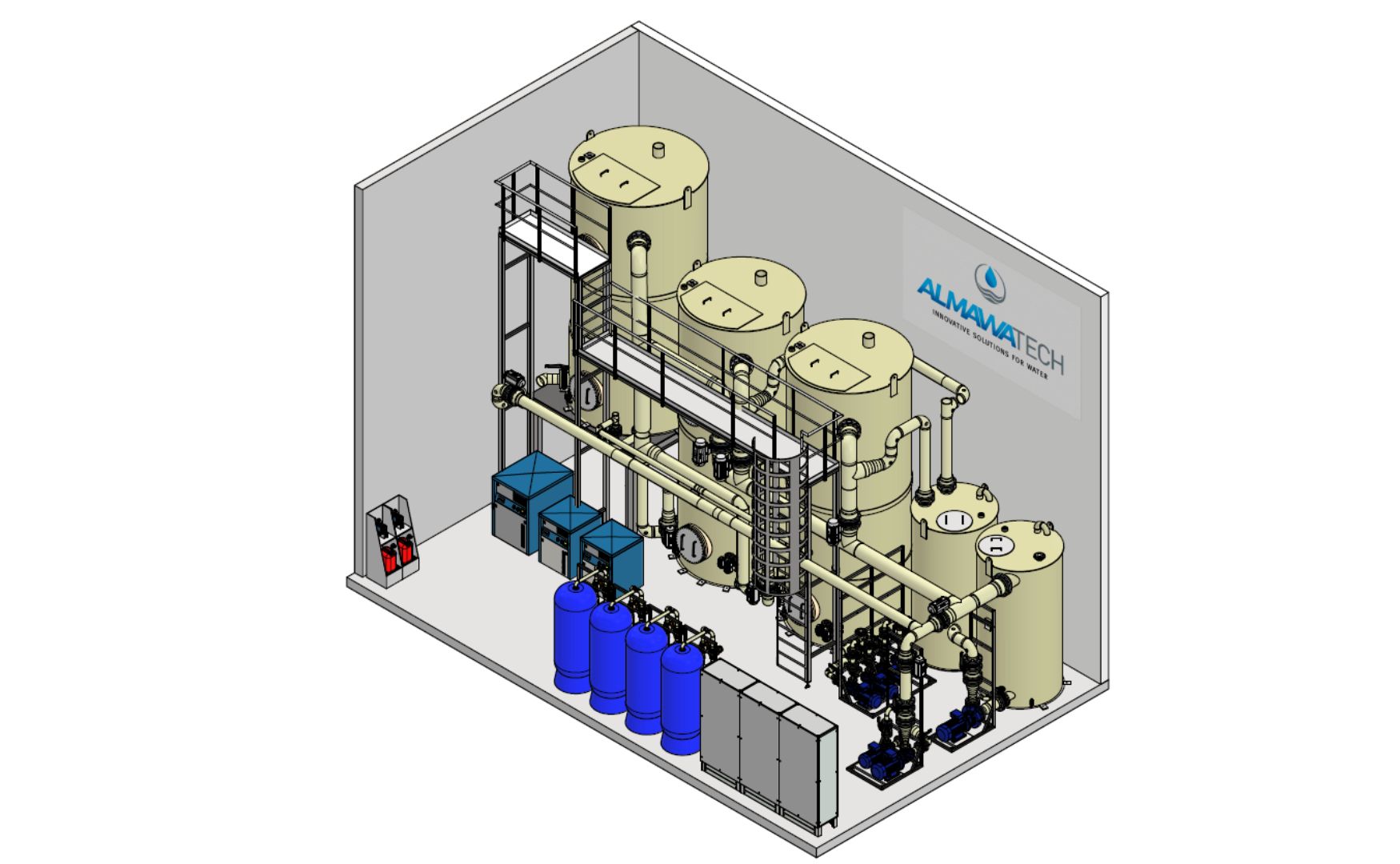
Photo: 3D design of our ALMA BioFil Compact biofiltration system with nitrification and denitrification
2. chemical-physical processes
Ammonia stripping:
Ammonia is removed from the wastewater by increasing the pH value and aeration.Ion exchange:
Selectively removes ammonium and nitrate ions from the water flow.Precipitation of nitrogen compounds:
Chemicals such as PAC (polyaluminum chloride) are used to precipitate ammonium.
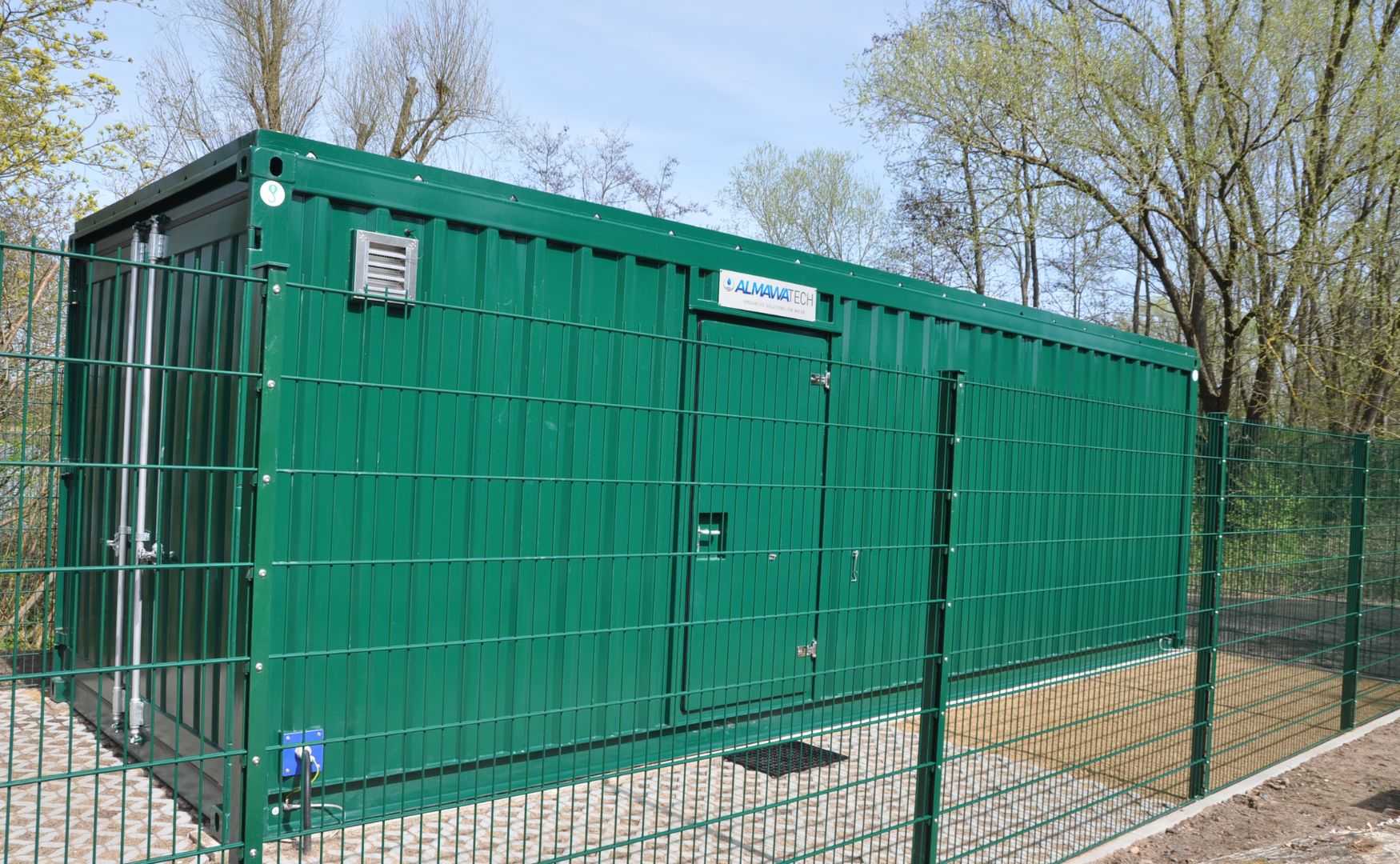

Photo: Our ALMA NeoDAF flotation system installed in the ALMA Module technical room container for removing phosphates and nitrogen from a lake
3. Membrane process
- Nanofiltration (NF) and reverse osmosis (RO):
These technologies provide a physical barrier against nitrogen compounds and enable them to be separated from the wastewater.
4. advanced oxidation processes (AOPs):
Combine oxidizing agents such as ozone or hydrogen peroxide with UV light to remove nitrogenous organic compounds.

Photo: Our ALMA OSMO Process reverse osmosis system with water softener and pre-filtration
Areas of application
Nitrogen reduction is indispensable in many industries:
- Food and beverage industry: Wastewater with high organic nitrogen content.
- Chemical industry: Often contains complex nitrogenous compounds.
- Pharmaceutical industry: High nitrate and ammonium concentrations.
- Metal processing and electroplating: Nitrogen-containing process wastewater.
Legal requirements
In Germany, the Wastewater Ordinance (AbwV ) regulates the maximum permissible nitrogen concentrations in industrial and municipal wastewater. These values must be adhered to by means of suitable treatment measures in order to avoid environmental damage.
Conclusion
Nitrogen reduction is an essential part of modern water and wastewater treatment. Nitrogen compounds can be efficiently removed using a combination of biological, chemical-physical and membrane-based processes. ALMAWATECH offers customized solutions that enable economical and environmentally friendly nitrogen treatment, tailored to the specific requirements of different industries.
For further information on our products, please feel free to contact us at any time!