Dissolved substances are substances that are completely dissolved in a liquid, such as water, and therefore cannot be removed by mechanical separation processes such as sedimentation or filtration. These substances include salts, organic compounds, gases and dissolved metals and play a crucial role in industrial water and wastewater technology. They are usually measured as Total Dissolved Solids (TDS), using the unit mg/l (milligrams per liter).
Definition and delimitation
A solute is a substance that dissolves completely in a solvent, typically water. Dissolution occurs at the molecular or ionic level, making the substance no longer visually recognizable. A compound is called a solute if its particle size is less than 1 nanometer. Larger particles (1 nm to 1 µm) are called colloidal, while even larger particles are considered suspended.
Solubility
The solubility of a substance indicates how much of it can be dissolved in a certain amount of solvent. This depends on several factors:
- Temperature: Higher temperatures generally increase the solubility of solids, while the solubility of gases decreases.
- Pressure: With gases, a higher pressure increases solubility (Henry's law).
- Chemical nature of the solvent and the dissolved substance: Polarized or ionic substances dissolve better in polar solvents such as water.
Examples:
- Salts such as sodium chloride dissolve in water due to their ionic bond.
- Gases such as carbon dioxide dissolve in water, depending on the partial pressure and temperature.
Table of contents
Technical background
Types of dissolved substances
Inorganic compounds
- Salts such as sodium chloride, calcium carbonate and magnesium sulphate.
- ions such as chloride, nitrate and phosphate.
Organic compounds
- Small organic molecules such as sugars, alcohols and acids.
- Poorly degradable substances such as PFAS (per- and polyfluorinated alkyl compounds).
Gases
- Oxygen, carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulphide.
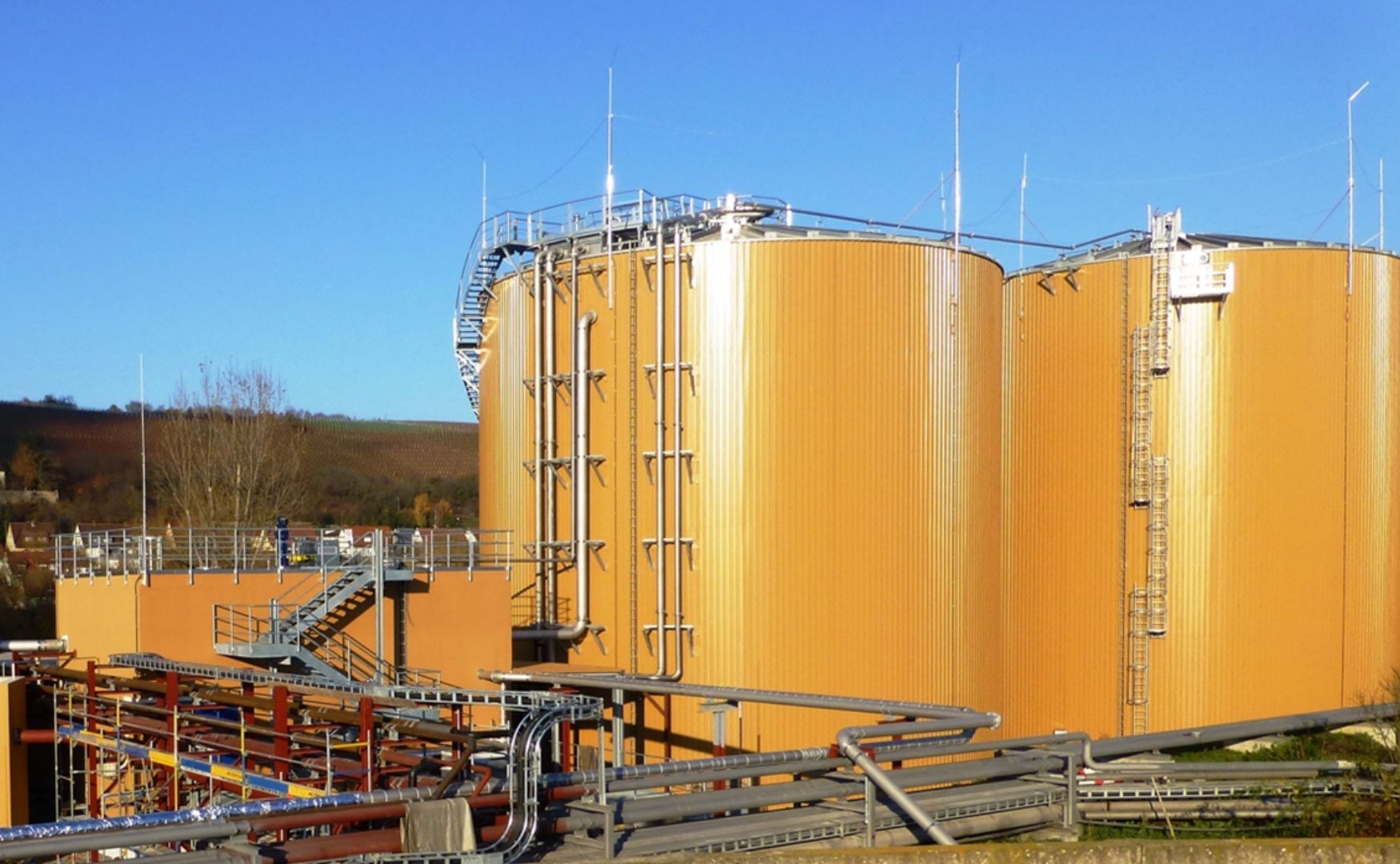

Photo: ALMA BHU GMR biogas plant for the removal of dissolved organic substances
Treatment process for removing dissolved substances
- Reverse osmosis and nanofiltration separate dissolved substances through pressure filtration with semi-permeable membranes. They are particularly effective at removing salts, organic substances and heavy metals.
- Ion exchange resins specifically remove cations or anions, for example calcium or nitrate.
Distillation and evaporation
- Physical processes that separate dissolved substances by evaporating the solvent.
Adsorption
- Activated carbon or GAK filters adsorb organic dissolved substances such as pesticides or dissolved hydrocarbons.
Precipitation and flocculation processes
- can remove metals and sparingly soluble salts from water by shifting the pH value and forming precipitation products.
- Biological treatment specifically uses microorganisms to break down dissolved organic compounds such as hydrocarbons or nitrogen compounds. In biological reactors such as activated sludge process, MBBR systems or biofilters these substances are metabolized. This produces products such as water, carbon dioxide or nitrogen, which can be discharged into the environment. This method is particularly common in the food and beverage industry or in wastewater treatment plants.
Conclusion
The control and removal of dissolved substances is a key aspect of industrial water treatment, as it has a decisive influence on quality and operational safety. Specific dissolved substances can be efficiently removed using targeted processes such as membrane technologies, biological treatment, ion exchange or adsorption.
For further information on our products, please feel free to contact us at any time!