Disposal refers to the professional handling of waste, in particular its collection, transportation, treatment, recycling and disposal. In an industrial context, this includes both solid and liquid waste, including hazardous special waste. Disposal serves to minimize environmental and health risks and to comply with legal requirements.
Table of contents
Waste categorization
Waste is divided into different categories according to its origin and hazardousness, including
- Waste similar to household waste
- Industrial waste
- Hazardous waste (e.g. sludge containing heavy metals, waste oils, solvents)
- Liquid hazardous waste such as emulsified oils, acidic waste water or solvent residues.
A precise analysis of the waste composition is crucial in order to determine the appropriate treatment or disposal routes.
Legal requirements
Waste disposal in Germany is subject to strict regulations, which are governed by the Closed Substance Cycle Waste Management Act (KrWG) and the Waste Catalogue Ordinance (AVV). These regulations define obligations for waste producers, transporters and disposal companies and ensure that waste is fully documented and handled in an environmentally friendly manner.
Treatment processes for liquid hazardous waste
1. physico-chemical treatment
This process is one of the most important methods for treating liquid hazardous waste. It combines mechanical and chemical processes to remove pollutants or render them harmless.
NeutralizationAcids and alkalis are brought to a pH value in the neutral range by adding neutralizing agents such as milk of lime, caustic soda or sulphuric acid. This is particularly relevant for chemical industrial wastewater.
Precipitation and flocculation: Dissolved heavy metals or other pollutants are converted into insoluble compounds by precipitants such as ferric chloride or polyaluminum chloride. These particles are then bundled by flocculation and can be removed in so-called CP plants or flotation plants.
Emulsion splitting: Chemical splitting is used for wastewater containing oil-water mixtures. Special splitting agents help to separate the phases.
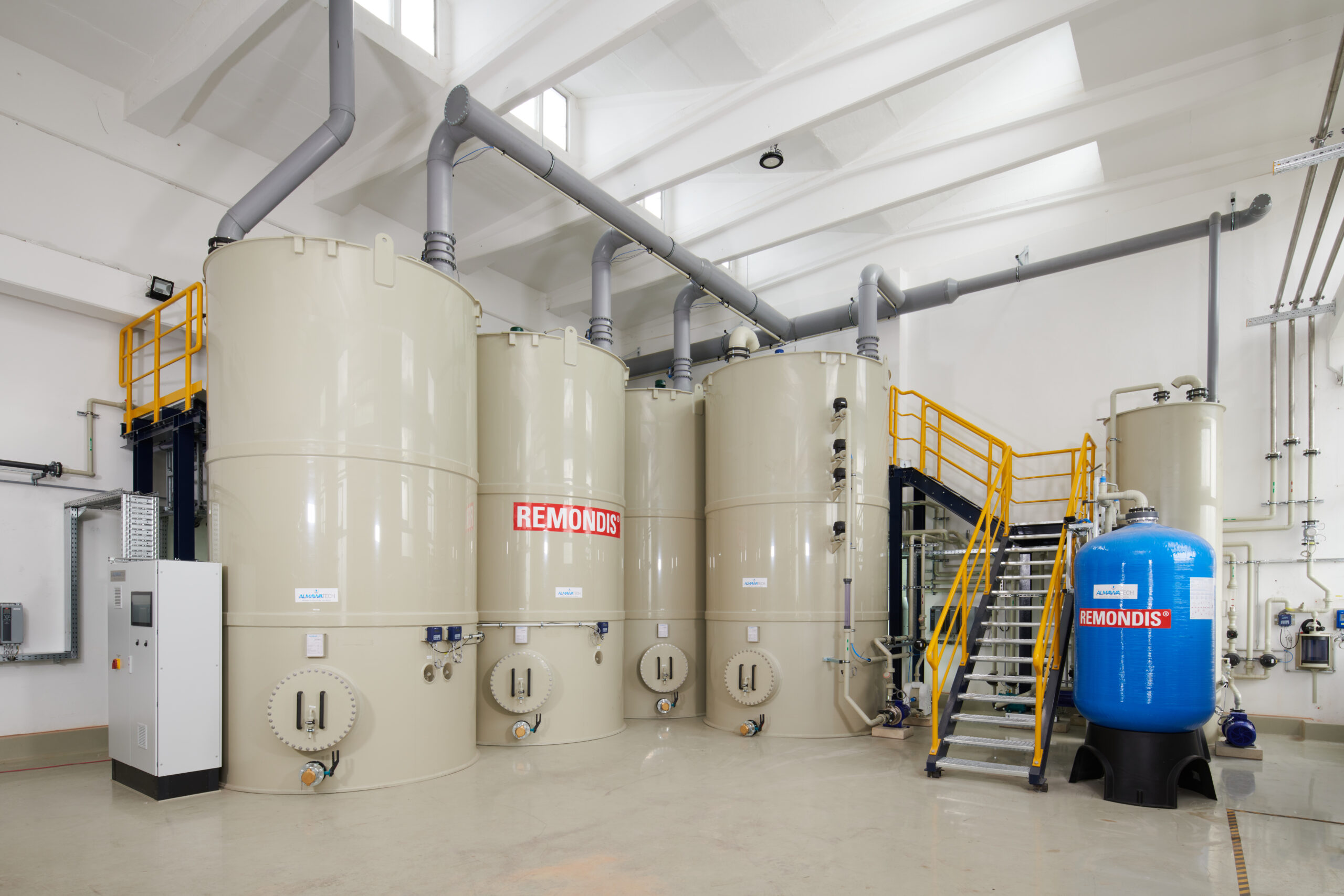

Photo: CP system ALMA CHEM MCW for the elimination of heavy metals, AOX, hydrocarbons and cyanides
2. thermal processes
Thermal processes are ideal for destroying organic pollutants or recovering valuable resources.
- Distillation: Here, solvents are recovered by evaporation and condensation.
- Incineration: Waste with a high organic load that cannot be treated in any other way is incinerated. This not only ensures safe disposal, but can also recover energy.
3. biological processes
Biological processes offer an efficient solution for organically contaminated wastewater, e.g. from food production.
- Aerobic processes: Microorganisms break down organic compounds in an aerated environment.
- Anaerobic processes: These processes take place in the absence of oxygen and convert organic substances into biogas, which can be used to generate energy.

4. membrane process
Membrane processes are indispensable when it comes to separating very fine particles or dissolved substances.
- Ultrafiltration: Removes particles, bacteria and macromolecules.
- Nanofiltration: For the removal of ions, especially polyvalent salts and organic compounds.
- Reverse osmosis: High retention rate for dissolved salts and organic substances. Often used to concentrate hazardous waste.
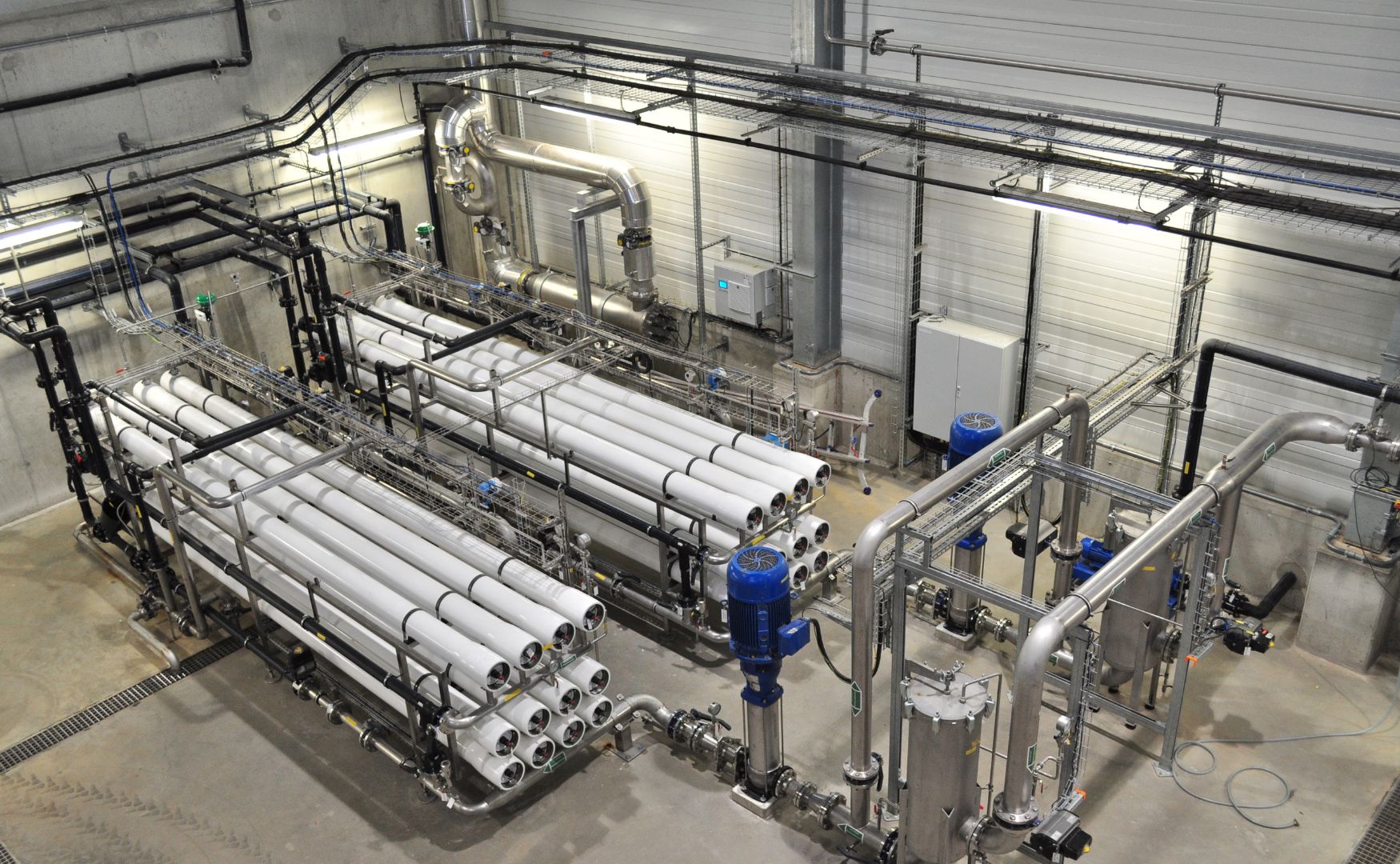

Photo: Reverse osmosis system with prior precipitation and flocculation(ALMA BHU BiosS-Treat)
Role of waste management companies
Waste management companies handle the professional treatment and disposal of waste. They operate specialized facilities for physico-chemical, thermal or biological treatment and offer services such as
- Analysis and categorization of waste
- Provision of containers and transport solutions
- Implementation of treatment and recycling processes
Recovery and recycling
The recycling of waste materials is a central component of the circular economy. In industrial wastewater treatment, heavy metals that have been removed by precipitation or filtration can be reused as raw materials in metal production. Purified solvents can be reused in chemical processes. Mineral residues, for example from the chemical industry, find new uses in the construction industry as fillers or cement components. There is a particular focus on water recycling: purified wastewater is treated using membrane processes such as reverse osmosis and can be fed back into the production cycle, which reduces the use of fresh water.
Removal
Non-recyclable or hazardous waste that cannot be used as energy must be disposed of safely. Hazardous waste landfills receive such materials and store them under strictly controlled conditions in order to prevent environmental pollution. For organic waste or materials with a high calorific value, thermal treatment in the form of controlled incineration is a common method. In modern waste incineration plants, the energy released is used to generate electricity or process steam. This method minimizes the volume of waste and reduces potential environmental hazards.
ALMAWATECH solutions
ALMAWATECH offers specially developed plants for the pre-treatment of liquid hazardous waste, including CP plants and flotation plants as well as membrane plants. Our ALMA CHEM MCW-systems enable flexible and efficient waste treatment directly on site. We also offer comprehensive pilot tests to determine optimum treatment parameters on an individual basis.
Conclusion
The treatment of liquid hazardous waste is essential for industrial wastewater management. With the right technologies and partners such as ALMAWATECH, companies and waste management companies can achieve both ecological and economic goals while reliably complying with legal requirements.
For further information on our products, please feel free to contact us at any time!