In industrial water technology, cooling water is a key factor for the efficient and safe operation of systems. It is used to dissipate process heat and ensure optimum operating temperatures. The properties and quality of the cooling water have a decisive influence on the performance, service life and cost-effectiveness of cooling systems. Without proper treatment and monitoring, problems such as corrosion, biological growth, legionella and deposits can occur, which can significantly impair operating efficiency and, in the worst case, lead to system failures.
This article highlights the technical background, the typical challenges and the proven technologies for the preparation and treatment of cooling water in industry.
Table of contents
The importance of cooling water
Cooling water is used in many industrial processes, including power plants, refineries, chemical plants, food processing and production facilities. The quality and treatment of cooling water have a significant influence:
Heat exchange performance: Deposits or biofilms can significantly reduce heat transfer.
Operating costs: soiling or damage increases energy and maintenance costs.
System safety: Corrosion or scaling can cause material damage and lead to operational failures.
Environmental compatibility: The handling of cooling waste water must comply with legal regulations.

Photo: Cooling tower
Typical challenges when using cooling water
1. scaling (deposits) Scaling is caused by the precipitation of poorly soluble salts such as calcium carbonate, calcium sulphate or silicates. These deposits can drastically reduce the efficiency of the heat exchanger.
2 Corrosion Corrosion is an electrochemical reaction that is promoted by dissolved oxygen, chlorides or acidic pH values in the cooling water. It leads to material loss and leaks in the systems.
3. biofouling Biofouling is caused by the colonization and growth of microorganisms such as bacteria, algae and fungi. These organisms can form biofilms that hinder heat exchange and increase the risk of corrosion.
4. fouling due to suspended matter Suspended matter such as sand, rust particles or organic substances can settle and clog the pipes.
Technologies and processes for cooling water treatment
1. treatment of cooling tower blowdown water
Desalination of cooling systems produces blowdown water, which may contain dissolved salts, organic substances and solids. This water can be treated using modern technologies such as ultrafiltration (UF) and reverse osmosis (RO). Ultrafiltration removes suspended solids and microbiological contamination, while reverse o smosis reduces dissolved salts. The treated water can then be fed back into the cooling circuit, saving fresh water and minimizing the environmental impact.
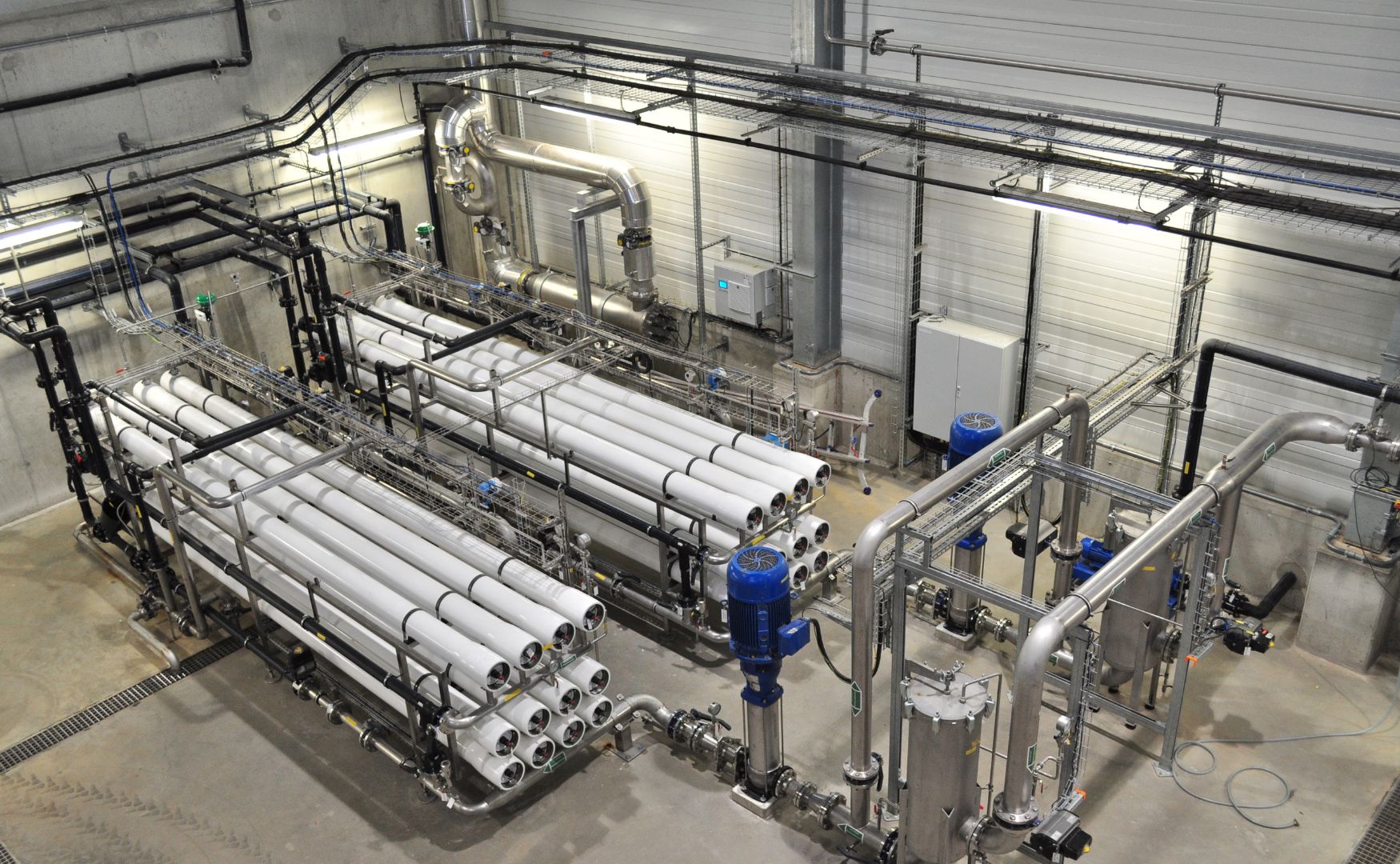

Photo: Treatment of cooling tower blowdown water using our ALMA OSMO reverse osmosis system to save fresh water
2. water treatment for cooling tower systems from well or river water
Two approaches can be used to produce water of suitable quality for cooling tower systems from well or river water:
Ion exchange: The combination of cation and anion exchangers removes dissolved salts from the water. This significantly reduces scaling and corrosion.
Ultrafiltration and reverse osmosis: Ultrafiltration removes suspended solids, colloids and microorganisms, while reverse osmosis eliminates dissolved salts and organic compounds. This process is particularly suitable when high purity requirements are placed on the cooling water.
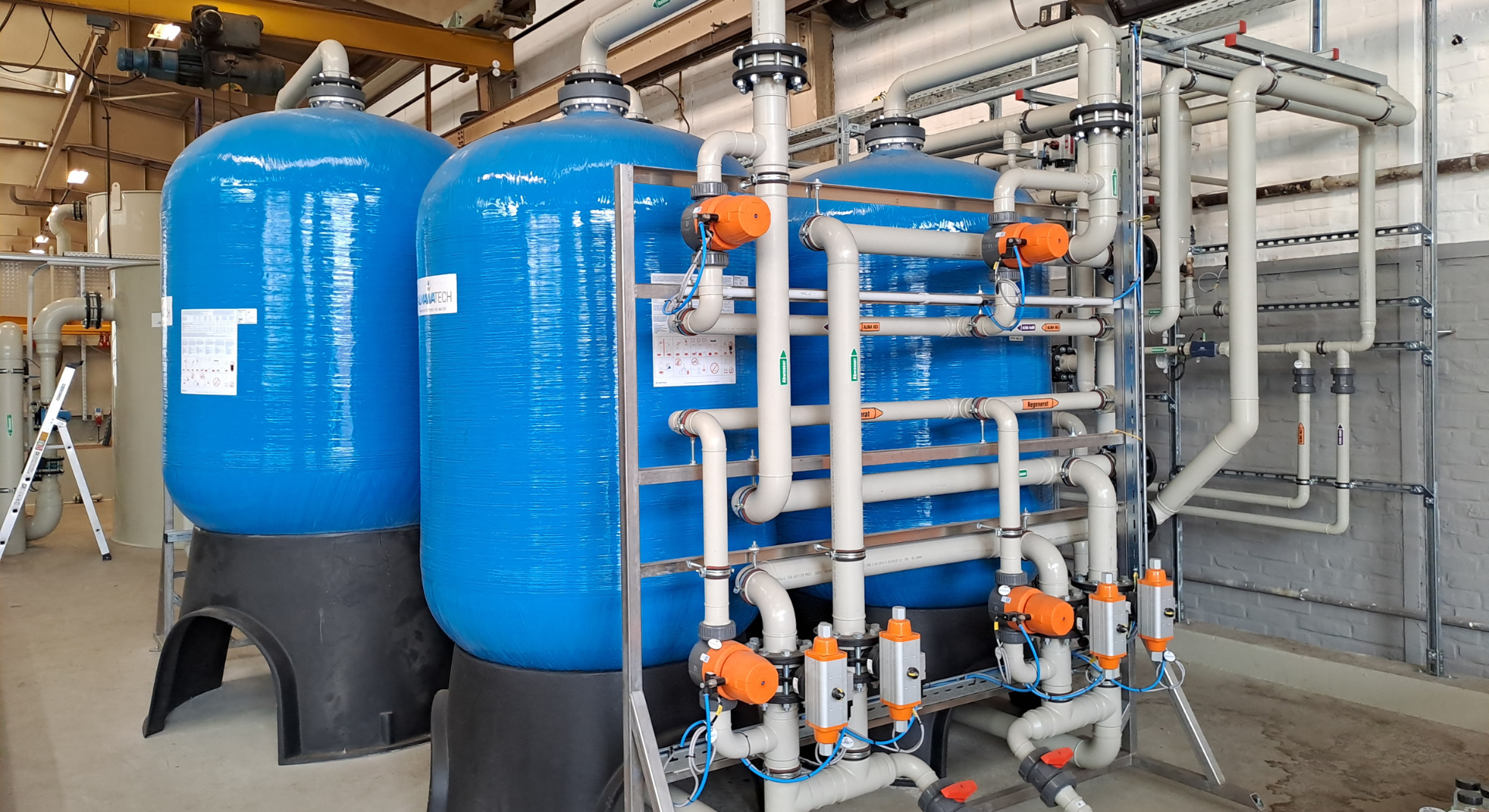

Photo: Our ALMA ION ion exchanger system with cation and anion resin
3. chemical processes
Corrosion inhibitors: These chemicals, such as phosphates or organic film formers, form a protective layer on the metal surfaces and prevent corrosion.
Antiscalants & hardness stabilizers: Antiscalants such as polyphosphates or polymers inhibit the formation of deposits by stabilizing the salts in the water.
Biocides: Oxidizing biocides (e.g. sodium hypochlorite) and non-oxidizing biocides (e.g. isothiazolinones) are used to control the growth of microorganisms.
pH control: The pH value is regulated by dosing acids or alkalis to minimize scaling and corrosion.
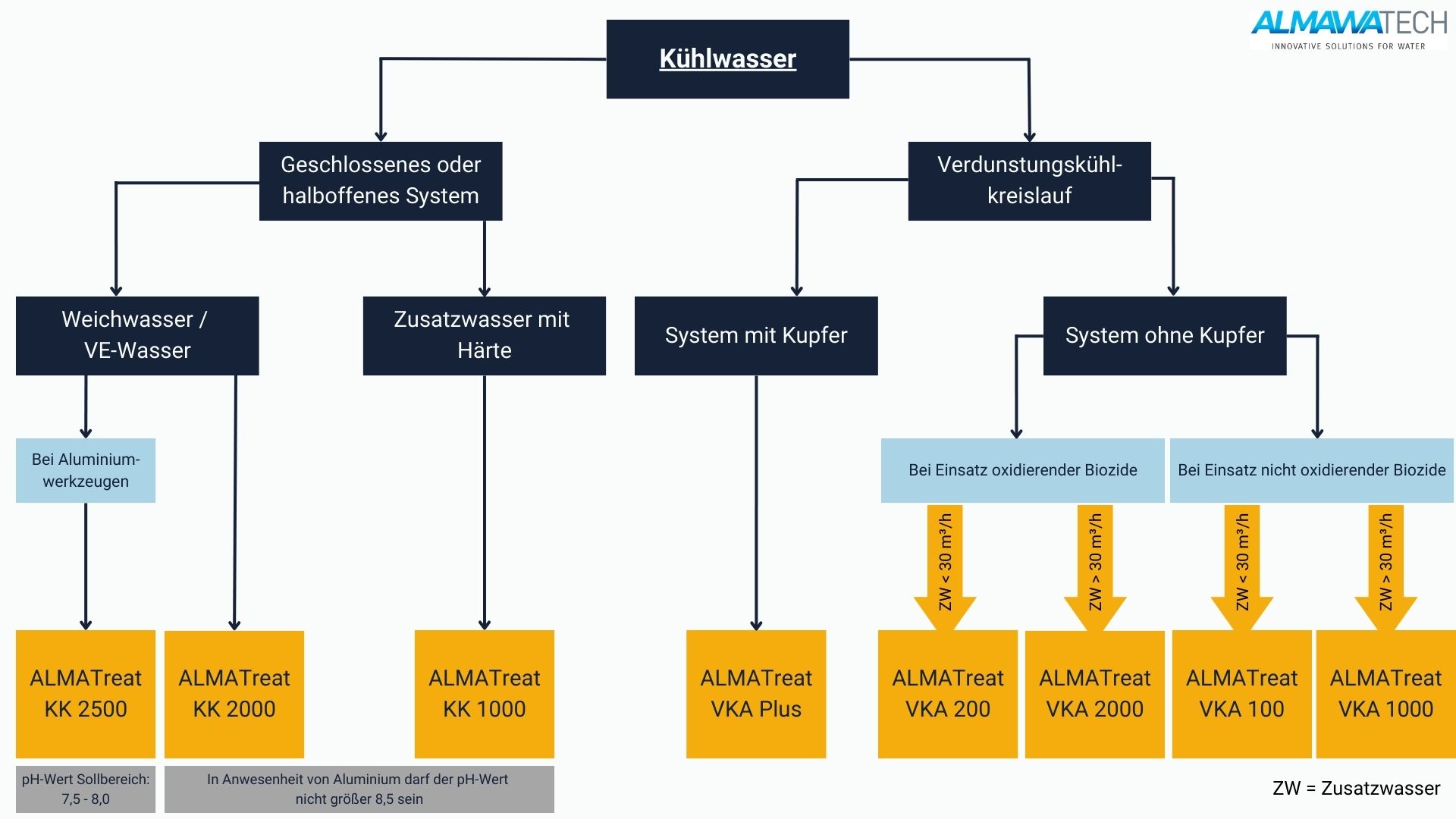
Photo: Product overview of various corrosion inhibitors, dispersants and hardness stabilizers in the ALMA AQUA cooling water product series
4. physical procedures
Filtration: Multi-media pore filters and microfiltration systems remove suspended solids and particles from the cooling water. These systems help to reduce fouling and scaling.
UV disinfection: UV light is used to kill microorganisms and prevent biofouling.
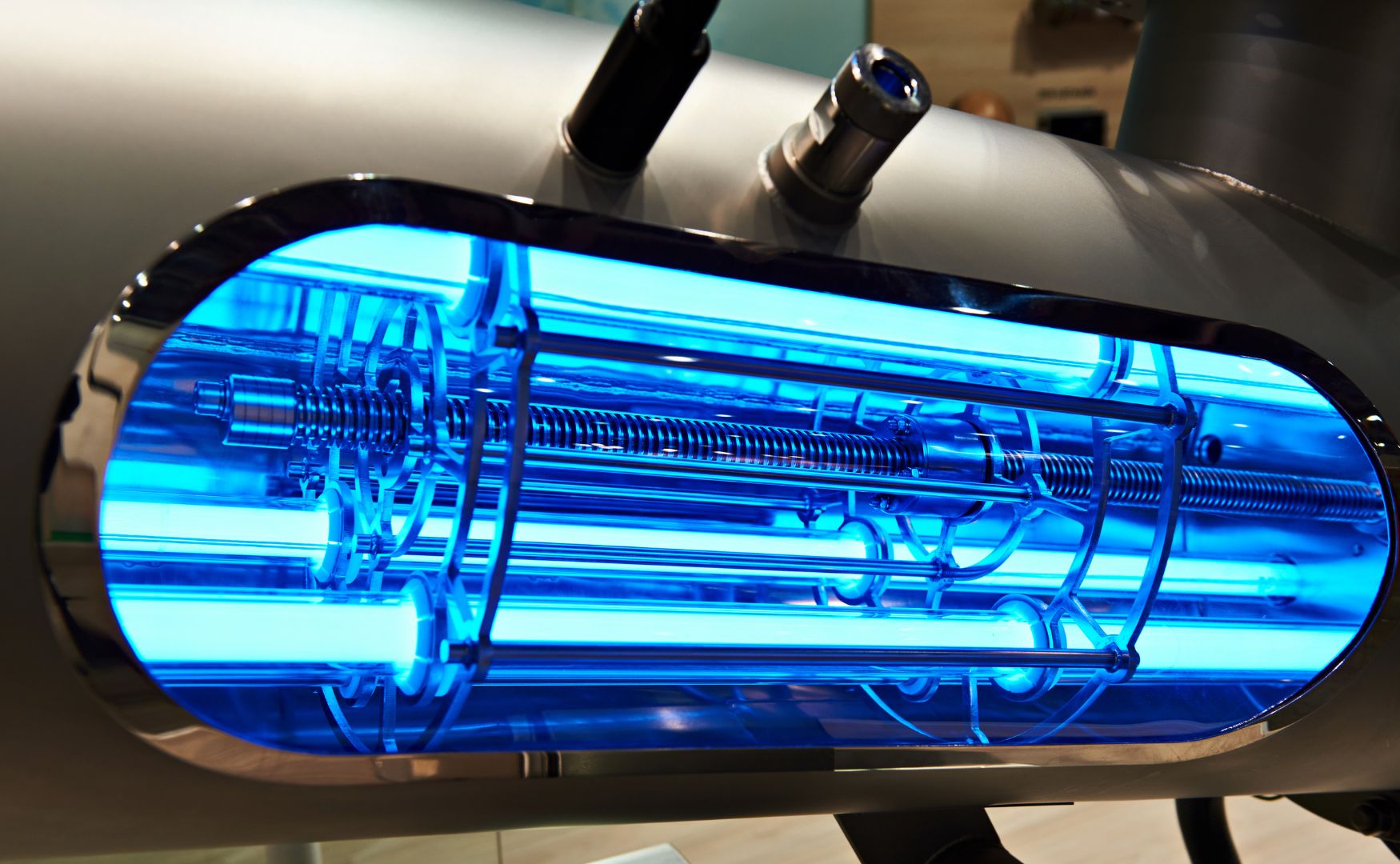
Photo: Our ALMA OXI UV system for disinfection and hygienization
Solutions for optimizing cooling water treatment
1. online monitoring systems By continuously monitoring water parameters such as pH value, conductivity, COD or the concentration of corrosion inhibitors, plant operators can react quickly to deviations.
2. individual water analyses A detailed analysis of the feed water and cooling system is essential in order to select the optimum combination of chemical additives and physical technologies.
3. use of innovative products ALMAWATECH offers, for example, highly effective corrosion inhibitors, biocides and hardness stabilizers that have been specially developed for industrial cooling systems. Our products are designed to minimize both environmental impact and chemical consumption.
4. regular maintenance Cleaning heat exchangers, pipes and filters ensures that deposits and fouling have no chance of impairing efficiency.
Practical examples
1. power plant cooling: River or sea water is often used for cooling in power plants. The challenge is to minimize the effects of inorganic deposits and biofouling. This is where biocides and antiscalants are used in combination with sand filters.
2. chemical industry: Corrosion control is particularly important in chemical plants, as aggressive process chemicals can get into the cooling water. A combination of corrosion inhibitors and physical cleaning processes ensures reliable system performance.
3. food industry: The requirements for hygiene and water quality are particularly high here. UV disinfection and non-oxidizing biocides are often used to prevent microbiological contamination.
4. treatment of cooling tower blowdown water: Blowdown in cooling systems produces blowdown water that may contain dissolved salts, organic substances and solids. This water can be treated using modern technologies such as ultrafiltration (UF) and reverse osmosis (RO). Ultrafiltration removes suspended solids and microbiological contamination, while reverse o smosis reduces dissolved salts. The treated water can then be fed back into the cooling circuit, saving fresh water and minimizing the environmental impact.
Conclusion
Cooling water is an indispensable component of industrial processes. Targeted treatment ensures the efficiency and safety of systems, reduces operating costs and complies with environmental regulations. With innovative technologies and products, ALMAWATECH supports companies in operating their cooling systems sustainably and economically.
For further information on our products, please feel free to contact us at any time!







