The oxidation plant is an essential component in water and wastewater treatment. It is used for the targeted removal of organic and inorganic pollutants through chemical or physical-chemical oxidation processes. Such systems are widely used in industrial water technology, particularly in the treatment of contaminated wastewater, the reduction of micropollutants, the removal of odors and disinfection.
This article provides a detailed description of how oxidation plants work, the technologies used, the chemical background and specific applications. In addition, the challenges in planning and operation and their solutions are presented.
Table of contents
Fundamentals of oxidation processes
Oxidation processes are based on the chemical reaction of electron donors (pollutants) with oxidizing agents, whereby the pollutants are converted into more harmless compounds. Various oxidizing agents and process variants are used in oxidation plants, which differ in their effectiveness and objectives.
Typical oxidizing agents:
Ozone (O₃):
- Strong oxidizing agent for the treatment of organic compounds and disinfection.
Chlorine (Cl₂):
- Classic oxidizing agent for disinfection and sterilization processes.
Hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂):
- High oxidizing power, often in combination with UV light or catalysts.
Potassium permanganate (KMnO₄):
- Used to remove iron, manganese and hydrogen sulphide.
UV light:
- Promotion of radical formation in combination with oxidizing agents such as ozone or H₂O₂.
Design and components of an oxidation system
An oxidation system consists of several essential components that enable and optimize the oxidation process. The structure varies depending on the oxidation process used.
1. oxidizing agent dosing system
- Function: Precise dosing of oxidizing agents such as ozone, chlorine or hydrogen peroxide.
- Technology:
- Dosing pumps for liquid oxidizing agents.
- Ozonizers for the on-site generation of ozone.
2. reactor chamber
- Function: Provision of the required contact time and mixture between the oxidizing agent and the medium to be treated.
- Design:
- Pressure reactors: For processes that take place under high pressure.
- Contact basins: Open systems for large-volume applications.
3. mixing systems
- Technology:
- Diffusers, Venturi injectors or static mixers for even distribution of the oxidizing agent.
4. control system
- Function: Monitoring and control of dosing, flow, pressure and temperature.
- Technology:
- Automated control with sensors (e.g. redox or pH measuring devices).
5. exhaust gas or by-product treatment
- Function: Removal or neutralization of by-products such as excess ozone or resulting chlorine compounds.
- Technology:
- Activated carbon filter for gas treatment.
- Neutralization systems for waste water.
Functionality and variants of oxidation systems
The functionality of an oxidation systemdepends heavily on the oxidation process selected. The most common processes are explained in detail below.
1. ozone systems
- Use:
- Removal of micropollutants, disinfection, color reduction.
- Mechanism:
- Direct oxidation by ozone molecules and indirect oxidation by hydroxyl radicals (-OH).
2. UV/H₂O₂ systems (UV-supported oxidation)
- Use:
- Degradation of organic compounds such as pharmaceutical residues and pesticides.
- Mechanism:
- UV radiation activates hydrogen peroxide to form hydroxyl radicals.
3. chlorine dosing systems
- Use:
- Disinfection, oxidation of iron and manganese.
- Mechanism:
- Oxidation of pollutants by hypochlorous acid (HOCl).

Photo: Our reactor for wet-chemical oxidation ALMA BHU UXI using ozone or according to Fenton
Applications of oxidation systems
Oxidation systems are essential in a wide range of industrial applications:
1. industrial wastewater treatment
- Examples:
- Removal of COD-contaminated organic pollutants.
- Treatment of toxic substances such as cyanides.
2. drinking water treatment
- Examples:
- Disinfection and removal of iron and manganese.
- Degradation of geosmin and 2-MIB (flavor and odorant).
3. cooling water treatment
- Examples:
- Control of biofouling through oxidation of organic substances.
- Oxidation of hydrogen sulphide to prevent odors.
4. removal of micropollutants
- Examples:
- Treatment of wastewater from the pharmaceutical and chemical industries.
- Removal of endocrine disruptors.
Challenges and optimization
1. corrosion
Oxidizing agents such as ozone and chlorine can attack system components.
- Solution: Use ozone and chlorine-resistant materials such as PTFE, PVDF or V4A stainless steel.
2. by-products
Depending on the oxidizing agent, by-products may be formed that require further treatment.
- Examples:
- Bromate formation during ozone treatment of water containing bromide.
- Chlorinated organic compounds during chlorine oxidation.
3. energy requirement
Oxidation processes such as ozone generation or UV oxidation are energy-intensive.
- Solution: Integration of energy efficiency measures such as heat recovery.
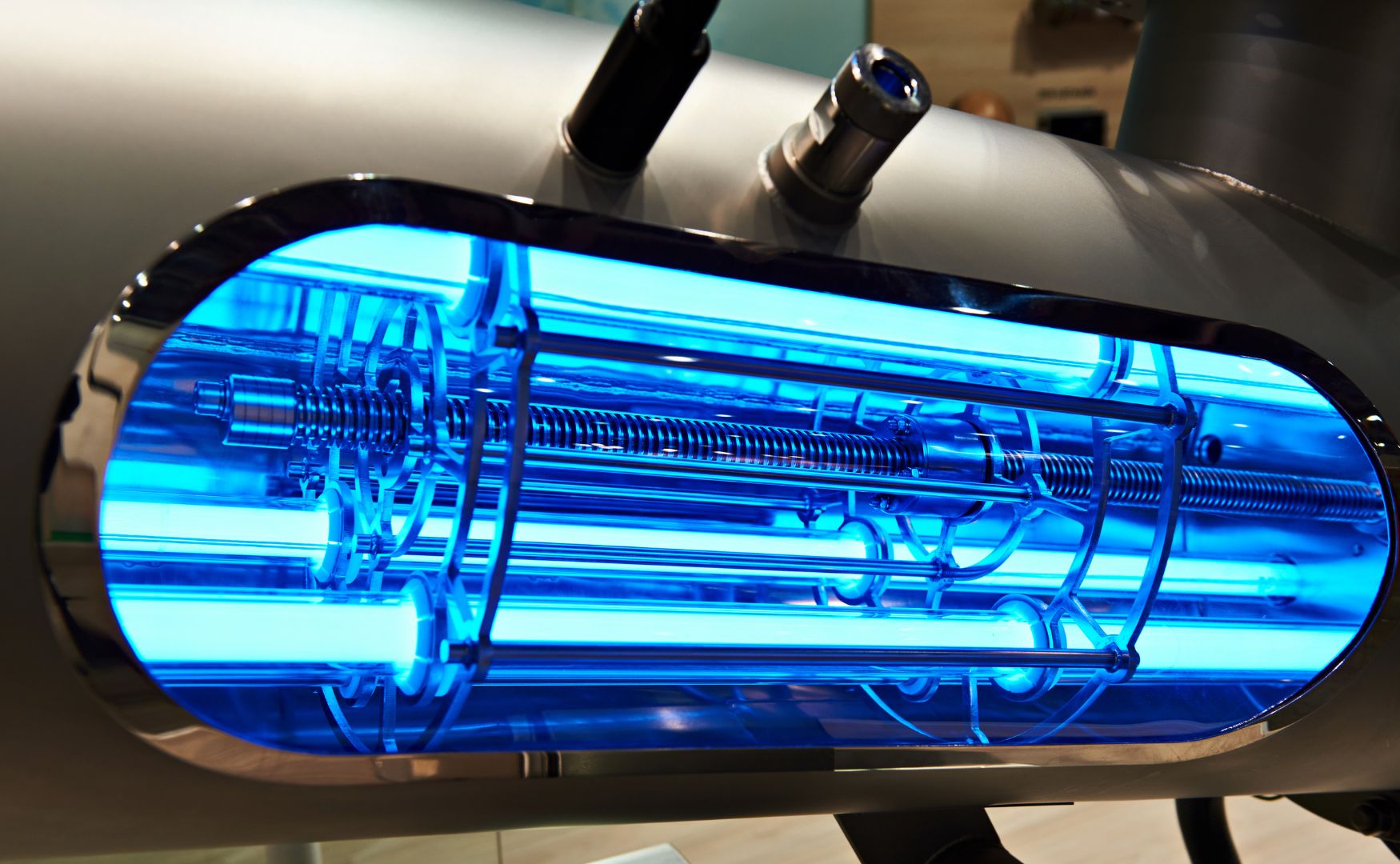
Photo: UV reactor with defined UV spectrum for the formation of highly radical hydroxyl radicals of the ALMA OXI UV
Conclusion
Oxidation systems are an indispensable technology in water and wastewater treatment. With their ability to remove stubborn pollutants, they make a decisive contribution to compliance with legal limits, to improving water quality and to the sustainable use of resources. The choice of a suitable oxidation process and careful planning of the system components are crucial for effectiveness and efficiency. Modern developments such as the integration of energy-efficient technologies and the optimization of dosing open up new possibilities for use in demanding applications.
For further information on our products, please feel free to contact us at any time!