Direct dischargers are companies, businesses or facilities that discharge their wastewater requiring treatment directly into natural bodies of water such as rivers, lakes or coastal waters without this wastewater first passing through a municipal or industrial wastewater treatment plant. The discharge is subject to the condition that the wastewater is treated in such a way that it meets the legal requirements and environmental protection requirements.
Table of contents
Technical requirements and regulations
In order to be approved as a direct discharger, companies must comply with strict legal limits, which are set by ordinances in the respective countries, such as the Wastewater Ordinance (AbwV) in Germany. These limits relate to the concentration of pollutants such as COD (chemical oxygen demand), BOD (biochemical oxygen demand), nitrogen compounds (e.g. ammonium, nitrate), phosphorus as well as heavy metals and toxic chemicals.
The official permits for direct dischargers require detailed proof of the treatment performance of the wastewater treatment plants used. This evidence is provided through continuous monitoring and regular analysis of the discharged wastewater.
Typical industries as direct dischargers
Companies from industries with high water consumption and complex pollutant loads in particular tend to operate their own wastewater treatment plants and act as direct dischargers. These industries include:
- Food and beverage industry (dairies, slaughterhouses, breweries)
- Chemical industry (production of chemicals, petrochemicals)
- Metal processing (electroplating, surface treatment)
- Pharmaceutical industry
- Pulp and paper industry
- Power generation (power plants with cooling water systems)
Wastewater treatment processes for direct dischargers
Direct dischargers require sophisticated wastewater treatment systems to meet the strict discharge limits. Common processes include
1. biological wastewater treatment
Processes such as the activated sludge process or biogas plants use microorganisms to biodegrade organic compounds and pollutants. This is an effective method for reducing COD and BOD, particularly for wastewater from the food industry.
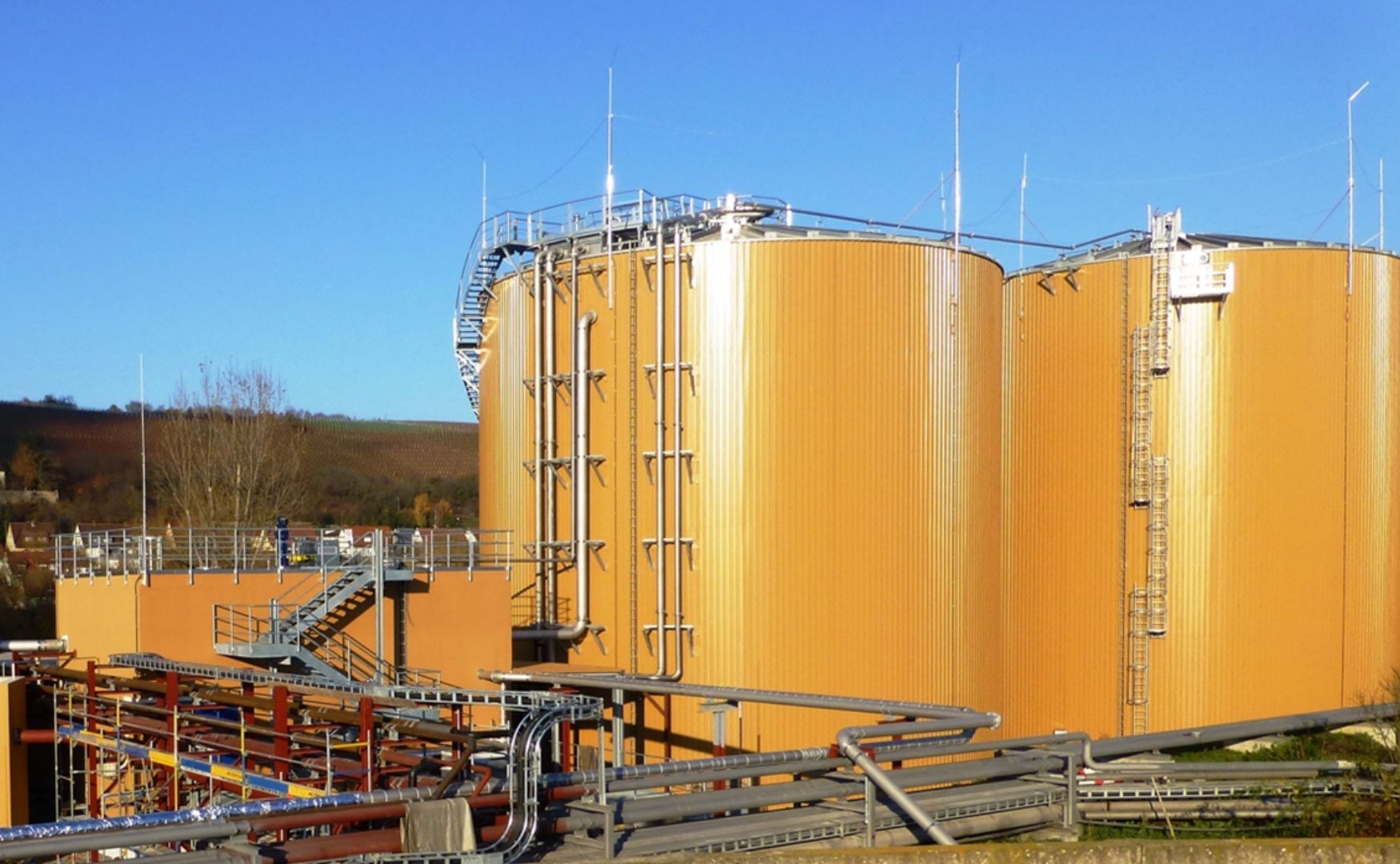

Photo: Example of an anaerobic biological wastewater treatment plant for the production of biogas(ALMA BHU GMR)
2. CP systems
CP plants (chemical-physical plants) such as the ALMA CHEM MCW rely on processes such as precipitation, neutralization and oxidation to remove substances that are difficult to degrade or toxic, including heavy metals or AOX.

Photo: Example of a CP system for the removal of heavy metals, cyanide, AOX and hydrocarbons(ALMA CHEM MCW)
3. membrane process
Reverse osmosis systems (RO) or ultrafiltration systems (UF) are particularly suitable for removing dissolved substances and micropollutants from wastewater. These processes are often used in combination with biological or chemical-physical pre-treatment to produce high quality water for direct discharge or even for reuse (water reuse). reuse (water reuse) reuse.
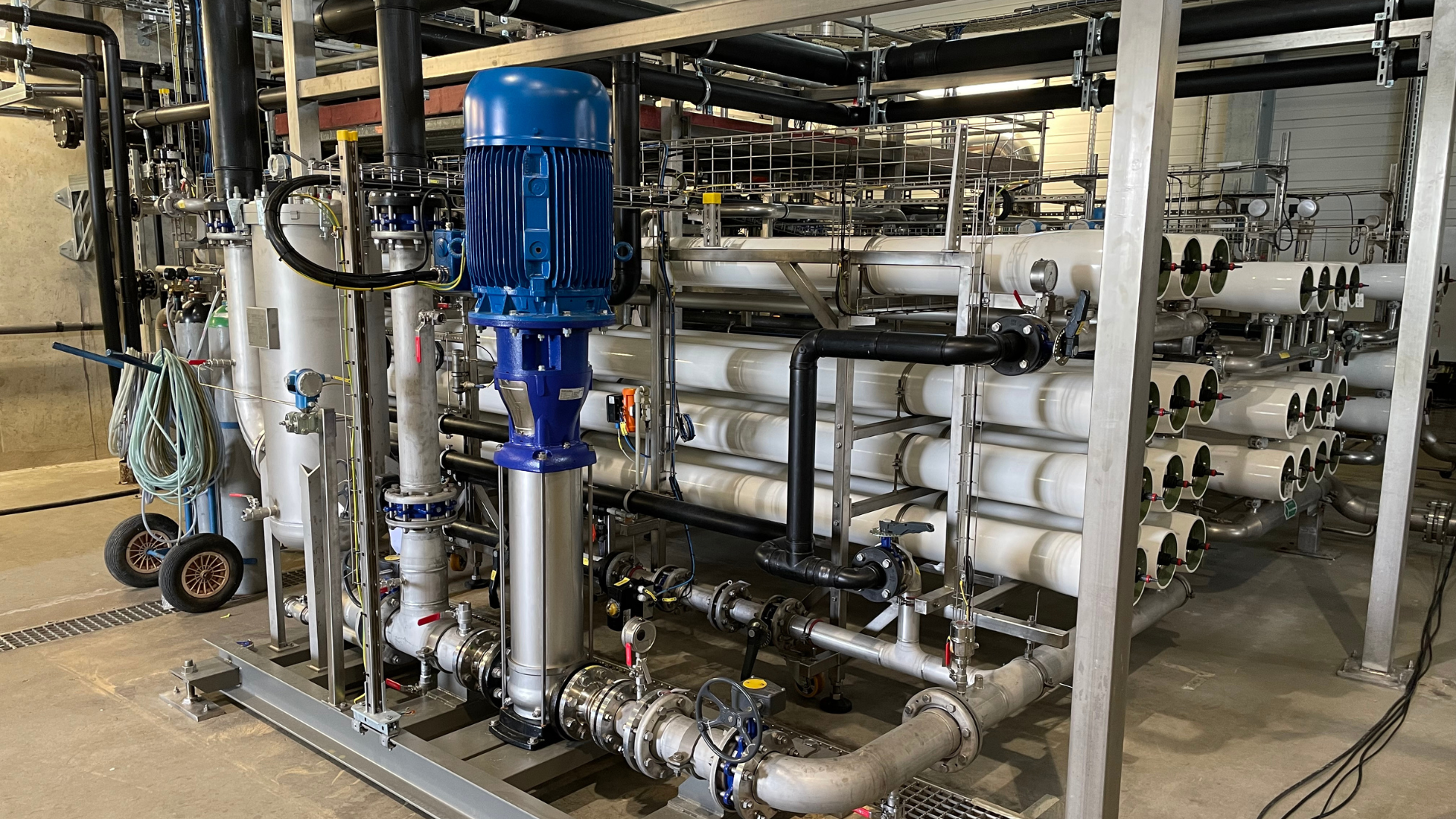

Photo: ALMA BiosS-Treat reverse osmosis system for in-house water reuse
4. flotation process
Dissolved air flotation (DAF) systems, such as the ALMA NeoDAF, are used to remove fats, oils and suspended solids. They are particularly effective in the food industry and metal processing to reduce lipophilic and organic compounds.
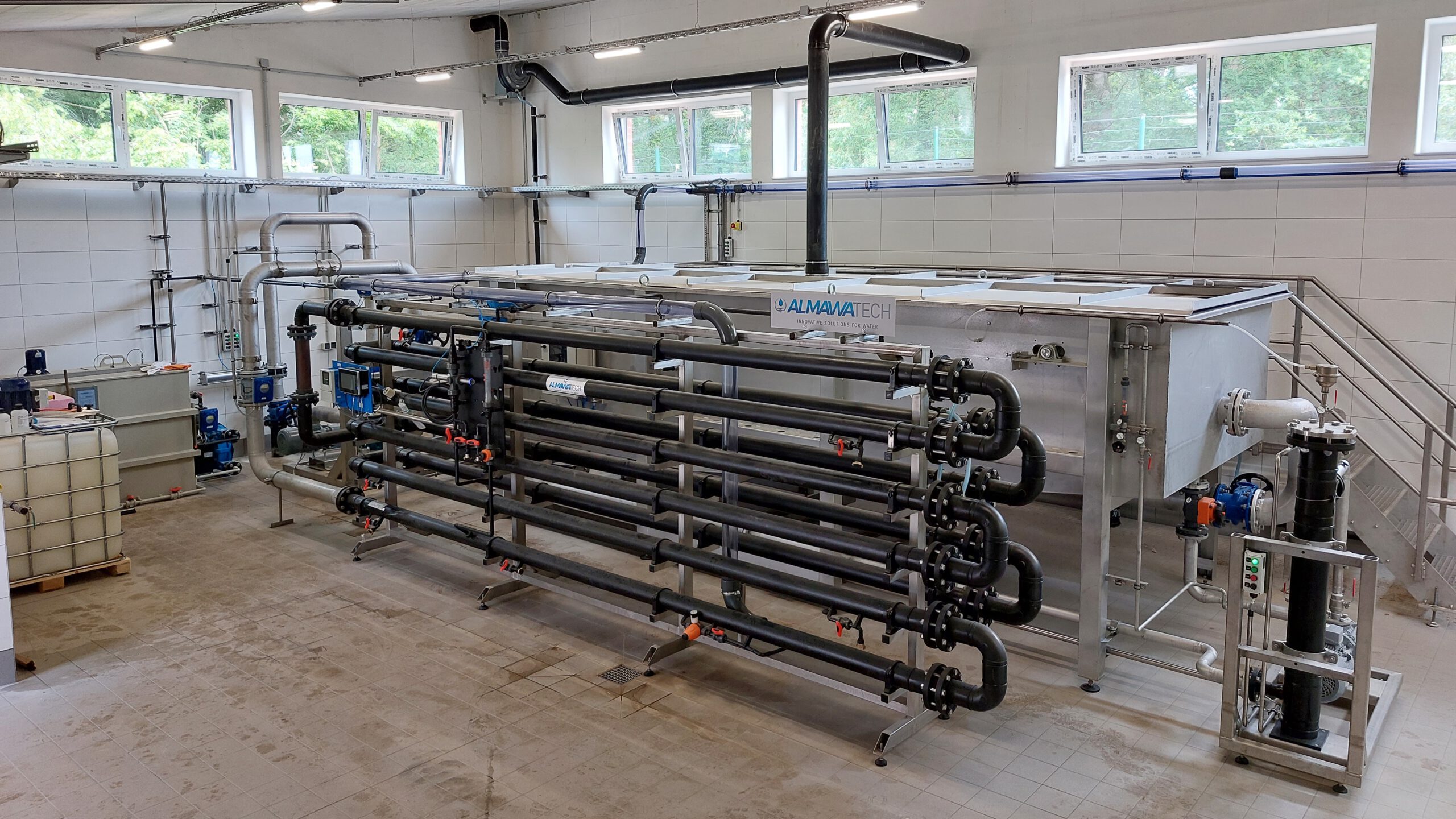

Photo: Our ALMA NeoDAF flotation plant for the pre-treatment of highly contaminated wastewater streams
5. neutralization systems
Depending on the composition of the wastewater, neutralization is required to stabilize the pH value of the wastewater. This can be done using acids, alkalis or innovative processes such as CO₂ neutralization with flue gas.
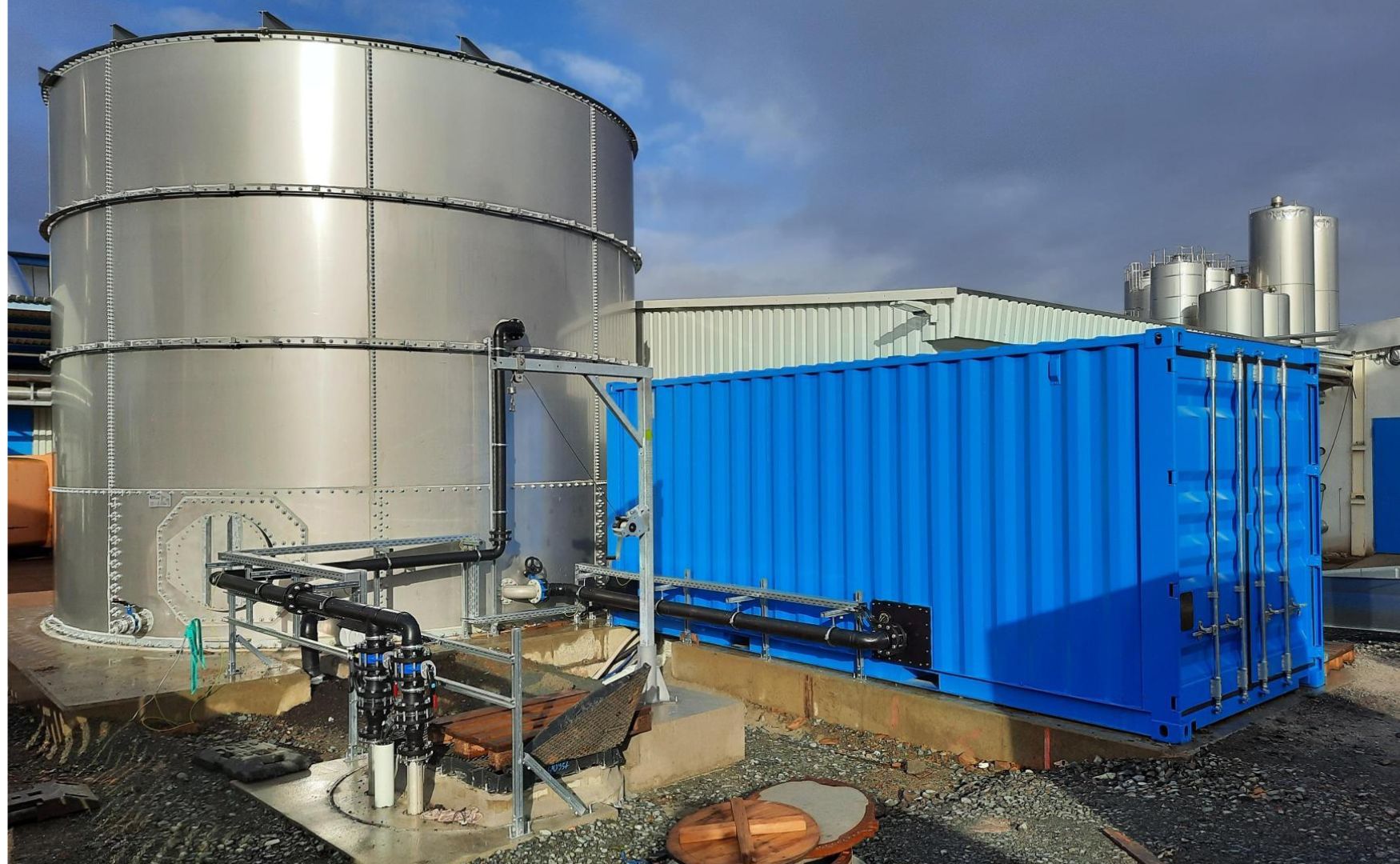

Photo: Example of a neutralization system in container design(ALMA Neutra)
Advantages of direct discharge
Direct discharge offers several operational and economic advantages for companies:
- Independence from municipal wastewater treatment plants: Direct dischargers are not dependent on external wastewater disposal, but can control the treatment directly in their own company.
- Customized treatment strategies: Companies can tailor their wastewater treatment specifically to their production processes and pollutant loads.
- Water recycling options: With modern treatment technologies such as reverse osmosis, direct dischargers can reuse the purified water internally (e.g. as cooling or process water), which lowers operating costs and reduces water consumption.
Challenges for direct dischargers
- High investment and operating costs: Operating your own wastewater treatment plants requires technical expertise and investment in modern technologies in order to achieve the legally prescribed purification targets.
- Strict monitoring requirements: Compliance with the limit values must be proven through regular monitoring and reporting. Companies must ensure that their systems are always working efficiently in order to avoid penalties and operational failures.
Conclusion
Direct dischargers have a great responsibility to treat their wastewater in accordance with the applicable environmental standards and to ensure water protection. With customized solutions such as ALMAWATECH's wastewater treatment plants, including biological systems, CP plants and membrane systemscompanies can safely meet the strict requirements and use resources efficiently at the same time.
For further information on our products, please feel free to contact us at any time!