Wastewater treatment is a multi-stage process that aims to remove pollutants and contaminants from wastewater in order to treat the water so that it can be discharged into the environment or reused. This process is crucial in both the municipal and industrial sectors in order to comply with legal regulations, protect the environment and conserve water resources. Wastewater treatment comprises mechanical, biological, chemical and physical processes, which are coordinated and combined in different ways depending on the origin and contamination of the wastewater.
Table of contents
Technical background and stages of wastewater treatment
Wastewater treatment usually consists of several stages, ranging from coarse clarification to biological degradation processes and final chemical treatment. Depending on the specific requirements, wastewater is treated differently in wastewater treatment plants.
1st mechanical stage - pre-treatment
Mechanical pre-treatment is the first step in wastewater treatment and is used to remove coarse solids and suspended solids from the wastewater. Physical methods such as screens, sieves, sand and grease separators and sedimentation tanks are used here.
- Rakes and sieves: These remove coarse solids such as paper, plastic or organic materials that could clog the system.
- Grit trap: Sand, gravel and other heavier particles are separated here to relieve the downstream process steps.
- Grease separator: Oils and grease floating on the surface of the water are collected in special separators.
Mechanical treatment ensures that the wastewater is in a condition that enables effective treatment in the subsequent stages.
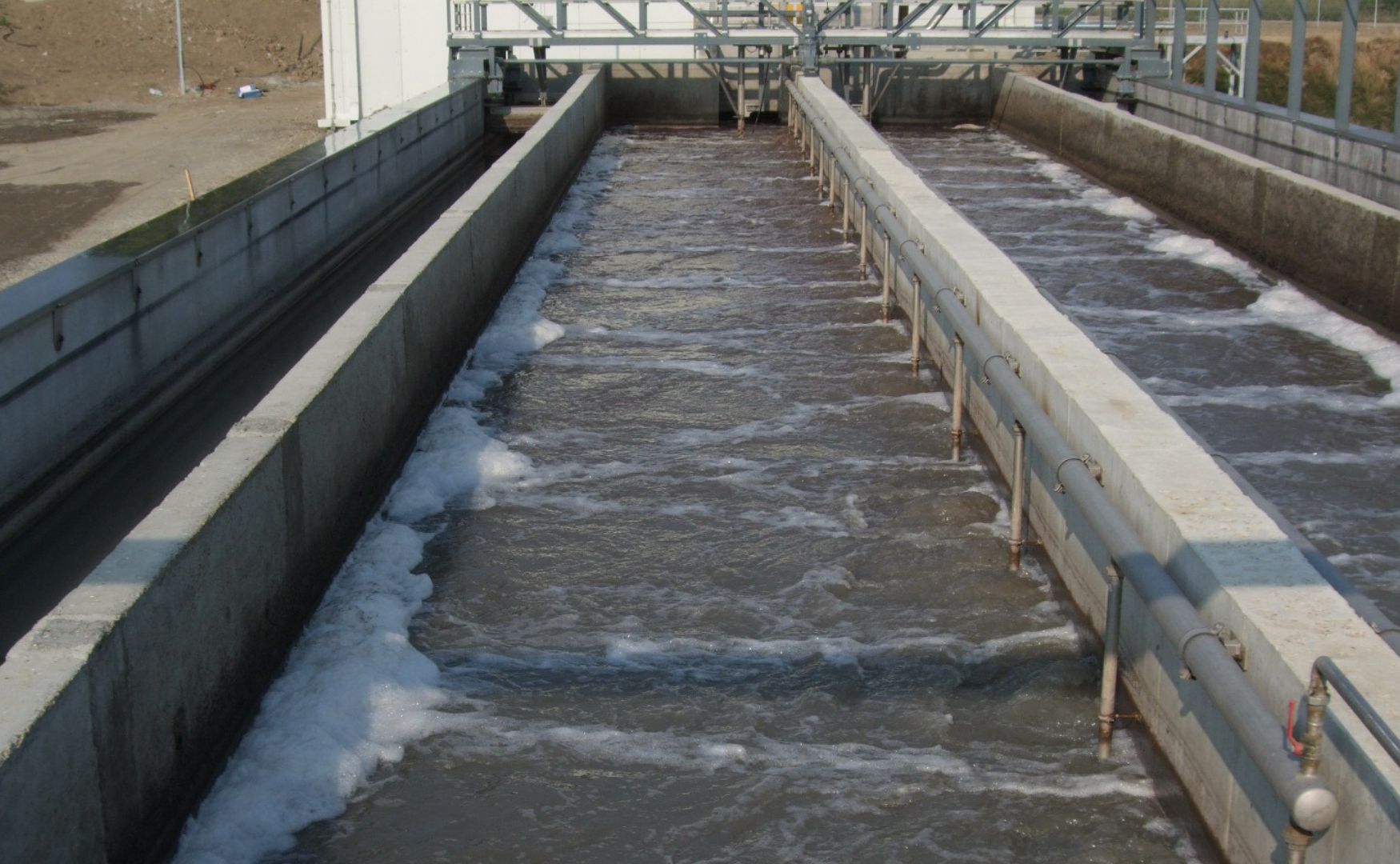

Photo: Example of an aerated grit chamber that removes sedimenting coarse solids as well as floating and fatty substances. The system is part of the pre-treatment of our ALMA BHU BIO system
2. biological stage - decomposition of organic substances
In the biological stage, organic impurities in the wastewater are broken down with the help of microorganisms. This is a key step in wastewater treatment, as the majority of organic substances contained in wastewater are biodegradable. The most commonly used biological processes are
Activated sludge process:
In this process, the wastewater is mixed in aeration tanks with active activated sludge consisting of microorganisms. These microorganisms break down the organic substances with the addition of oxygen.
Fixed bed and floating bed reactors:
In these reactors, microorganisms are colonized on carrier materials through which the wastewater flows. These reactors offer high biological purification performance in a small space.
Denitrification and nitrification:
These two biological processes serve to break down nitrogen compounds. In nitrification, ammonium is oxidized to nitrate, while in denitrification, nitrate is reduced to gaseous nitrogen, which escapes into the atmosphere as a harmless gas.
A particular example of the biological stage is the use of biogas plants such as our ALMA BHU GMR, which are used for the anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge. Here, biogas (consisting of methane and carbon dioxide) is produced under exclusion of air, which can be used to generate energy. This makes wastewater treatment partially energy self-sufficient.
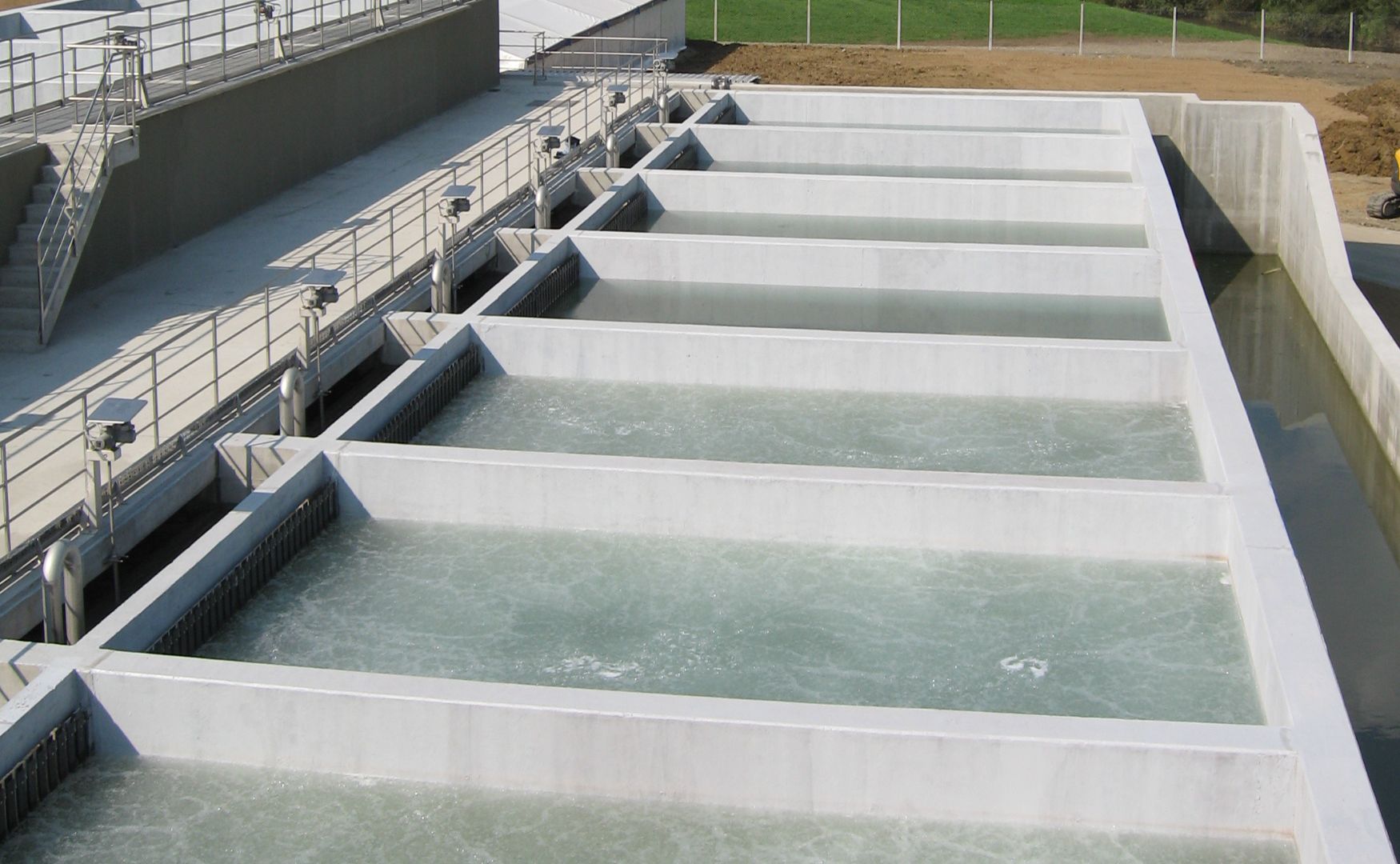

Photo: Photo of our biologically activated filtration, a combination process of mechanical cleaning and biodegradation(ALMA BHU BAF)
3rd chemical-physical stage - pollutant removal
In the chemical-physical stage, specific pollutants that are not or only with difficulty degradable by biological processes are removed. This is particularly important for industrial wastewater, which often contains specific pollutants such as heavy metals, organic solvents or other chemical compounds. Wastewater treatment plants that work on the principle of precipitation and flocculation are often referred to colloquially as CP plants (chemical-physical plants).
Precipitation and flocculation:
Chemical precipitants, such as aluminum salts or ferric chloride, are added to convert dissolved substances into solid particles. These particles form flocs, which are removed by sedimentation or flotation.
Flotation:
Finely dispersed air bubbles bind to suspended solids and bring them to the surface, where they are skimmed off. Flotation is particularly suitable for removing fats, oils and very fine solids.
In technical terms, flotation systems are referred to as dissolved air flotation, as the water is first saturated with air under pressure and then expanded. This expansion process creates fine air bubbles that adhere to the pollutants and cause them to float. An example of such a flotation system is our ALMA NeoDAF.
Neutralization:
Here, the pH value of the wastewater is regulated to bring it to a value that is suitable for discharge or further treatment stages. Acids, bases, flue gas or CO2 are added to neutralize the wastewater.
One example of a neutralization system is our ALMA Neutra.
Oxidation:
In this stage, persistent organic pollutants are converted into less harmful compounds through the use of oxidizing agents such as ozone or hydrogen peroxide.
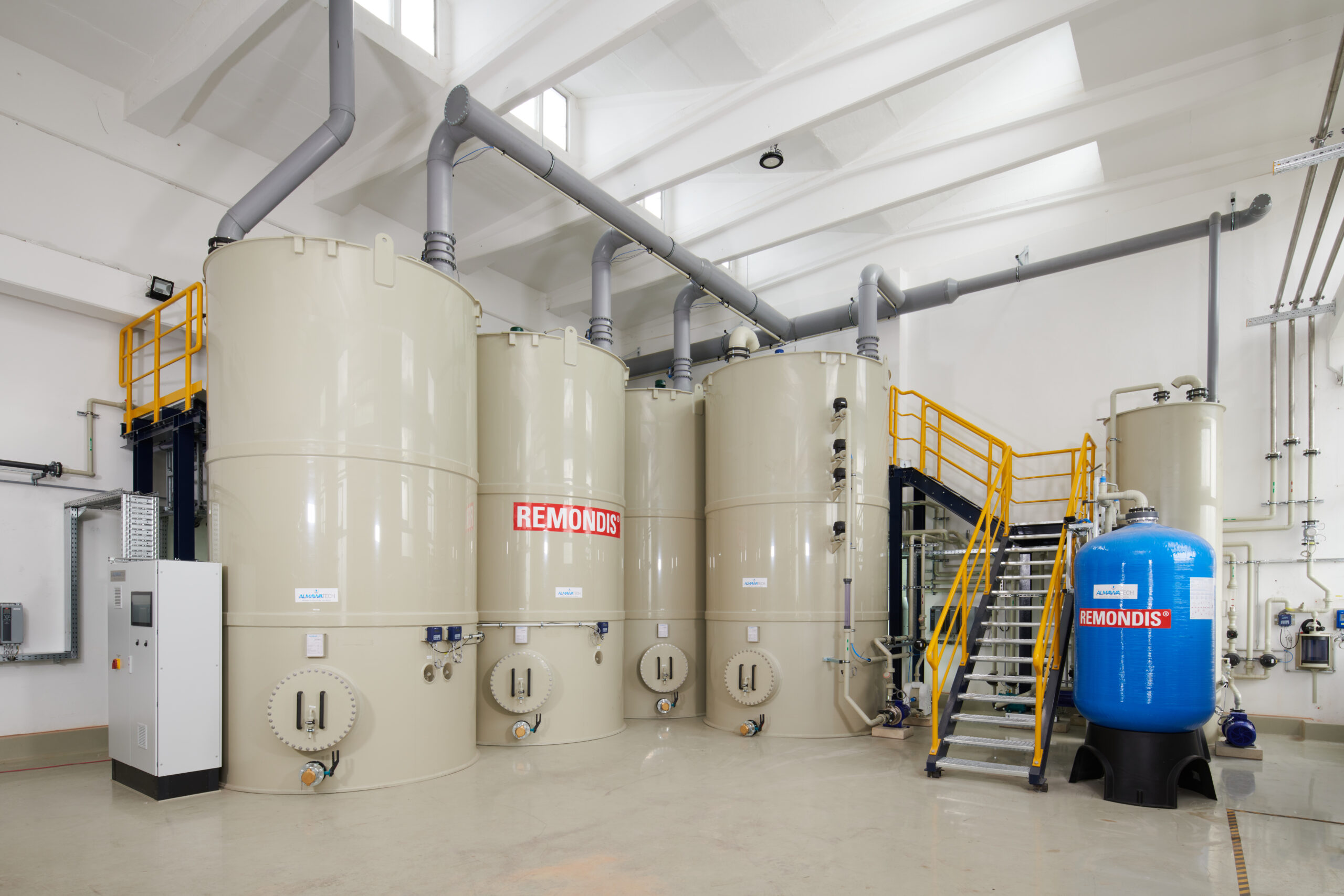

Photo: Example of a CP system for the removal of heavy metals, AOX and hydrocarbons(ALMA CHEM MCW)
4. membrane process - fine cleaning
Modern wastewater treatment plants often use membrane processes to remove the finest particles, microorganisms and dissolved pollutants from wastewater. The most common processes include
Microfiltration and ultrafiltration:
These processes separate solids and colloids from water using fine membranes that only allow water molecules and very small impurities to pass through.
Reverse osmosis:
In reverse osmosis, water is forced through a semi-permeable membrane that retains almost all dissolved substances, including salts and organic molecules. Reverse osmosis is often used in the reprocessing of wastewater and in the extraction of process water from wastewater.
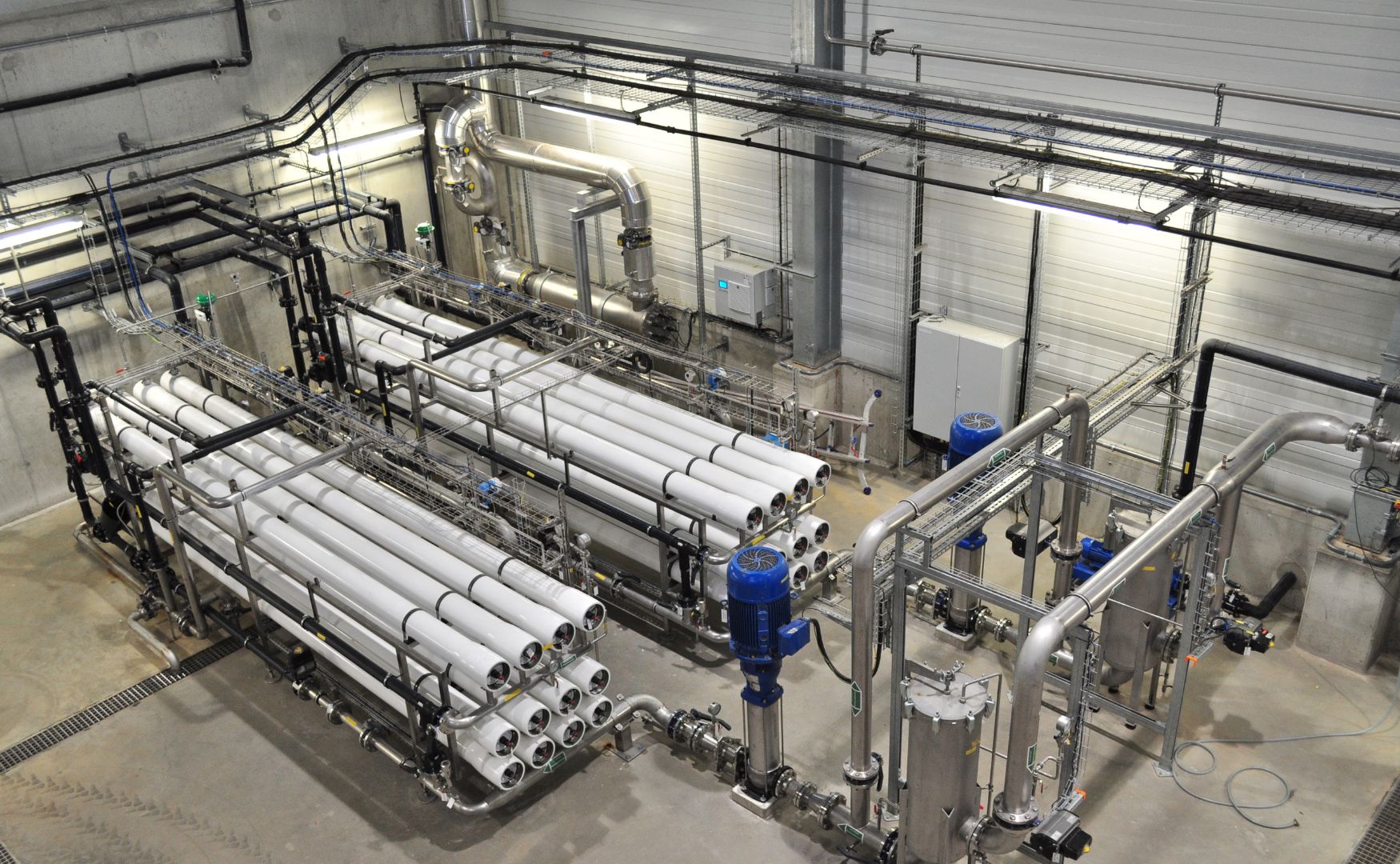

Photo: Example of one of our reverse osmosis systems for the production of process water from wastewater(ALMA BHU BiosS-Treat)
5. tertiary and quaternary stage - removal of micropollutants
In the tertiary and quaternary stages, the wastewater is further purified to remove micropollutants such as pharmaceutical residues, pesticides and hormone compounds. Activated carbon filtration, ozonation or UV treatment are used here. These processes aim to break down the smallest trace substances that remain in the water even after biological and chemical purification.
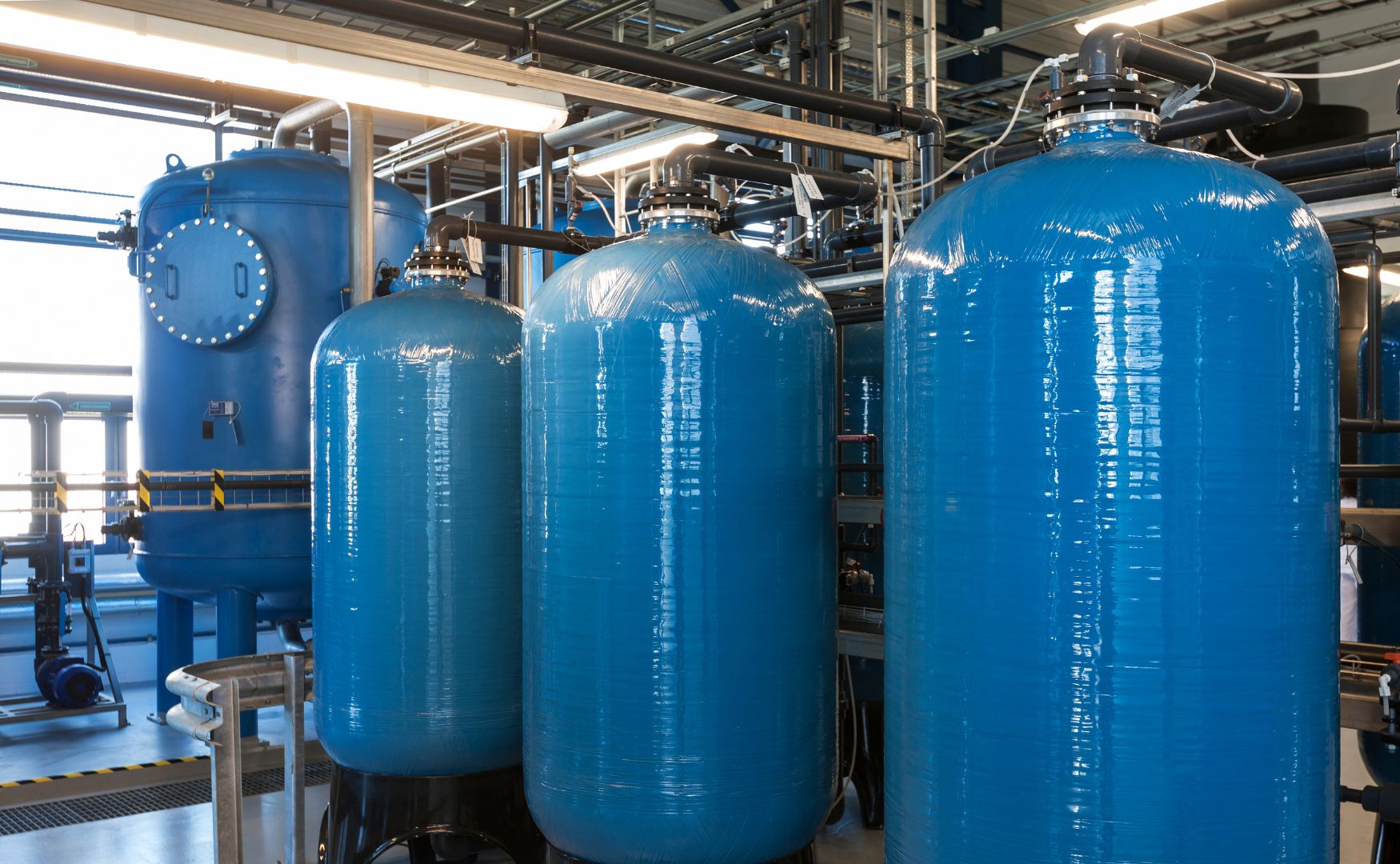

Photo: Activated carbon filter installed in GRP tanks(ALMA Fil AK)
Types of wastewater systems and application examples
Municipal wastewater treatment plants:
Municipal plants treat wastewater from households, businesses and smaller industries. They usually consist of the stages described above and provide comprehensive treatment of the wastewater before it is discharged into rivers or lakes.
Industrial wastewater treatment plants:
Industrial plants are often specialized systems that are adapted to the respective type of wastewater. For example, wastewater from food production, electroplating or petrochemicals requires specific chemical and physical processes to remove pollutants. Chemical-physical plants(CP plants) and flotation plants(ALMA NeoDAF) are often used here.
Water recycling plants:
These plants treat wastewater so that it can be reused in industrial processes. They play an important role in the circular economy and help to reduce water consumption.
Conclusion
Wastewater treatment is a highly complex process involving a combination of mechanical, biological, chemical and physical processes. Depending on the type of wastewater and the legal requirements, various technologies and processes are combined to ensure the safe discharge or reuse of the water.
For further information on our products, please feel free to contact us at any time!