The water balance is a key aspect for companies that want to use their water resources efficiently and reduce their ecological footprint. It describes the inflow, outflow and storage of water within a defined system, such as a production plant or an entire site. Particularly in water-intensive industries, such as the chemical, metal processing or food industries, the water balance enables potential savings to be identified and the use of water to be sustainably optimized through recycling systems or efficiency measures.
Table of contents
Water balance: why companies should draw it up
A detailed water balance helps companies to systematically analyze and specifically improve their water use. The main objectives are
Reduction in fresh water consumption
Fresh water is a limited resource whose use is becoming increasingly regulated and costly. A precise water balance shows where fresh water can be replaced by treated process or waste water.
Minimization of wastewater volumes
The cost of disposing of wastewater increases with its volume and pollution. Companies can significantly reduce these wastewater volumes through measures such as recycling and wastewater recycling.
Compliance with regulatory requirements
National and international regulations, such as the Water Framework Directive (WFD), require companies to provide evidence of efficient water use and compliance with discharge limits.
Sustainability and cost savings
An optimized water balance lowers operating costs, reduces environmental impact and contributes to meeting sustainability targets, which is perceived positively by customers and business partners in particular.
Improving the water balance through conservation measures
Companies can reduce water consumption and increase efficiency through simple and cost-effective measures:
Process optimization
- Optimized cleaning: Reduction of rinsing water volumes through the use of high-pressure systems or drying techniques.
- Efficient cooling circuits: Switching from open to closed cooling systems minimizes water consumption and evaporation losses. Alternatively, the blow-down water from the cooling circuit can be treated and reused using ultrafiltration and reverse osmosis.
Leakage and loss monitoring
- Regular inspections and the use of sensors to monitor leaks prevent water loss and enable early repairs.
Training and awareness-raising
- Employee training on efficient water use and regular reviews of water consumption processes help to minimize consumption.
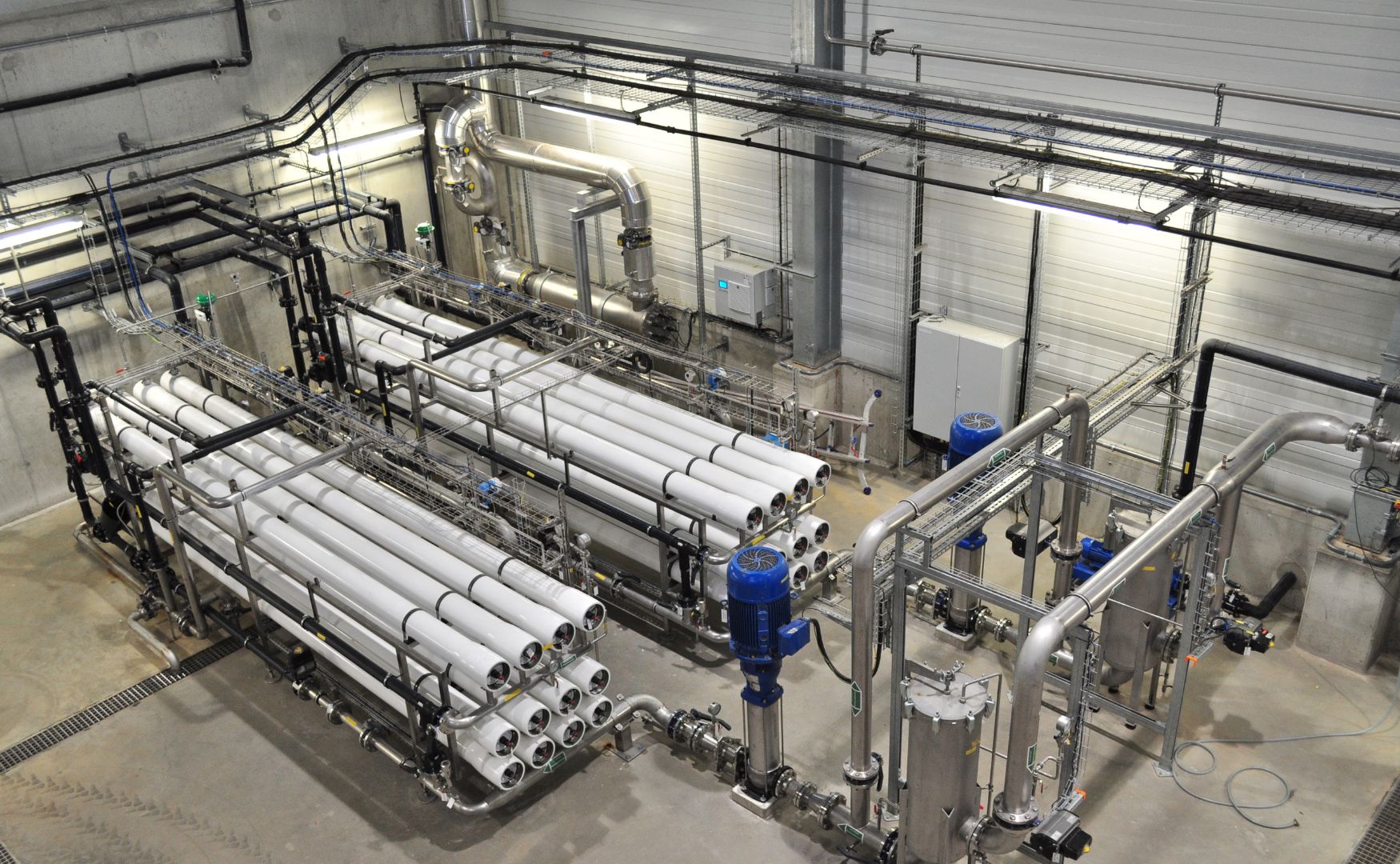

Photo: Our ALMA OSMO reverse osmosis system for in-house water recycling
Improving the water balance through water recycling
The integration of water recycling systems offers companies the opportunity to treat waste water and feed it back into the production process. This has several advantages:
Water treatment techniques
Different processes are used depending on the intended use and the required water quality:
- Filtration: Mechanical or membrane-based filtration (e.g. ultrafiltration) to remove suspended solids and particles.
- Ion exchangeRemoves dissolved ions in a targeted manner, e.g. hardness formers such as calcium and magnesium.
- Reverse osmosisFor the production of pure or process water with a low salt content.
- BiofiltrationDegradation of organic residues by microorganisms, especially in the case of contaminated wastewater.
Circulation systems
In many industries, recycled water can be fed directly back into closed cycles:
- Cooling water systems: Treatment of cooling water by means of ultrafiltration and reverse osmosis for reuse.
- Rinsing water: Recycling of cleaning water in production processes.

Photo: Our ALMA BioFilCompact biofiltration system offers efficient pre-treatment for reverse osmosis systems and is specially designed for use in industrial water recycling
Steps for implementing water balances and optimization measures
Creating a water balance
A precise water balance is the basis for all optimization measures. This includes
- Data collection: Measurement of all inflows, outflows and losses.
- Categorization: Subdivision of water flows into fresh water, process water, waste water and losses.
- Analysis: Identification of inefficiencies such as leaks or unnecessary drains.
Development of an optimization plan
Based on the water balance, measures are identified that have the greatest impact on water use. These include the selection of suitable technologies, such as recycling plants, and the adaptation of processes.
Monitoring and control
Continuous monitoring of the water balance ensures that the measures are successful and that fluctuations are detected at an early stage. Modern SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems enable real-time monitoring of water flows and consumption.
Conclusion
Creating and optimizing a water balance is a crucial step for companies that want to make their water use more efficient and operate more sustainably. By implementing conservation measures and using modern water recycling systems, companies can significantly reduce their fresh water requirements, cut operating costs and at the same time meet legal and environmental requirements.
An optimized water balance not only helps to conserve resources, but also increases a company's competitiveness and promotes its position as a pioneer in sustainable water management.
For further information on our products, please feel free to contact us at any time!