Waste acids are used or spent acids that are produced in various industrial processes, such as metal processing, electroplating or surface treatment. These acids have lost their original concentration or purity, but are still reactive and often contain impurities such as metal salts or organic substances. Instead of disposing of them as waste, spent acids can be efficiently used for neutralization in industrial neutralization plants as well as in precipitation and flocculation plants. This offers companies the opportunity to reduce both disposal costs and operating resource costs.
Table of contents
Technical background
Waste acids still contain sufficient acid capacity to neutralize alkaline wastewater or to be used in chemical processes for the precipitation of metals and other pollutants. This residual capacity makes them a valuable resource that can be used to control the pH value and precipitate unwanted substances without having to purchase additional acids such as sulphuric acid or hydrochloric acid.
Application of used acids in practice
1. neutralization of waste water
Used acids can be used in neutralization systems to neutralize alkaline wastewater, which often comes from cleaning processes or cooling water treatment. By adding used acids, the pH value of the wastewater is brought into a neutral range so that it can be further treated or discharged in accordance with legal requirements. This reduces the need for fresh acids and thus saves operating costs.
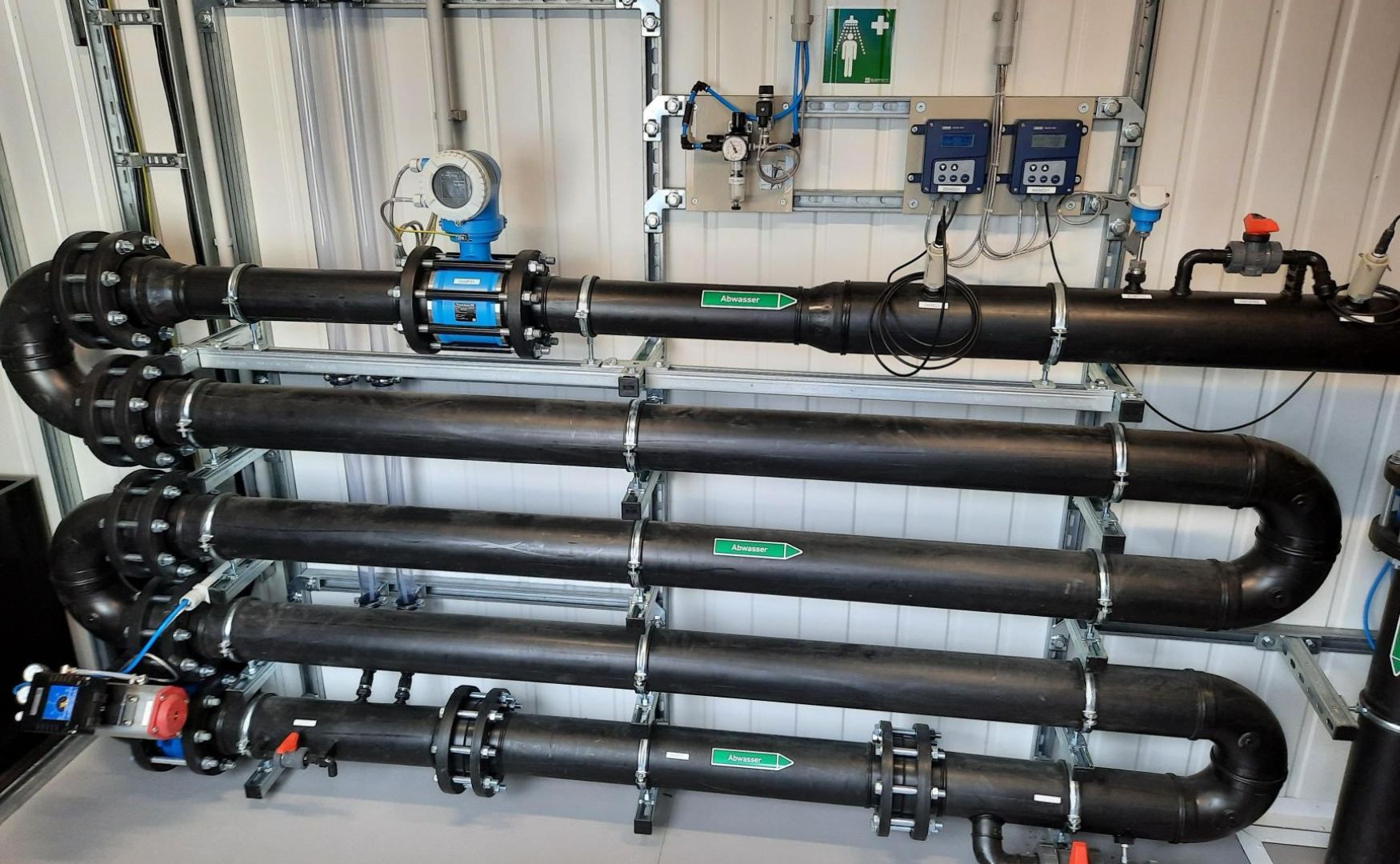

Photo: Reaction loop with pH-value-controlled dosing of acid and alkali(ALMA Neutra)
2. precipitation and flocculation processes / CP systems
Used acids can also be used in precipitation and flocculation plants, also known as CP plants, to remove metal ions or phosphates from wastewater. In many industrial processes, the pH value of the wastewater is lowered by adding acid in order to precipitate metals as hydroxides. Here, used acids can be used as a substitute for new chemicals, which not only lowers the cost of acid chemicals, but also reduces the disposal costs for the used acids.
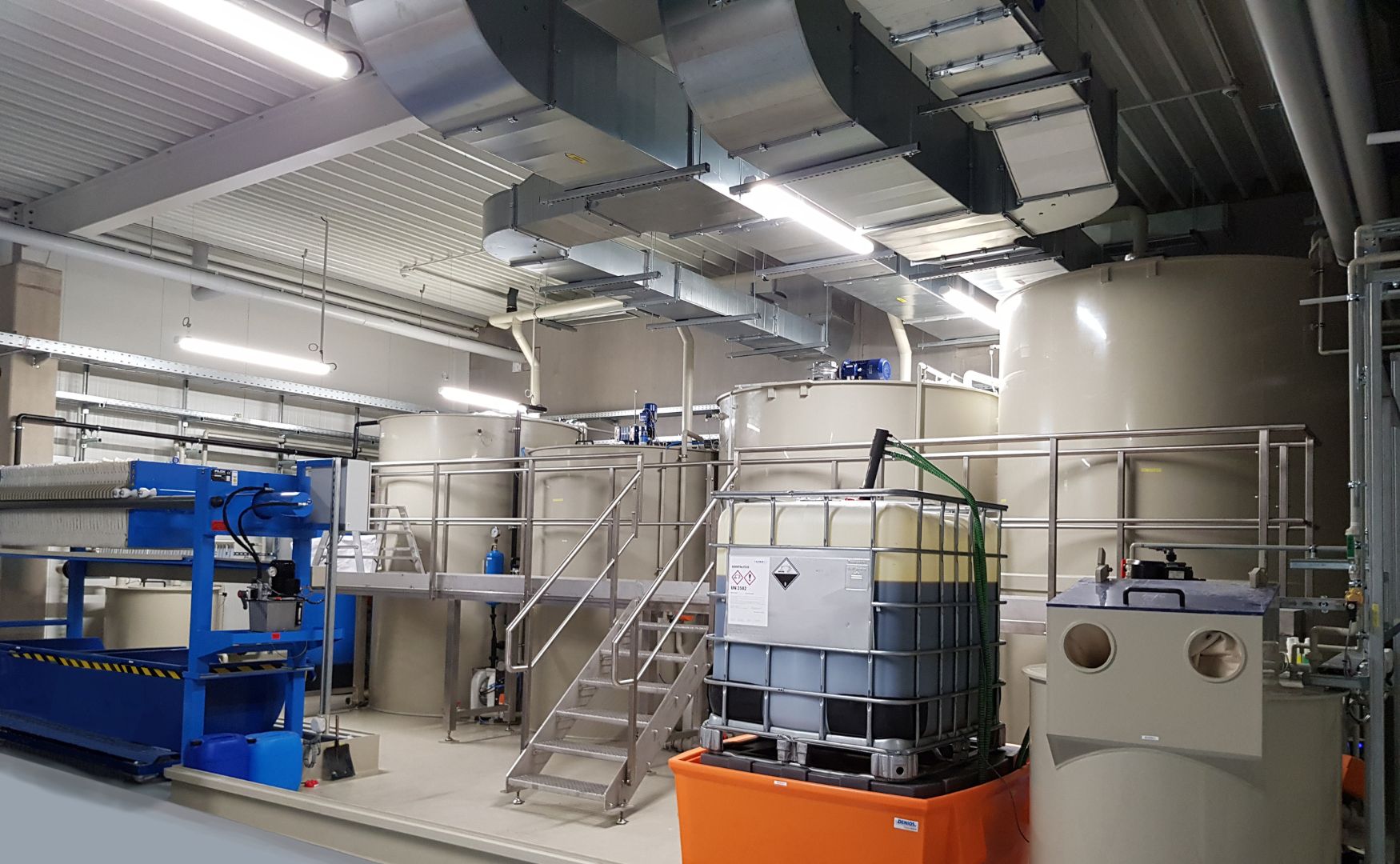

Photo: CP system with sludge dewatering through our chamber filter press(ALMA CHEM MCW)
3. combined processes
In companies where both alkaline and acidic wastewater is produced, the internal use of used acids for neutralization offers an ideal opportunity to treat both waste streams economically. By efficiently combining acidic and alkaline wastewater, the cost of additional neutralization chemicals can be completely avoided.
Advantages of using used acids in neutralization systems
Cost savings on operating resources
- Instead of buying fresh acids for neutralization processes or precipitation reactions, used acids can be used directly in these applications. This significantly reduces the need for additional operating resources.
Reduced disposal costs
- The reuse of used acids reduces the amount of hazardous waste that has to be disposed of at high cost. Used acids no longer have to be treated and disposed of as hazardous waste, which leads to considerable savings.
Sustainable process optimization
- The use of used acids contributes to the conservation of resources and improves the sustainability of operational processes. The reuse of chemicals reduces the environmental impact and simultaneously reduces the ecological footprint of the plant.
Example from practice
In electroplating plants that produce both acidic and alkaline wastewater, an internal circulation system is often implemented in which used acids are used to neutralize alkaline wastewater. This saves on fresh neutralization agents such as sulphuric acid or hydrochloric acid and reduces operating costs. At the same time, high disposal costs for used acids are eliminated as they are reused in the process.
Optimal conditions for the use of used acids
Companies that regularly generate used acids in their processes should always check whether internal reuse is possible. Prerequisites for the efficient use of used acids in neutralization and precipitation processes are
- Sufficient residual capacity of the acids to effectively control the pH value.
- Compatibility of the impurities in the used acids with the treated wastewater in order to avoid undesirable by-products or reactions.
- Process monitoring for precise dosing of used acids to ensure process stability and efficiency.
Conclusion
Used acids offer great potential to be reused in industrial processes for neutralization (ALMA Neutra neutralization plant) and in CP plants (such as the ALMA CHEM MCW). By utilizing this residual capacity, companies can achieve considerable savings in operating resources and disposal costs. In industries where used acids are generated, the possibility of reuse should always be considered, as it not only saves costs but also contributes to more sustainable production.