EGSB reactor (Expanded Granular Sludge Bed reactor) is an advanced technology for anaerobic wastewater treatment and belongs to the family of high-performance biogas plants. Developed to treat wastewater with a high organic load, the EGSB reactor uses a combination of anaerobic sludge granules and high water flow rates to efficiently break down organic substances and convert them into biogas (mainly methane and CO₂).
Table of contents
Technical principles of the EGSB reactor
The EGSB reactor is based on the principle of anaerobic degradation and is a further development of the UASB reactor (Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket). In the EGSB reactor, the flow rate of the wastewater is increased, causing the sludge granulate to be distributed in an expanded, loose layer. The increased contact surface between organic matter and anaerobic microorganisms results in more efficient wastewater treatment and biogas production.
Structure of an EGSB reactor
A typical EGSB reactor consists of:
Inflow and distribution system:
- The wastewater is introduced at the bottom of the reactor and evenly distributed to ensure optimum flow through the anaerobic sludge.
Granular mud pad:
- The reactor contains granulated anaerobic sludge with a high microbial density. The microorganisms decompose the organic components of the wastewater and convert them into biogas.
Expansion zone:
- Due to the high flow rate and the slight swirling of the sludge, a loose sludge layer is formed, which differs from the solid layer in the UASB reactor and ensures efficient contact with the wastewater.
Three-phase separator:
- The EGSB reactor is equipped with a three-phase separator that separates biogas, treated water and sludge. The biogas is used to generate energy, the treated water leaves the reactor and the sludge is retained in the reactor to ensure continuous biological activity.
Biogas outlet:
- The resulting biogas is discharged via a special pipe and can be used for energy or stored.
How the EGSB reactor works
In the EGSB reactor, the wastewater flows at an increased speed from the bottom to the top through the granulated sludge cushion. The microorganisms in the sludge break down the organic substances contained in the wastewater in the absence of oxygen. This anaerobic decomposition produces methane, which is contained in the biogas. The increased flow improves the exchange of substances between the wastewater and the microorganisms, resulting in faster and more efficient organic load reduction. The process is so efficient that effective purification is achieved even with high wastewater loads.
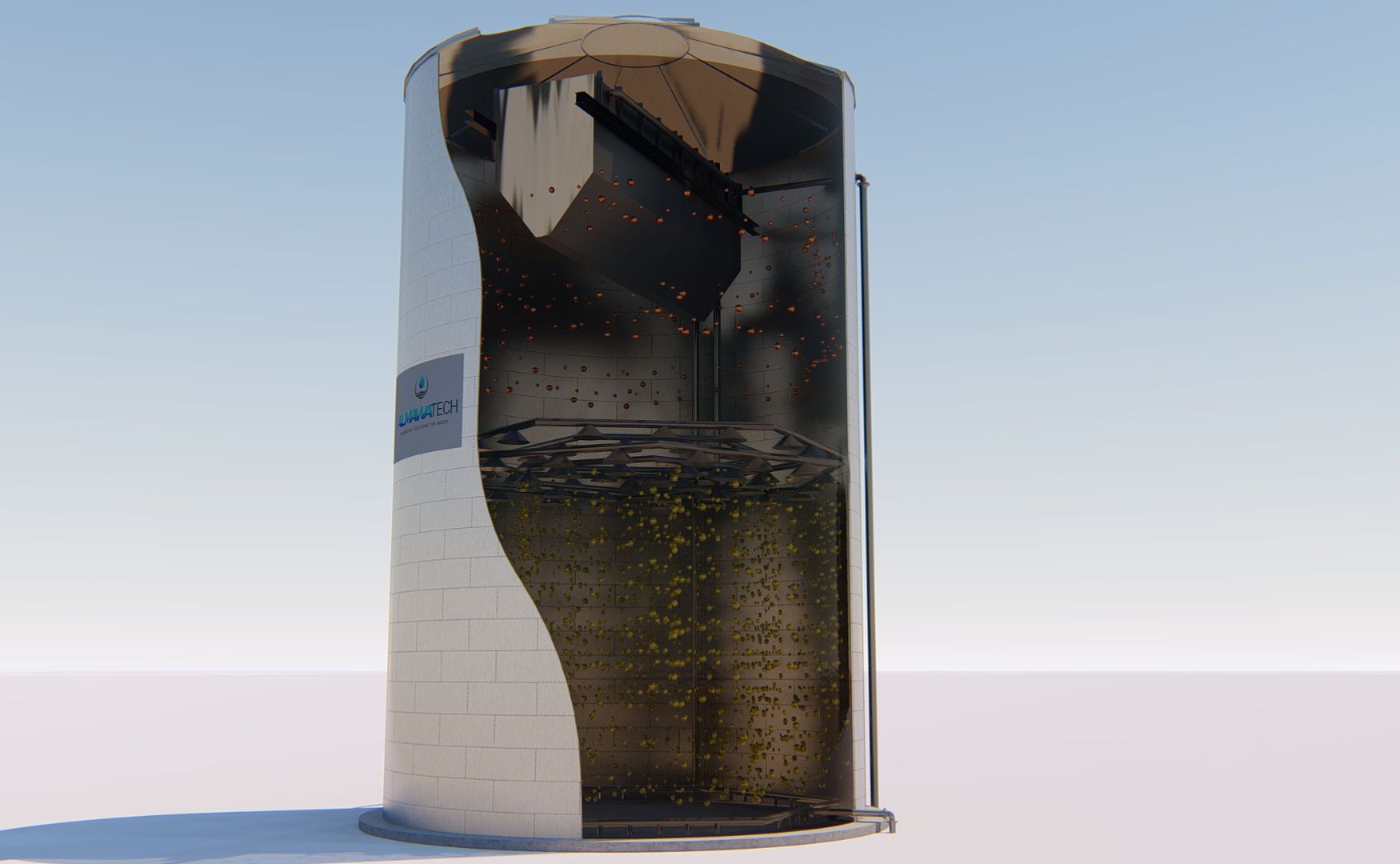
Photo: Schematic representation of our ALMA BHU BIO EGSB reactor
Technical advantages of the EGSB reactor
High degradation performance:
- The high flow velocity and the expanded sludge layer result in an improved contact time and degradation performance, which makes the EGSB reactor particularly efficient.
Compact design:
- As the EGSB reactor 's high load capacity enables a compact design, it is particularly space-saving and is suitable for industries with limited space.
High biogas production:
- The system produces biogas, which can be used as a renewable energy source and helps to cover the system's own requirements. This reduces operating costs and increases the energy efficiency of the entire system.
Robustness under varying wastewater conditions:
- EGSB reactors are adaptable and can be operated stably even with changing organic loads and temperatures. This makes them particularly suitable for various industrial wastewaters, e.g. from the food, beverage and paper industries.
Areas of application of the EGSB reactor
The EGSB reactor is particularly suitable for treating industrial wastewater with a high organic load and is therefore frequently found in the following industries:
Food and beverage industry:
- Waste water from food and beverage production contains high concentrations of organic substances such as sugar and fats. The EGSB reactor is ideal for breaking down these substances and converting them into biogas.
Paper and pulp industry:
- The paper industry produces wastewater with a high concentration of dissolved organic substances. The EGSB reactor can treat these efficiently and ensures reliable wastewater treatment and biogas production.
Whey processing and dairies:
- Wastewater from dairies is rich in organic substances and can be treated efficiently using EGSB reactors. Here, the technology offers an economical and ecological solution for wastewater treatment and energy generation.
Pharmaceutical industry and chemical industry:
- Industrial wastewater with complex organic compounds and high organic loads can be successfully degraded with the EGSB reactor. The technology offers stable performance and reduces the need for energy-intensive post-treatment.
Challenges and maintenance of the EGSB reactor
Sludge management: Operation of the EGSB reactor requires regular monitoring of the sludge density in order to maintain optimum degradation performance. Too high a sludge load can lead to blockages.
Biofouling and deposits: High concentrations of organic and inorganic substances can lead to deposits in the reactor. Regular maintenance is required to ensure degradation efficiency.
Temperature control: The anaerobic degradation process is temperature-dependent. To ensure constant performance, the temperature of the reactor must be kept within an optimal range, which can be a challenge, especially at lower ambient temperatures.
EGSB reactor compared to other anaerobic reactors
Compared to traditional reactors such as the UASB the EGSB offers increased performance and resilience due to its high flow velocity and expanded sludge layer. Compared to a conventional anaerobic reactor, the EGSB reactor can break down smaller particles and dissolved organic substances more effectively, making it an ideal solution for heavily polluted industrial wastewater.
Conclusion
The EGSB reactor is an ultra-modern and efficient solution for anaerobic wastewater treatment. Its compact design, high degradation capacity and biogas production capability make it particularly suitable for industries with organically contaminated wastewater. By integrating EGSB reactors, companies can not only improve their wastewater treatment, but also reduce costs through biogas production and operate more sustainably. In wastewater treatment, the EGSB react or offers an optimum combination of performance, compactness and economical energy generation.








