Denitrification is a biological process that plays an important role in industrial and municipal wastewater treatment. It refers to the conversion of nitrate (NO₃-) and nitrite (NO₂-) to gaseous nitrogen(N₂), which escapes into the atmosphere. This process is carried out by special bacteria under anoxic conditions (i.e. in the absence of oxygen), which use nitrate as an electron acceptor for their metabolism when oxygen is not available.
Table of contents
Technical background and functionality
The nitrogen cycle in wastewater comprises several steps in which nitrogen compounds are converted by microbiological processes. In the first step, nitrification, ammonium (NH₄⁺) is oxidized to nitrate by nitrifying bacteria. Denitrification follows this process and reduces the nitrate formed back to nitrogen gas, which is released harmlessly into the atmosphere.
The process of denitrification takes place in several stages:
- Reduction of nitrate (NO₃-) to nitrite (NO₂-): This first step is carried out by denitrifying bacteria that use nitrate as an electron acceptor.
- Reduction of nitrite to nitric oxide (NO): In the second step, nitrite is reduced to nitric oxide.
- Reduction of nitrogen monoxide to dinitrogen monoxide (N₂O): This step reduces the nitrogen monoxide to nitrous oxide.
- Reduction of dinitrogen monoxide to nitrogen gas (N₂): The final step of denitrification leads to the formation of gaseous nitrogen, which escapes into the atmosphere.
Areas of application in industrial wastewater treatment
Denitrification is frequently used in the treatment of wastewater from the food and beverage industry, the chemical and pharmaceutical industries and in municipal wastewater treatment plants. These wastewaters often contain high concentrations of nitrate and nitrite, which must be safely removed by biological degradation processes in order to meet legal limits and avoid environmental damage.
Technical requirements
Certain operating conditions are required for denitrification to take place effectively:
- Anoxic conditions: The process only takes place in the absence of free oxygen, so the oxygen content in the reactor must be strictly controlled.
- Organic substrates: Denitrifying bacteria require a carbon source for their metabolism. In many cases, methanol or acetic acid is added as an external carbon source if the wastewater does not contain sufficient organic matter.
- pH value and temperature: The pH value should ideally be between 6.5 and 8.5, and the temperature also influences the efficiency of denitrification. Temperatures between 10 °C and 30 °C are ideal.

Photo: Denitrification and nitrification basin for industrial wastewater from the food industry in Chile, ALMA BHU BIO plant
Advantages of denitrification
- Effective nitrogen removal: By reducing nitrate and nitrite to gaseous nitrogen, the nitrogen content in wastewater is significantly reduced, making it easier to comply with legal requirements.
- Environmental protection: Denitrification prevents the eutrophication of water bodies, which is caused by increased nitrogen inputs and can lead to algae blooms and oxygen deficiency in water bodies.
- Cost efficiency: As the process relies on natural, biological processes, the operating costs are generally lower than with chemical processes.
ALMAWATECH solutions for denitrification
ALMAWATECH offers innovative solutions for integrating denitrification into industrial and municipal wastewater treatment processes. Our biofiltration plants and anaerobic systems are specially designed to efficiently remove nitrogen:
ALMA BioFil Compact
This compact biofiltration system is ideal for smaller wastewater flows of up to 100 m³/h. It combines anoxic and aerobic zones to efficiently implement denitrification. This system is particularly suitable as pre-treatment before membrane filtration systems such as reverse osmosis to reduce nitrogen compounds and reduce the risk of fouling in the membranes.
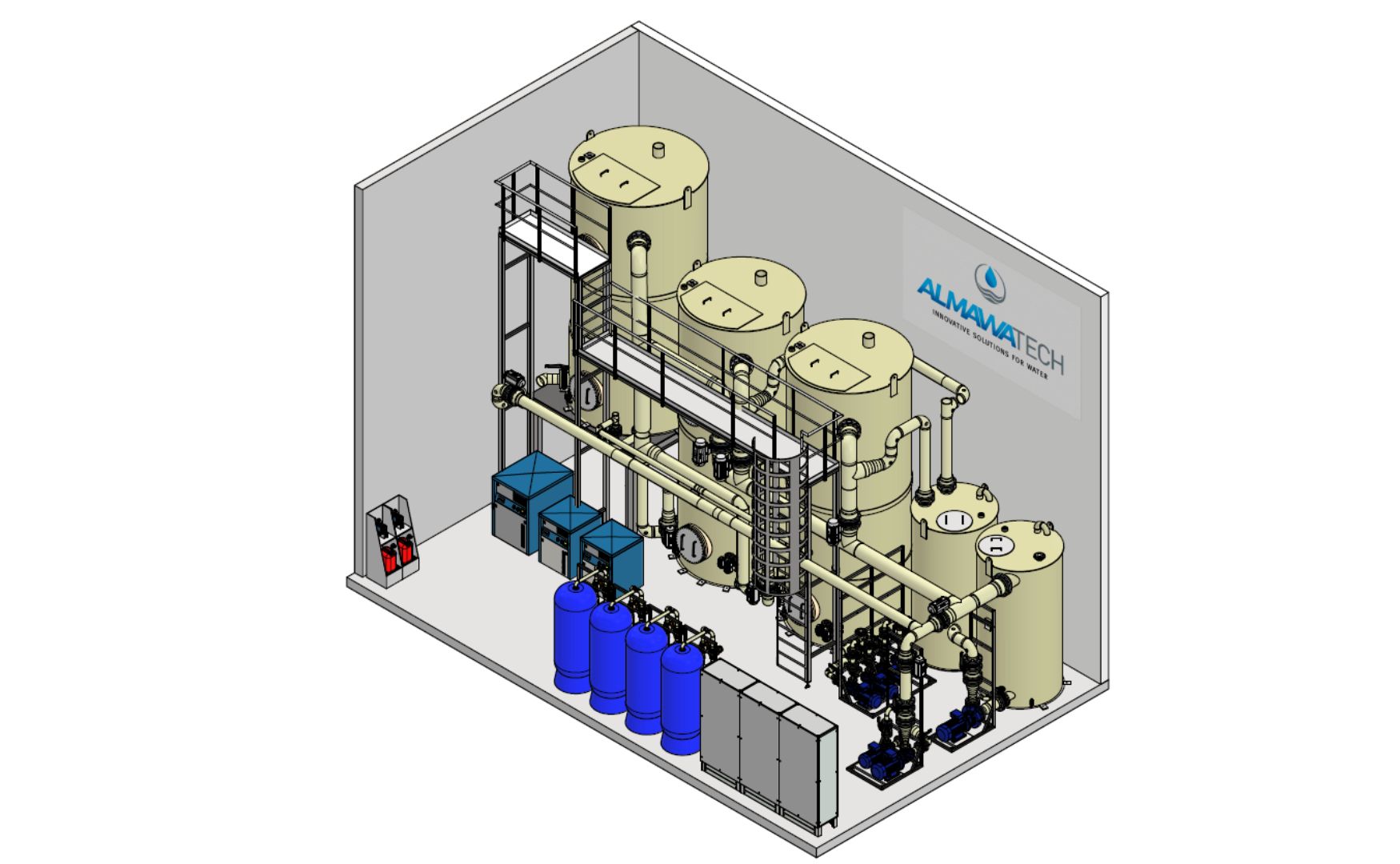
Photo: 3D design of our biologically activated ALMA BioFil Compact filtration system
ALMA BHU BAF
A large-scale biofiltration plant in concrete construction for water flows of up to 1,000 m³/h. This plant enables high-grade denitrification and can be used in combination with other biological processes to ensure complete wastewater treatment.
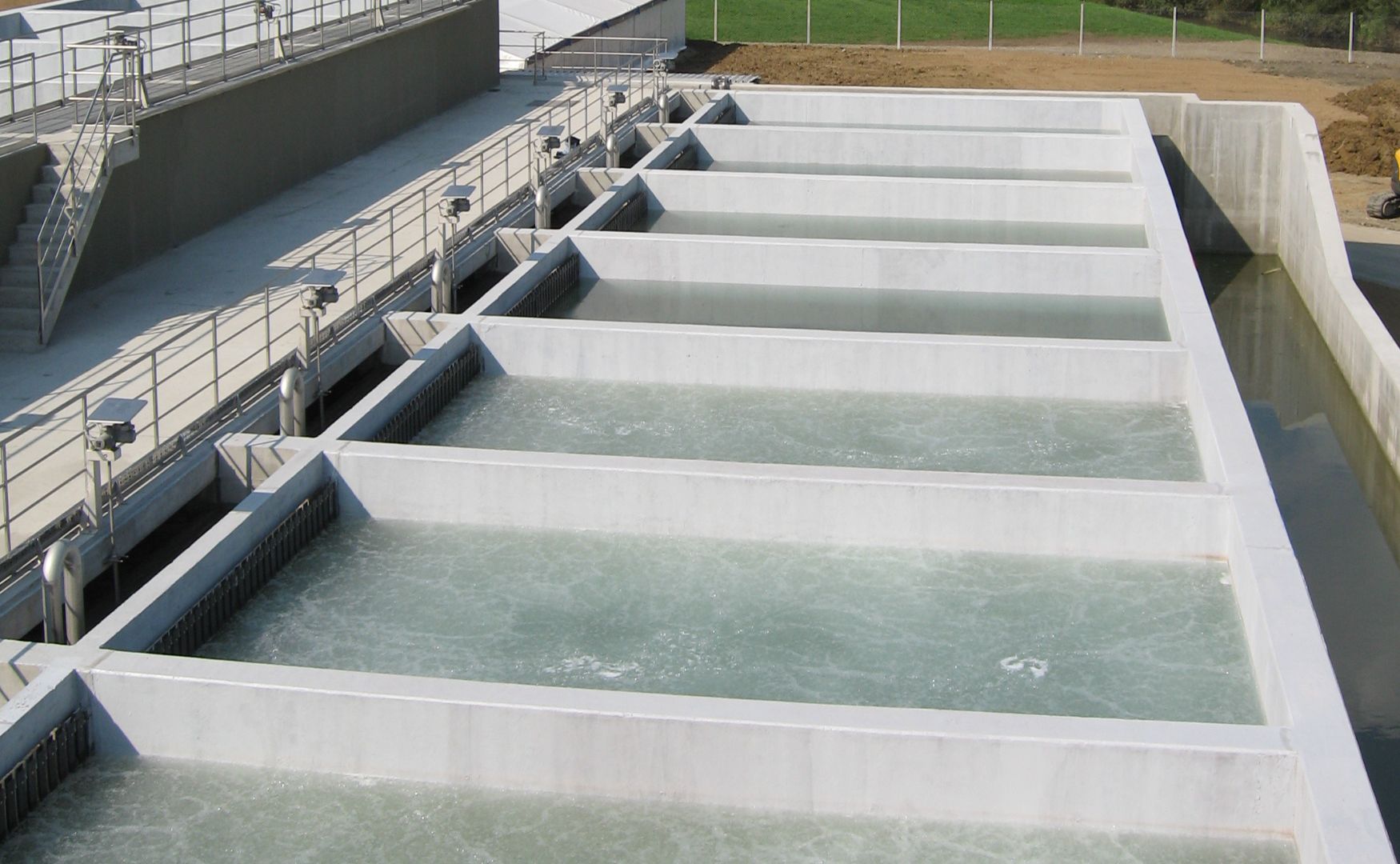

Photo: Photo of our biologically activated filtration, a combination process of mechanical cleaning and biodegradation(ALMA BHU BAF)
ALMA BHU Bio
The ALMA BHU Bio is an activated sludge system that has been specially developed for large wastewater flows of up to 500 m³/h. It combines denitrification and nitrification in an efficient system that can remove up to 99% of biodegradable organic material (BOD). A special feature of the system is the recirculation into the denitrification stage and a final sludge separation with sludge recirculation to ensure continuous and efficient nitrogen removal.
Conclusion
Denitrification is an indispensable process in industrial and municipal wastewater treatment that contributes to the reduction of nitrogen compounds and thus ensures compliance with strict environmental regulations. With the right technologies, such as those offered by ALMAWATECH, these processes can be implemented efficiently and cost-effectively to ensure clean and sustainable wastewater treatment.








