Polyaluminum chloride (PAC) is a chemical precipitant that is widely used in industrial water and wastewater treatment. It belongs to the group of aluminum compounds and is usually supplied as a liquid or powder. Polyaluminium chloride is characterized by its high effectiveness in flocculation and coagulation, especially in applications where fast and efficient separation of solids is required. It can be used in numerous industrial processes and its versatility makes it suitable for applications requiring high purity and clarity of water.
Table of contents
Technical background and properties of polyaluminum chloride
Polyaluminium chloride is produced by the partial hydrolysis of aluminum chloride. This produces high-molecular aluminum complexes that have stronger flocculation properties than classic precipitants such as aluminum sulfate. The special feature of PAC is the high cation charge, which is created by the hydrolysis of the aluminium and ensures rapid neutralization of the charges on suspended solids. The high charge density of the polyaluminum chloride promotes coagulation, which leads to more efficient floc formation and therefore better separation of particles and colloidal substances.
Polyaluminum chloride has the following important properties:
- High cation charge: Due to its positive charge, PAC attracts negatively charged particles and neutralizes their surface, causing the particles to agglomerate and form larger flocs.
- Rapid floc formation: The hydrolyzed aluminum complexes promote rapid and stable floc formation, which facilitates sedimentation and separation of solids.
- Wide pH range: PAC is effective in a wide pH range (approx. 5 to 8), which makes it particularly adaptable to different wastewaters.
- Lower residual aluminum values: Compared to other aluminum precipitants, PAC often leaves less residual aluminum in the water after precipitation, which helps meet stringent quality standards.
Functionality and application of polyaluminum chloride in practice
Polyaluminium chloride is mainly used for coagulation and flocculation in water treatment. The mode of action of PAC is based on the neutralization of the charges on the suspended particles in the wastewater, causing the particles to aggregate with each other and form flocs. These flocs are large and stable enough to be removed by sedimentation or filtration. PAC is particularly effective in removing turbidity, heavy metals, phosphates and organic substances.
Typical applications
Drinking water treatment:
- In drinking water treatment, PAC is often used to remove turbidity and colloidal particles. It binds fine particles and organic substances that contribute to the turbidity of the water and thus ensures clear water quality. Due to its high effectiveness at low dosage, PAC is particularly popular in municipal waterworks.
Wastewater treatment in industry:
- PAC is used in industrial wastewater treatment to remove phosphates and heavy metals. The aluminum ions bind to the negative charges of phosphates and heavy metal compounds, resulting in poorly soluble precipitation products that settle as sludge.
- In the pulp and paper industry, PAC is used to remove organic substances and solids from wastewater that are produced during the processing and bleaching of pulp.
- PAC is also used in the food and beverage industry to improve water quality and meet strict environmental requirements, especially when high concentrations of organic matter and turbidity need to be removed.
Textile and dyeing industry:
- In the textile industry, PAC is often used to precipitate and remove dyes and organic compounds that enter the wastewater during dyeing processes. PAC helps to reduce residual turbidity and treat the water for reuse in production.
Cooling water treatment:
- PAC is used in closed cooling water circuits to remove impurities and solids that can lead to the formation of deposits and biofouling. Treatment with PAC stabilizes the water quality and extends the service life of the cooling circuits.
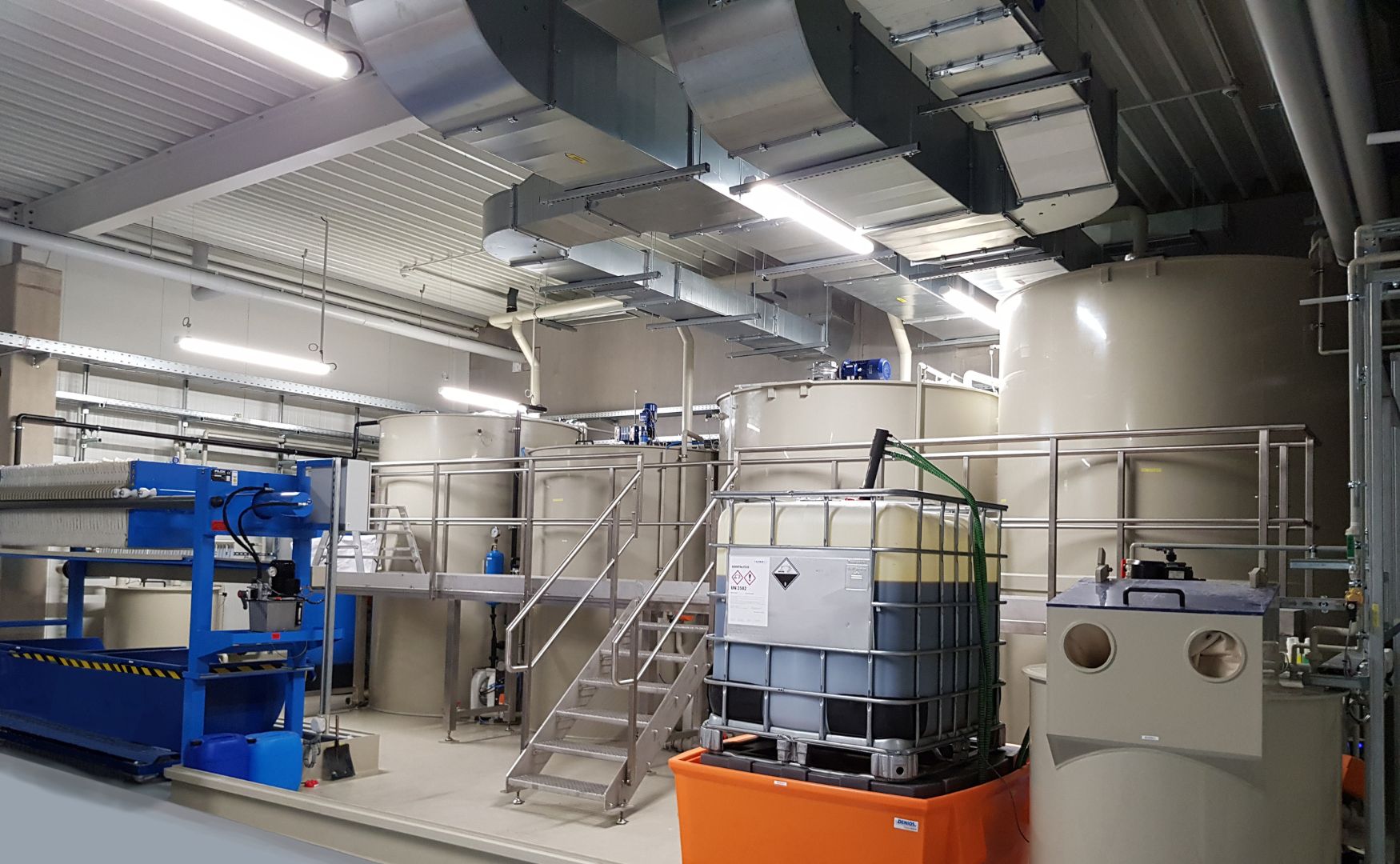

Photo: CP system (precipitation and flocculation system) ALMA Chem MCW with ferric chloride dosing
Advantages and challenges of using polyaluminum chloride
Advantages:
- High efficiency at low dosage: PAC enables effective coagulation and flocculation even at low dosages, which reduces chemical costs.
- Fast and stable floc formation: The high aluminum complexes promote the formation of stable flocs, which facilitates the separation of solids by sedimentation or filtration.
- Versatility in the pH range: PAC is effective in a wide pH range and can therefore be used in different types of wastewater without the need to adjust the pH value significantly.
- Reduced residual aluminum concentrations: The efficiency of the PAC enables a lower residual aluminum concentration in the treated water, which improves environmental compatibility and compliance with legal limits.
Challenges:
- Corrosiveness: PAC solutions are slightly corrosive and require corrosion-resistant storage and dosing. Materials such as plastic or stainless steel are necessary to prevent corrosion damage to systems.
- Sensitivity to water hardness: If the water is very hard, calcium and magnesium compounds can be deposited with PAC, which can lead to blockages and deposits. In such cases, it is necessary to adjust the dosage or pre-treat the water.
- Sludge volume: The use of PAC leads to the formation of sludge, which must subsequently be disposed of or treated. Efficient sludge treatment is therefore an important aspect when using polyaluminum chloride.
Polyaluminum chloride at ALMAWATECH: ALMA AQUA Wastewater
As a specialist in industrial water and wastewater treatment, ALMAWATECH offers a wide range of precipitants, including polyaluminium chloride in various concentrations and purity levels. Our ALMA AQUA wastewater product line includes tailor-made solutions that are optimized for specific requirements and applications. Our experienced team will provide you with comprehensive advice and, on request, carry out laboratory analyses to determine the optimum dosage and application for your wastewater. In this way, we guarantee maximum efficiency and cost effectiveness in wastewater treatment and ensure that environmental standards are met.
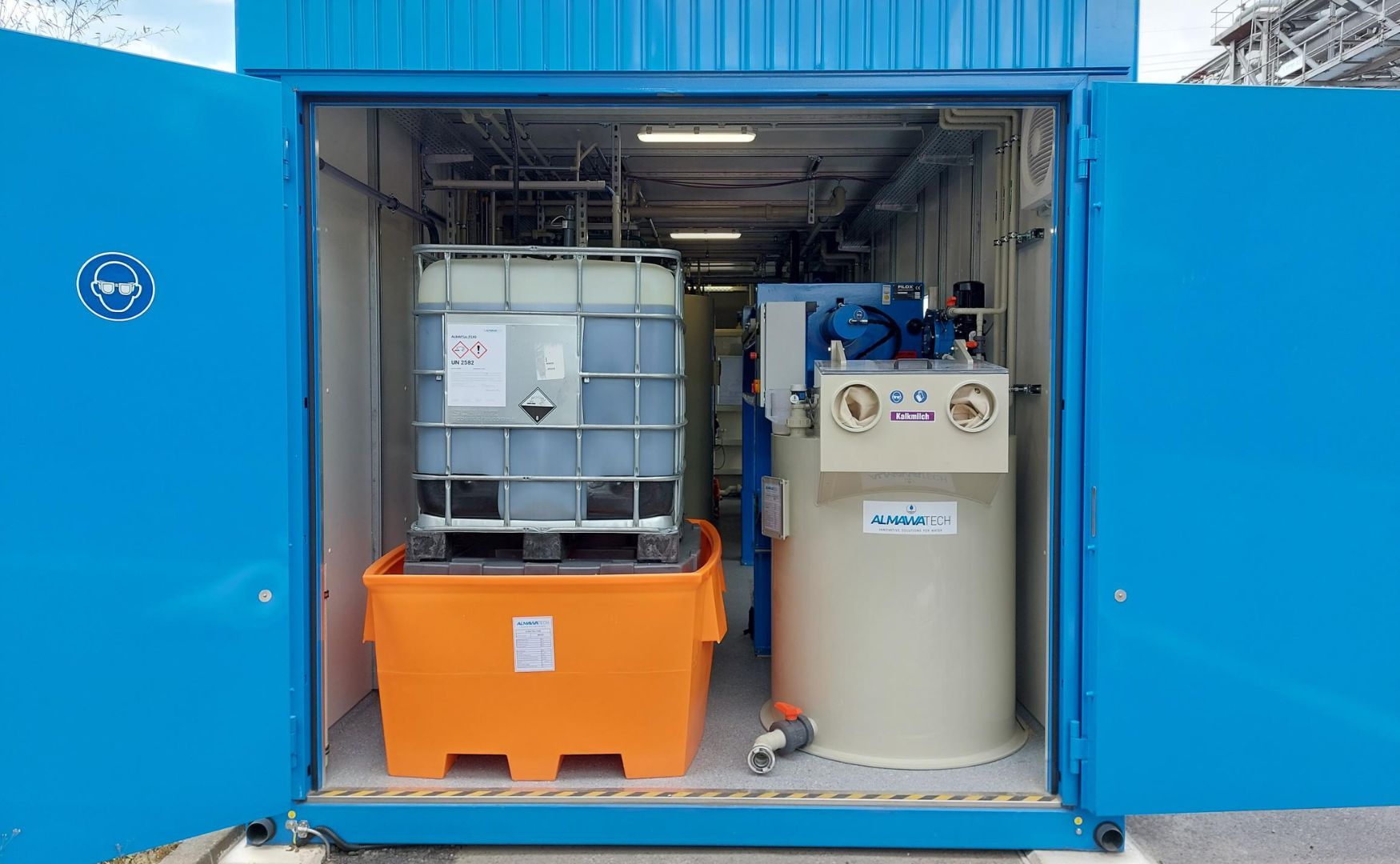

Photo: IBC dosing station for ferric chloride, installed in the ALMA Modul technical room container
Conclusion
Polyaluminium chloride is a versatile and highly effective precipitant in water and wastewater treatment, characterized by its high charge density, rapid floc formation and flexibility in the pH range. It is used in numerous industries, including drinking water treatment, the textile and food industries and cooling water treatment. ALMAWATECH's customized PAC solutions enable efficient particle separation, cost reduction and compliance with strict environmental regulations. With the support of our experienced team and our wide range of products, we ensure that your wastewater treatment is optimized and sustainable.
For further information on our products, please feel free to contact us at any time!