Nitrification is a key biological process in the nitrogen cycle that plays a decisive role in industrial wastewater treatment. In this process, ammonium (NH₄⁺) is oxidized to nitrate (NO₃-) by special bacteria in two stages. This oxidation is particularly important for removing nitrogen from wastewater, as ammonium can have a toxic effect in high concentrations and pollute the environment.
Table of contents
Technical background and mode of operation
Nitrification consists of two successive steps that are carried out by different groups of bacteria:
1. ammonium oxidation to nitrite (NO₂-):
- In the first stage, ammonium-oxidizing bacteria (AOB) convert the ammonium (NH₄⁺) to nitrite (NO₂-). An example of this type of bacteria is Nitrosomonas.
- Reaction equation:
2. nitrite oxidation to nitrate (NO₃-):
- In the second stage, nitrite-oxidizing bacteria (NOB), such as Nitrobacter, oxidize the nitrite to nitrate.
- Reaction equation:
Areas of application
In industrial and municipal wastewater treatment, nitrification is an important step in breaking down nitrogen compounds and meeting the legal requirements for discharging wastewater into bodies of water. Typical areas of application are
- Municipal wastewater treatment plants: Nitrification is often used in conjunction with denitrification to minimize the nitrogen content in wastewater.
- Industrial wastewater: Especially in the food and beverage industry, the chemical industry and the pharmaceutical industry, nitrification is a crucial process for reducing the nitrogen load in wastewater.

Photo: Denitrification and nitrification basin for industrial wastewater from the food industry in Chile, ALMA BHU BIO plant
Operating conditions
In order for nitrification to run efficiently, certain operating conditions must be met:
- Oxygen supply: As nitrification is an aerobic process, a sufficient amount of oxygen must be available in the reactor. The oxygen content in the water should be between 2 - 3 mg/l to ensure bacterial activity.
- Temperature: The optimum temperature for nitrification is between 15 and 30 °C. Below 10 °C, the process slows down considerably.
- pH value: The ideal pH range is between 6.5 and 8.5, as the activity of nitrifying bacteria is impaired outside this range.
- Carbon sources: As nitrification consumes oxygen and reduces alkalinity, an additional carbon source (such as acetic acid) may be necessary to stabilize the pH value.
Advantages of nitrification
- Reduction of toxic nitrogen compounds: The conversion of ammonium to nitrate reduces toxic nitrogen compounds in wastewater, which is important to prevent environmental pollution.
- Improving water quality: By reducing ammonium and nitrite, nitrification improves the quality of purified water that is discharged into rivers, lakes or groundwater.
- Flexibility in process control: Nitrification can be specifically combined with denitrification to completely remove the nitrogen by converting the nitrate into gaseous nitrogen, which escapes harmlessly into the atmosphere.
ALMAWATECH solutions for nitrification
ALMAWATECH offers innovative technologies for the efficient implementation of nitrification in industrial wastewater treatment plants. The following system solutions in particular are optimally adapted to the requirements of nitrogen removal:
ALMA BHU Bio
Our biologically activated activated sludge plant combines nitrification and denitrification in a modular system designed for large wastewater flows. This plant can process up to 500 m³/h of wastewater with a high nitrogen load. Nitrification takes place in the aerated stage, which is regulated by automatic control systems to optimize oxygenation and other parameters.
ALMA BioFil Compact
This compact biofiltration system for smaller wastewater flows (up to 100 m³/h) combines nitrification and denitrification in one efficient system. It is ideal as pre-treatment for downstream membrane systems and reduces nitrogen compounds that could lead to fouling in reverse osmosis systems.
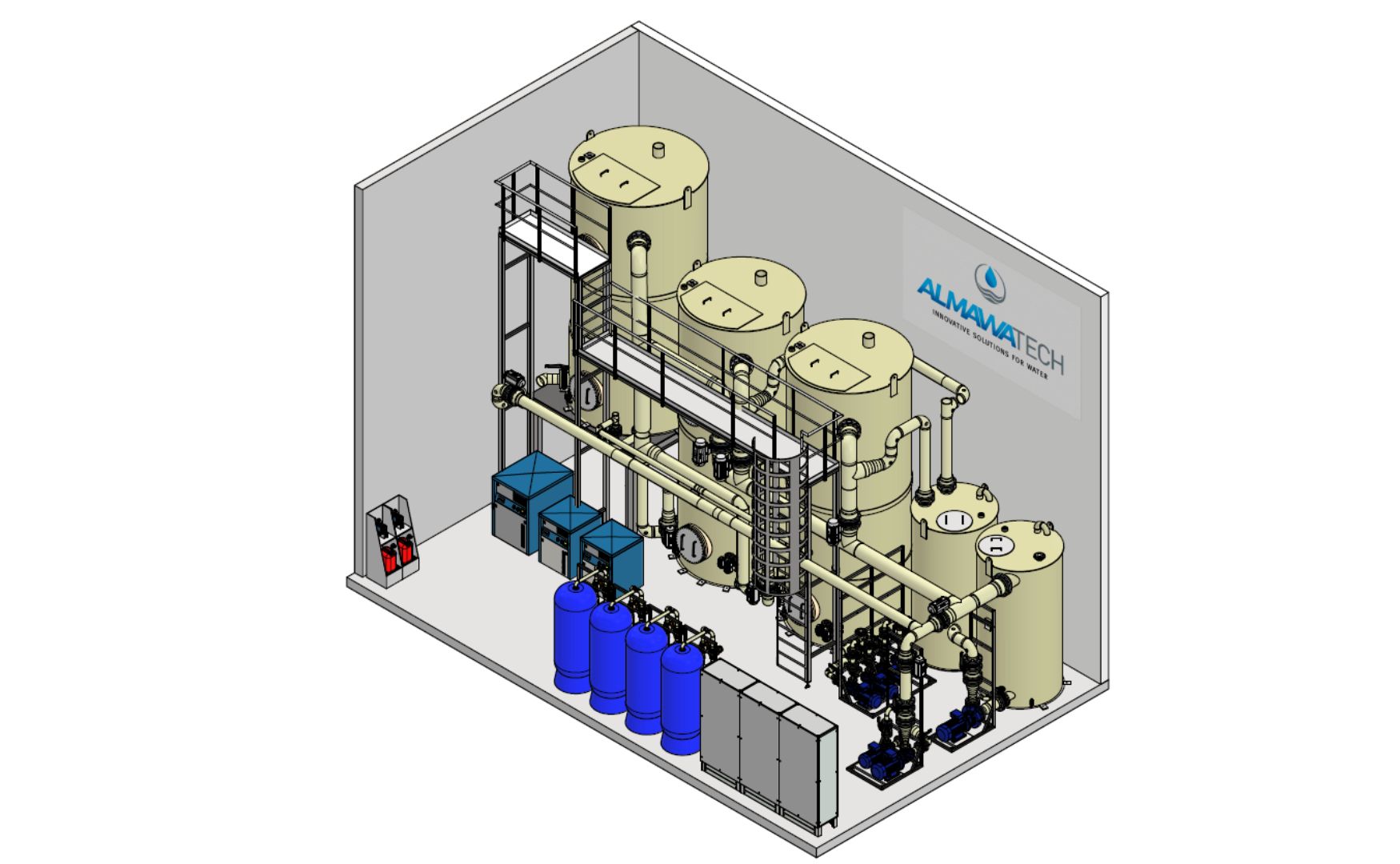
Photo: 3D design of our biologically activated ALMA BioFil Compact filtration system
ALMA BHU BAF
The large-scale concrete biofiltration plant offers efficient nitrification for wastewater flows of up to 1,000 m³/h. This plant uses an integrated system of aerobic and anoxic zones to maximize nitrogen removal. Particularly suitable for the food and beverage industry as well as municipal wastewater streams.
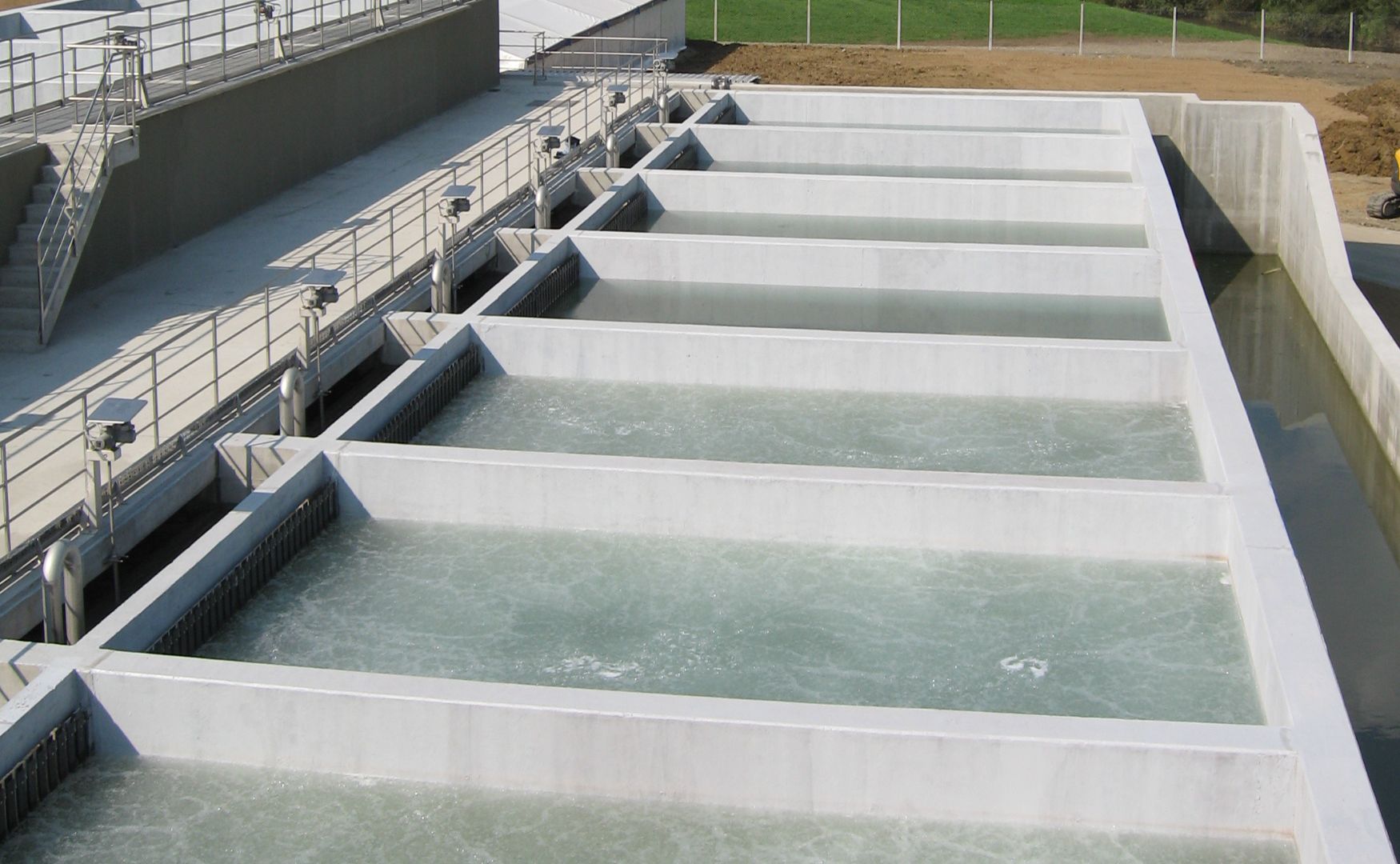

Photo: Photo of our biologically activated filtration, a combination process of mechanical cleaning and biodegradation(ALMA BHU BAF)
Conclusion
Nitrification is an indispensable process for nitrogen removal in industrial and municipal wastewater treatment. By converting ammonium into nitrate, it helps to improve water quality and reduce environmental pollution. With ALMAWATECH 's customized solutions, nitrification processes can be efficiently integrated into wastewater treatment to meet legal requirements and reduce operating costs.








