In industrial water treatment, alkalization refers to increasing the pH value of water or wastewater by adding alkaline chemicals. The aim is to change the water chemistry so that the pH value is brought into the desired range in order to prevent corrosion, stabilize biological processes or enable chemical reactions such as precipitation. In many industrial processes, such as cooling water treatment or in steam boiler systems, alkalization plays a central role in the operation and efficiency of the systems.
Table of contents
Technical background
Alkalization is achieved by adding bases or alkali chemicals that dissociate in the water and increase the concentration of hydroxide ions (OH-), which leads to an increase in the pH value. Frequently used alkalizing agents are
- Sodium hydroxide (NaOH): Also known as caustic soda, it is often used in water treatment to increase the pH value quickly and efficiently.
- Milk of lime (Ca(OH)₂): A suspension of hydrated lime and water, often used for pH regulation and as a precipitant in wastewater treatment.
- Sodium carbonate (Na₂CO₃): Also known as soda ash, it is used to buffer the pH value and prevent corrosion.
- Potassium hydroxide (KOH): A strongly basic solution used in special industrial processes.
The pH value is a key factor that influences numerous chemical and biological processes. A pH value that is too low (acidic) can promote corrosion and the degradation of system components, while a pH value that is too high (alkaline) can lead to scale formation and other operational problems. Therefore, precise alkalization is crucial for process control.
Importance of alkalization in industrial practice
Alkalization is used in various areas of industrial water and wastewater treatment to achieve different goals:
1. corrosion protection
In steam boiler systems and cooling water systems, controlling the pH value is essential to prevent corrosion. A pH value that is too low leads to corrosive conditions that can attack metals and shorten the service life of the system. Alkalization brings the pH value into a range where the risk of corrosion is minimized. In many cases, special corrosion inhibitors are also used to provide additional protection.

Photo: Corrosion in steam boiler systems can cause considerable damage and impair operating efficiency. For more information on our corrosion inhibitors, alkalizing agents and oxygen binding agents, visit our website and discover our operating fluids for boiler systems(ALMA AQUA boiler systems) and cooling water circuits(ALMA AQUA cooling water).
2. wastewater treatment
In industrial wastewater treatment, alkalization is often used to neutralize acidic wastewater. Certain industrial processes, such as electroplating or food processing, produce highly acidic wastewater that must be neutralized before being discharged into the sewer system. By adding bases, the pH value can be adjusted to the legally prescribed range before the water is further treated or discharged.
3. precipitation and flocculation processes
Many chemical reactions, such as the precipitation of heavy metals or phosphate elimination, are strongly pH-dependent. Alkalization is often necessary to bring the pH value into the range in which the substances to be precipitated can be optimally separated. For example, in heavy metal precipitation, milk of lime is often added to precipitate the metals into hydroxides, which are then removed from the wastewater by flocculation and filtration processes.
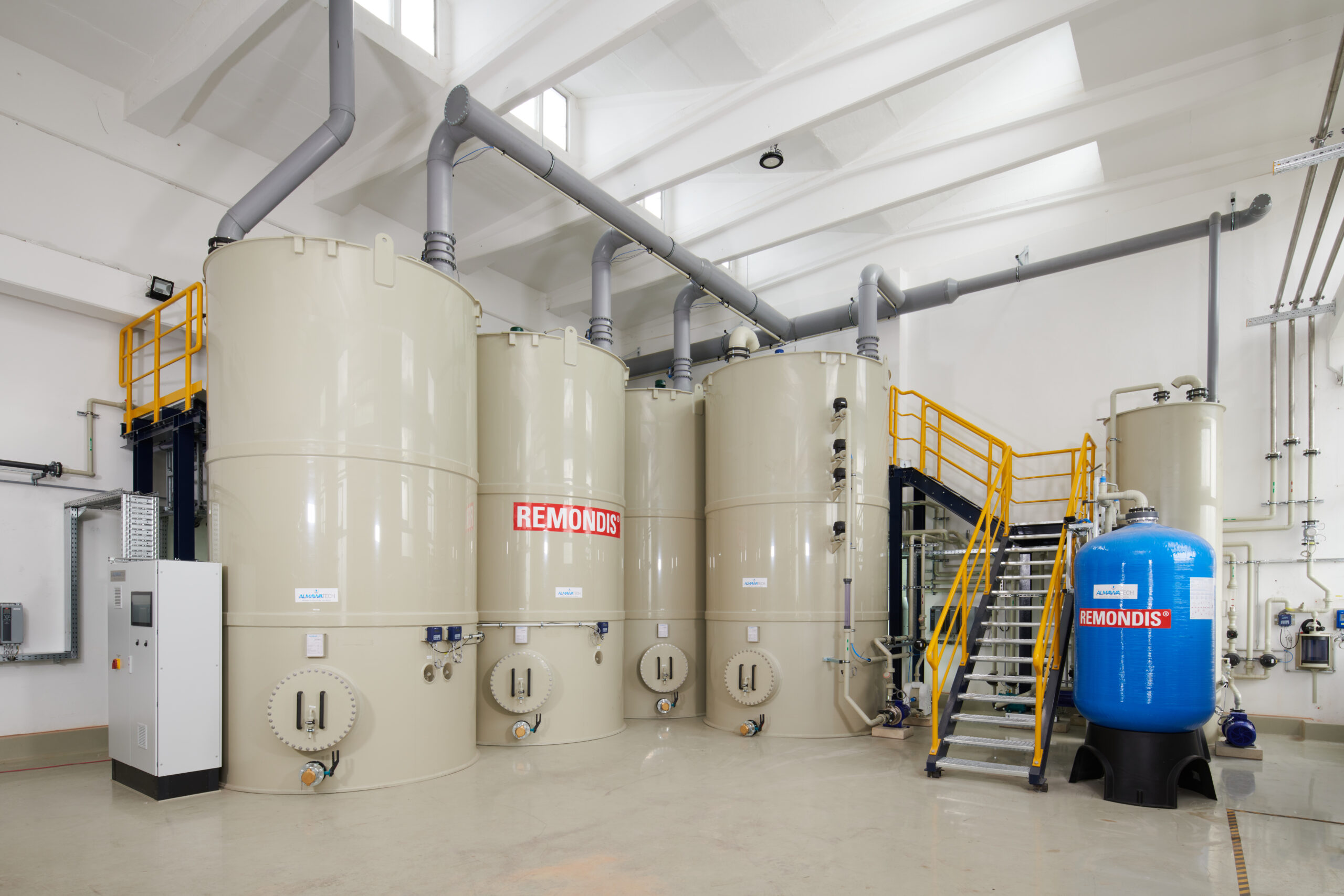

Photo: Precipitation and flocculation plant, also known as CP plant, for the elimination of heavy metals, AOX, hydrocarbons and cyanide(ALMA CHEM MCW)
4. biological processes
In biological wastewater treatment plants, such as aeration tanks, the pH value influences the activity of the microorganisms that break down organic pollutants. A pH value that is too low can disrupt the biological processes or even lead to the death of the microorganisms. Therefore, the pH value is kept stable by alkalization in order to promote biological activity and ensure efficient wastewater treatment.
Products from ALMAWATECH - Alkalization in practice
As part of our industrial water treatment solutions, ALMAWATECH offers a range of pH control and alkalization products specifically designed for use in boiler systems, cooling water circuits and waste water treatment plants:
ALMA AQUA
Our comprehensive product range offers customized chemicals for pH regulation and corrosion protection in cooling and boiler water systems. These include caustic soda, milk of lime and specially formulated buffer solutions that bring the pH value into the optimum range and ensure stable water quality.
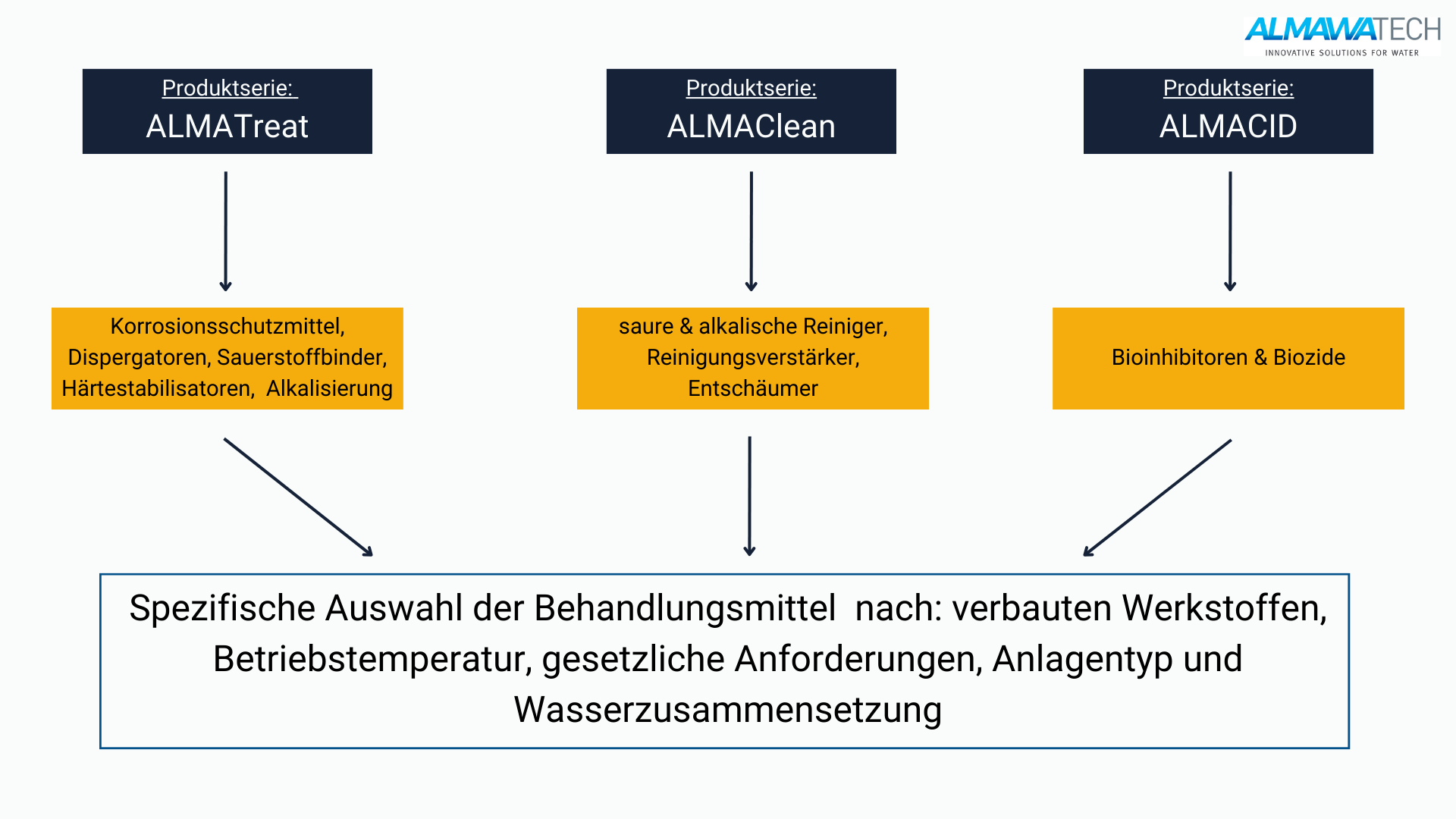
Photo: Product overview of our ALMA AQUA equipment for boiler systems and heating networks(ALMA AQUA boiler water)
Influence on the system design
The design of water treatment plants must take alkalization into account to ensure uniform and controlled pH regulation. In neutralization plants and precipitation reactors in particular, precise dosing of alkalizing agents is required to achieve the desired pH setting and maximize the efficiency of the purification processes. Automatic monitoring and control of the pH value using measurement, control and regulation technology (MCR) is widely used in modern plants and ensures that alkalization is carried out as required.
Conclusion
Alkalization is an indispensable process in industrial water and wastewater treatment that enables precise control of the pH value. It is essential to prevent corrosion, stabilize biological processes and support chemical reactions such as precipitation. With the right alkalizing agents and accurate pH control, operating costs can be reduced, plant performance optimized and regulatory compliance ensured.







