Wastewater neutralization is an essential process in industrial wastewater treatment that serves to bring the pH value of acidic or alkaline wastewater to a neutral range (pH 6.5-8.5). This step is crucial to avoid harmful effects on the environment and to meet the legal requirements for the discharge of wastewater. By using acids or bases, the pH value of the wastewater is regulated to make it suitable for further treatment or discharge. Neutralization is required in numerous industries, especially in the chemical industry, metal processing and food production, where aggressive chemicals enter the wastewater.
Table of contents
Technical background and process of wastewater neutralization
Depending on the process, industrial wastewater can have very different pH values, ranging from highly acidic to highly alkaline. Neutralization aims to eliminate these extremes and bring the wastewater into the neutral range. Chemical neutralization agents are used for this purpose:
- Caustic soda (NaOH) or milk of lime (Ca(OH)₂) to raise the pH value of acidic wastewater.
- Sulphuric acid (H₂SO₄) or hydrochloric acid (HCl) to reduce the pH value of alkaline waste water.
Neutralization takes place in neutralization reactors, whereby the pH value is continuously monitored. The neutralization agents are dosed according to the measured pH value to ensure precise regulation.
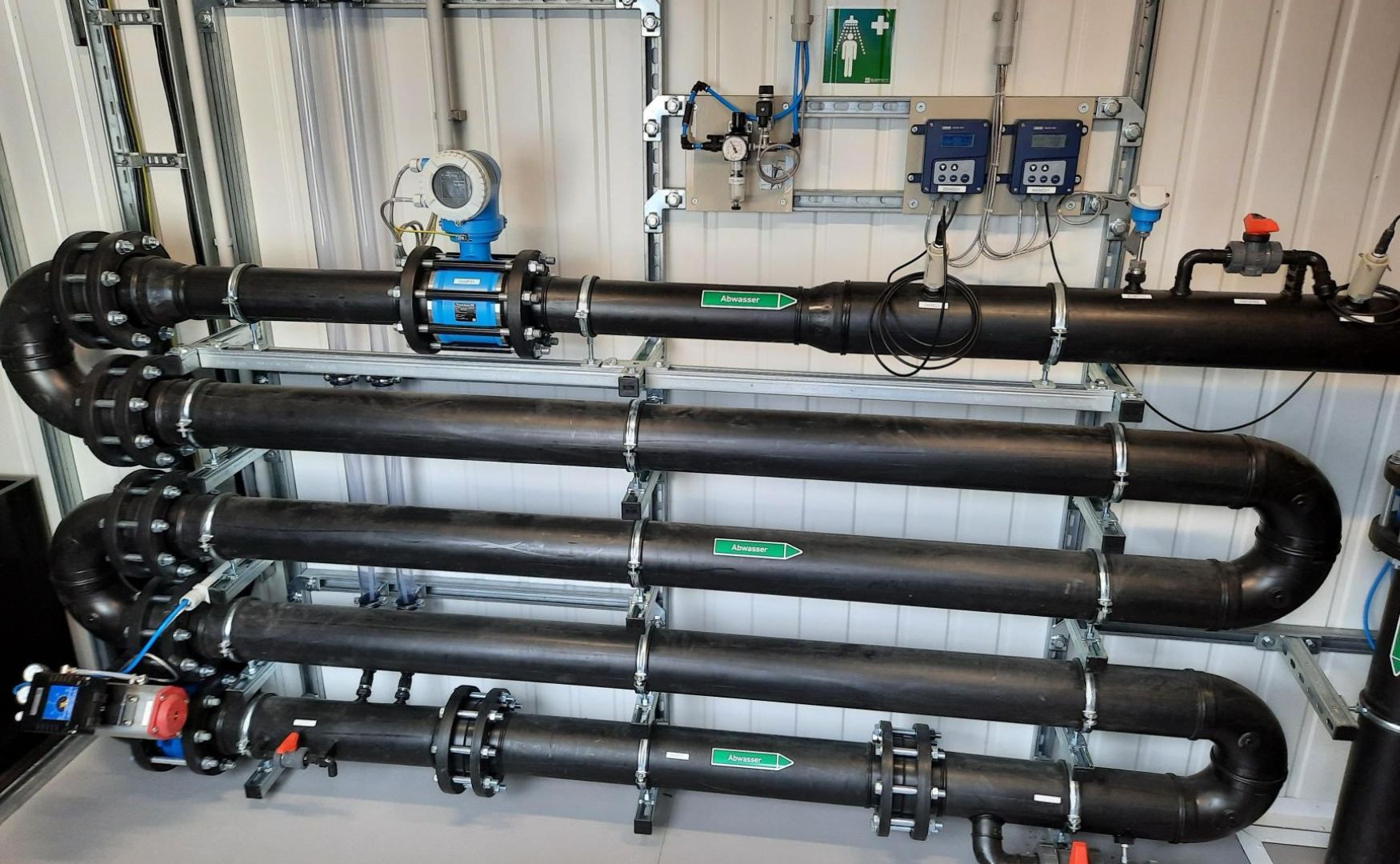

Photo: Reaction section of a pH-controlled neutralization system with automatic dosing of acid and alkali(ALMA Neutra)
CO₂ neutralization
CO₂ neutralization is an increasingly popular and environmentally friendly method of wastewater neutralization. In this process, carbon dioxide (CO₂) is used as a neutralizing agent to treat alkaline wastewater. CO₂ reacts with water to form carbonic acid (H₂CO₃), which is a mild acid and therefore effectively lowers the pH value of the wastewater.
This process is used in industries where mild pH corrections are sufficient, such as in the food and beverage industry and in cooling circuits. A major advantage of CO₂ neutralization is that it leaves no chemical by-products and reduces the risk of overdosing. It also offers the opportunity to make sensible use of CO₂ emissions and thus reduce the environmental impact.
Flue gas neutralization
A particularly sustainable approach to wastewater neutralization is flue gas neutralization, in which the CO₂ contained in the flue gas is used to neutralize alkaline wastewater. This method makes it possible to solve two problems at the same time: On the one hand, the wastewater is neutralized and, on the other, the CO₂ emissions from the plant are put to good use instead of being released into the atmosphere.
Technically speaking, the wastewater is mixed with flue gas, whereby the CO₂ contained in the flue gas reacts with the water to form carbonic acid, which lowers the pH value of the wastewater. This approach is particularly sustainable, as it reduces a company's CO₂ emissions and at the same time enables efficient pH control of the wastewater. This not only reduces the use of chemical acids, but also improves the company's carbon footprint.
Example: In the cement industry or in power plants, the CO₂ produced in the flue gas during the combustion of fossil fuels can be used for wastewater neutralization. This method helps to reduce the company's CO₂ footprint and is a cost-effective way of treating alkaline wastewater in an environmentally friendly way.

Photo: Example of a CO2 neutralization system in the ALMA module for a dairy(ALMA Neutra)
Examples of wastewater of industrial origin that must be neutralized
Electroplating industry: Waste water from electroplating often contains strong acids or bases as well as heavy metals. Neutralization is essential here to regulate the pH value and precipitate heavy metals before the water is further treated or discharged.
Food and beverage industry: Acidic wastewater is produced here, for example during fermentation processes or the cleaning of systems. CO₂ neutralization can be used to reduce the pH value in an environmentally friendly and efficient manner.
Dairy processing industry: Dairies produce both acidic wastewater due to the natural acidification of dairy products and alkaline wastewater due to the use of cleaning agents.
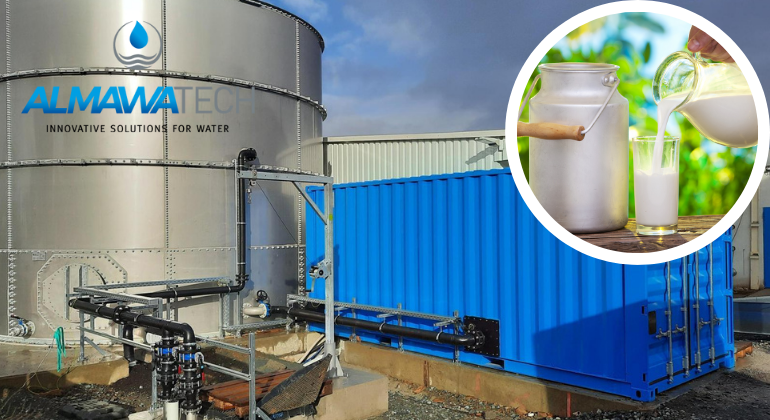

Photo: Example of a neutralization system in ALMA modular design with mixing and equalizing tank(ALMA Neutra)
Conclusion
Wastewater neutralization is a crucial step in industrial wastewater treatment to regulate extreme pH values and prevent environmental damage. CO₂ neutralization and flue gas neutralization provide industry with sustainable methods that not only treat wastewater efficiently, but also reduce CO₂ emissions from operations. These processes help to minimize the use of chemicals and make industrial processes more environmentally friendly.