A biocide is a chemical substance or microorganism that is specifically used to combat or inhibit the growth of harmful organisms such as bacteria, fungi, algae or viruses. Biocides play a central role in industrial water treatment and wastewater treatment, especially in cooling water systems, membrane systems (e.g. reverse osmosis), heat exchangers and other water circuits in which microbial growth is undesirable. Biocides are used to prevent the formation of biofilms, corrosion and deposits, which can impair the efficiency of the systems.

Photo: Biofilm on a heat transfer surface of a cooling water circuit
Table of contents
Types of biocides
Biocides can be divided into two main categories:
- Oxidizing biocides: These substances work by destroying cell components of microorganisms through oxidation, causing the cells to die. They are particularly effective against a broad spectrum of microorganisms. Frequently used oxidizing biocides include
- Chlorine (e.g. in the form of sodium hypochlorite, NaClO): Chlorine is one of the oldest and most widely used biocides. It is frequently used in cooling circuits and drinking water systems. Chlorine oxidizes cell membranes and destroys the cell structure.
- Chlorine dioxide (ClO₂): Chlorine dioxide is a powerful oxidizing agent that is efficient in disinfecting water and combating biofilms. It is also able to eliminate bacterial spores and resistant organisms such as legionella.
- Ozone (O₃): Ozone is another powerful oxidizing agent that effectively kills microorganisms. It has the advantage that it decomposes into oxygen after use and leaves no residue, making it a more environmentally friendly option.
2. non-oxidizing biocides: These biocides act by other mechanisms, e.g. by inhibiting cell division, damaging the cell walls of microorganisms or blocking enzyme systems. Non-oxidizing biocides are often used in systems where oxidizing biocides are undesirable or ineffective, such as in systems with sensitive membranes (e.g. reverse osmosis systems). Examples of non-oxidizing biocides are
- Isothiazolinones: These compounds inhibit the enzyme system of microorganisms, which leads to their death. They are effective against a wide range of bacteria and algae.
- Glutaraldehyde: Glutaraldehyde is a powerful disinfectant that denatures proteins in the cells of microorganisms, preventing them from growing and multiplying. It is particularly effective in the oil and gas industry and in cooling water systems.
- Quaternary ammonium compounds (QAVs): These compounds act by disrupting the cell membranes of bacteria and fungi. They are generally active as broad-spectrum biocides against bacteria and algae.
Areas of application of biocides
In industrial practice, biocides are used in many areas of water and wastewater treatment:
Cooling water systems: In open and closed cooling circuits, biofilms often form, which hinder heat transfer and increase the corrosion rate. Biocides are used here to control microbiological growth and thus ensure the efficiency of heat exchangers and cooling towers.
Membrane systemsIn reverse osmosis systems and other membrane systems, biofouling (the microbiological growth on membrane surfaces) can drastically reduce the performance of the membranes. Biocides are essential to inhibit the growth of microorganisms and thus extend the life of the membranes. The use of non-oxidizing biocides is preferable, as oxidizing biocides such as chlorine can damage the sensitive membrane structures.
Boiler water systems: Biocides are used in boilers and steam generation systems to prevent the growth of bacteria and algae in the feed water. This protects against microbially induced corrosion (MIC) and reduces the risk of deposits that impair heat exchange.
Water circuits in the food industry: In the food and beverage industry, microbiological control is of great importance in order to meet hygiene and quality standards. Biocides are used in cleaning systems, process water and cooling circuits to minimize microbiological contamination.
Technical background and mode of operation
The effect of biocides is highly dependent on the properties of the water and the type of system in which they are used. The most important factors include
Concentration: The effectiveness of a biocide depends on its concentration. As a rule, the biocide dosage is selected so that it maintains a sufficient concentration over a defined period of time to combat the microorganisms without damaging the system.
Contact time: Biocides require sufficient contact time with the microorganisms in order to develop their effect. Oxidizing biocides generally act more quickly, while non-oxidizing biocides require a longer contact time.
pH value: The pH value of the water influences the effectiveness of many biocides. For example, the disinfecting power of chlorine is severely limited in alkaline conditions, while it is very effective in neutral to slightly acidic conditions.
Temperature: Higher temperatures can increase the reactivity of biocides, but can also lead to faster degradation of the substance. Therefore, the operating conditions of the system must be taken into account when selecting the biocide.
Biofilms: Biofilms are particularly resistant to biocides as the microbial communities are embedded in a protective extracellular polymeric substance (EPS), which weakens the effect of the biocides. In such cases, higher biocide concentrations or the use of dispersants are required to dissolve the biofilms and effectively kill the microorganisms.
ALMAWATECH biocides and bioinhibitors for cooling water circuits: ALMA AQUA cooling water
ALMAWATECH offers with the ALMA AQUA cooling water-product range offers specialized biocides and bioinhibitors that have been specifically developed for use in industrial cooling water circuits. These products are designed to control the growth of microorganisms such as bacteria, algae and fungi while preventing the formation of biofilms and microbially induced corrosion (MIC). The ALMA AQUA cooling water range includes both oxidizing and non-oxidizing biocides to ensure comprehensive microbiological control, depending on the specific requirements of the system.
Our bioinhibitors also work by preventing the growth of microorganisms and thus maintaining heat transfer efficiency in the cooling circuit. Regular use of ALMA AQUA products minimizes deposits and fouling, extending the life of the system and reducing maintenance. These products are formulated to be environmentally friendly and meet strict legal requirements to ensure that operation is not only efficient but also sustainable.
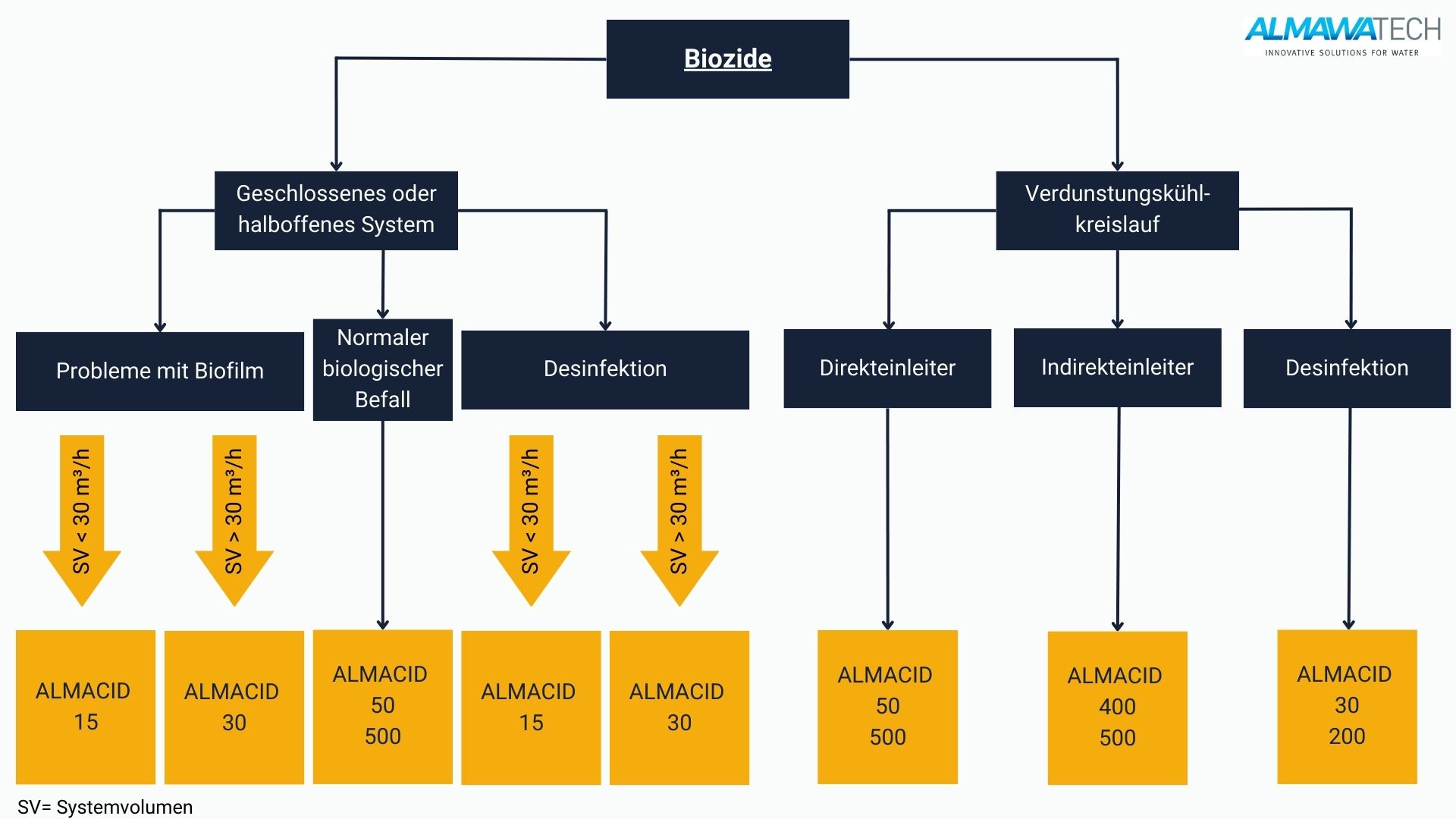
Photo: Overview of our biocides and bioinhibitors for cooling water applications (find out more about our products: ALMA AQUA cooling water)
Environmental aspects and safety
The use of biocides is subject to strict regulations, as many of these substances can be potentially harmful to the environment. Biocides must be selected and dosed in such a way that they control microbial contamination but do not pose a risk to the environment. Some biocides, particularly chlorine-based compounds, can form by-products that are toxic or mutagenic, such as trihalomethanes (THMs). Many plants are therefore switching to more environmentally friendly biocides, which break down more quickly and leave fewer harmful residues.
Conclusion
Biocides play a central role in industrial water treatment to control microbial growth and biofilm formation in water systems. The correct selection and dosage of biocides based on the specific requirements of the water system are crucial to operate the equipment efficiently while meeting environmental regulations. Innovative biocide strategies, such as the combination of oxidizing and non-oxidizing biocides and the use of dispersants, help to ensure the long-term operation of water treatment plants.
For further information on our products, please feel free to contact us at any time!







