A sedimentation tank is a technical device for the mechanical pre-treatment of water or wastewater in which solids are separated from the water by sedimentation. The basin uses gravity to separate suspended solids and thus reduce the solids content in the water or wastewater. Sedimentation tanks are often used in industrial water and wastewater treatment to reduce the load on subsequent purification stages and increase the efficiency of the system.
Table of contents
Technical background
The operating principle of a sedimentation tank is based on sedimentation. Solids that have a higher density than water sink under the influence of gravity to the bottom of the basin, where they are collected as bottom sediment (sludge). The cleaned water then flows out via an overflow at the top of the tank and is directed for further treatment or discharge. The efficiency of sedimentation depends on various factors:
- Particle size and density: The larger and denser the solids in the water, the faster they settle.
- Water flow velocity: Too high a flow velocity can disrupt sedimentation and lead to reduced particle separation. The flow velocity in the sedimentation tank must therefore be controlled.
- Residence time: The time that the water remains in the sedimentation tank determines how much time the particles have for sedimentation. Longer retention times improve the settling performance.
Types of sedimentation tanks
1. circular settling basin
In a circular sedimentation tank, the water flows radially from the center of the tank to the outside, while the sedimentation of the solids takes place in the lower area. The settled solids are often transported to the bottom of the tank by a central scraper and removed from there as sludge.
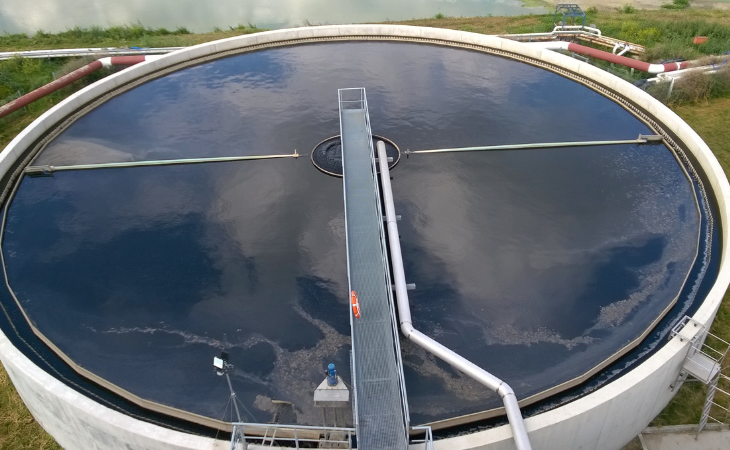

Photo: Round sedimentation tank for returning biomass from our ALMA BHU GMR biogas plant
2. longitudinal settling basin
In a longitudinal settling tank, the wastewater flows in a linear flow path from one end of the tank to the other. As it flows through the tank, the solids settle on the tank floor. Here too, the sludge is regularly removed, while the clarified water is discharged via an overflow channel on the surface.
3. lamella separator
An inclined clarifier or lamella clarifier works with inclined lamellas that increase the sedimentation surface and thus accelerate the settling process. This compact design enables more efficient separation of solids in a smaller space.
4. high-performance settling basin
High-performance sedimentation tanks are used in industrial processes with high volume flows or heavily contaminated wastewater. These basins are specially designed to ensure effective solids separation even at high flow rates. Additional technologies, such as flocculation, can be used to improve sedimentation by combining the particles into larger flocs.
Significance and application in practice
Sedimentation tanks are a fundamental component of mechanical pre-treatment in industrial water and wastewater treatment. Their main task is to reduce the suspended solids load in the wastewater before it enters the biological or chemical treatment processes. They thus prevent the downstream treatment stages from becoming overloaded or inefficient.
Application examples
1. municipal wastewater treatment plants
In municipal sewage treatment plants, the sedimentation tank is an indispensable part of the pre-treatment stage. Here, coarse solids and sediments are removed from the wastewater before the water enters the biological treatment stage. This improves the purification performance and protects the downstream processes from overloading.
2. industrial wastewater treatment:
In the metal processing or mining industry, wastewater often contains large quantities of suspended solids, such as sludge or mineral particles. Sedimentation tanks are used here to separate these solids and prevent them from entering the biological or chemical wastewater treatment system. By reducing the suspended solids, the downstream system components, such as membrane filtration or chemical precipitation systems, are protected from contamination.

Photo: A beautiful photo of an industrial wastewater treatment plant with sedimentation tank in winter
3. food and beverage industry
Wastewater from food processing often contains organic suspended solids and solids that need to be removed before biological treatment. This is where sedimentation tanks are used to separate the organic solids and optimize the biological treatment process.
4. paper industry
The pulp and paper industry produces large quantities of wastewater containing fibers. Sedimentation tanks are used to separate the fibers and solids before the wastewater is transferred to biological or chemical treatment.
Influence on the design of wastewater treatment plants
The size and design of a sedimentation tank depends heavily on the inflow load and the properties of the wastewater to be treated. Important factors that must be taken into account when planning a sedimentation tank are
- Volume flow: The tank must be large enough to cope with the flow of wastewater and ensure sufficient retention time for the particles to sink.
- Sludge production: The amount of sludge deposited varies depending on the load of the wastewater. Sludge removal must be carried out regularly and efficiently in order to maintain the operation of the tank.
- Water quality: The quality of the wastewater after sedimentation (discharge) is decisive for the success of wastewater treatment. The sedimentation performance of the sedimentation tank has a direct impact on the efficiency of subsequent treatment stages.
Advantages of sedimentation tanks
- Energy efficiency: As sedimentation tanks are based on gravity, they generally operate without high energy consumption, which makes them a cost-effective and sustainable solution for wastewater treatment.
- Simple maintenance: The construction and operation of a sedimentation tank is relatively straightforward and regular maintenance work, such as removing sludge, is easy to carry out.
- Versatility: Sedimentation tanks can be used in a variety of industries and can be adapted to different types of wastewater and suspended solids.
Conclusion
The sedimentation tank is an essential element in industrial and municipal wastewater treatment, which improves the efficiency and service life of subsequent treatment stages by separating solids. With its ability to effectively sediment suspended solids, it helps to meet legal requirements and protect the environment. Sedimentation tanks are versatile, energy efficient and a cost-effective solution for mechanical wastewater treatment.